|
Tanycyte
Tanycytes are highly specialized ependymal cells found in the third ventricle of the brain, and on the floor of the fourth ventricle. Each tanycyte has a long basal process that extends deep into the hypothalamus. It is possible that their function is to transfer chemical signals from the cerebrospinal fluid to the central nervous system. The term ''tanycyte'' comes from the Greek word tanus which means elongated. Structure Tanycytes are highly specialized ependymal cells (also called ependymoglial cells) with long basal processes. Tanycytes in adult mammals are found in the ventricular system, and the median eminence, a circumventricular organ. They are most numerous in the third ventricle of the brain, are also found in the fourth ventricle, and can also be seen in the spinal cord radiating from the central canal (also known as the ependymal canal), to the spinal cord surface. The long processes extend through the layer of astrocytes to cross the median eminence and form end- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumventricular Organ
Circumventricular organs (CVOs) ( circum-: around ; ventricular: of ventricle) are structures in the brain characterized by their extensive and highly permeable capillaries, unlike those in the rest of the brain where there exists a blood–brain barrier (BBB) at the capillary level. Although the term "circumventricular organs" was originally proposed in 1958 by Austrian anatomist Helmut O. Hofer concerning structures around the brain ventricular system, the penetration of blood-borne dyes into small specific CVO regions was discovered in the early 20th century. The ''permeable'' CVOs enabling rapid neurohumoral exchange include the subfornical organ (SFO), the area postrema (AP), the vascular organ of lamina terminalis (VOLT — also known as the ''organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis'' (OVLT)), the median eminence, the pituitary neural lobe, and the pineal gland. The circumventricular organs are midline structures around the third and fourth ventricles that are in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
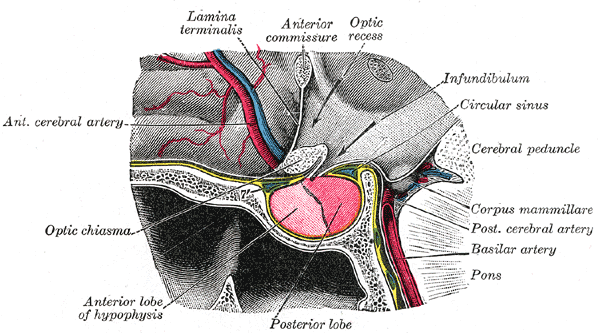
Third Ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected cerebral ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami. Structure The third ventricle is a narrow, laterally flattened, vaguely rectangular region, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and lined by ependyma. It is connected at the superior anterior corner to the lateral ventricles, by the interventricular foramina, and becomes the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') at the posterior caudal corner. Since the interventricular foramina are on the lateral edge, the corner of the third ventricle itself forms a bulb, known as the ''anterior recess'' (it is also known as the ''bulb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ependymal Cells
The ependyma is the thin neuroepithelial ( simple columnar ciliated epithelium) lining of the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The ependyma is one of the four types of neuroglia in the central nervous system (CNS). It is involved in the production of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and is shown to serve as a reservoir for neuroregeneration. Structure The ependyma is made up of ependymal cells called ependymocytes, a type of glial cell. These cells line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord, which become filled with cerebrospinal fluid. These are nervous tissue cells with simple columnar shape, much like that of some mucosal epithelial cells. Early monociliated ependymal cells are differentiated to multiciliated ependymal cells for their function in circulating cerebrospinal fluid. The basal membranes of these cells are characterized by tentacle-like extensions that attach to astrocytes. The apical side is cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Distinct Cell Types In The Adult Human Body
The list of human cell types provides an enumeration and description of the various specialized cells found within the human body, highlighting their distinct functions, characteristics, and contributions to overall physiological processes. Cells may be classified by their physiological function, histology (microscopic anatomy), lineage, or gene expression. Total number of cells The adult human body is estimated to contain about 30 trillion (3×1013) human cells, with the number varying between 20 and 100 trillion depending on factors such as sex, age, and weight. Additionally, there are approximately an equal number of bacterial cells. The exact count of human cells has not yet been empirically measured in its entirety and is estimated using different approaches based on smaller samples of empirical observation. It is generally assumed that these cells share features with each other and thus may be organized as belonging to a smaller number of types. Classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infundibular Recess
The pituitary stalk, also known as the infundibular stalk, infundibulum, or Fenderson's funnel, is the connection between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary, the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The floor of the third ventricle is prolonged downward as a funnel-shaped recess—the infundibular recess—into the infundibulum, where the apex of the pituitary is attached.''Grey's Anatomy'' It passes through the dura mater of the diaphragma sellae as it carries axons from the magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus down to the posterior pituitary where they release their neurohypophysial hormones, oxytocin and vasopressin, into the blood. Damage to the pituitary stalk blocks the release of antidiuretic hormone, resulting in polydipsia (excessive water intake) and polyuria (excessive urination, central diabetes insipidus). The diameter of the pituitary stalk at the level of optic chiasm is 3.3 mm, and at the pituitary gland insertion site is measured at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released from GnRH neurons within the hypothalamus. GnRH is inhibited by testosterone. The peptide belongs to gonadotropin-releasing hormone family. It constitutes the initial step in the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis. Structure The identity of GnRH was clarified by the 1977 Nobel Laureates Roger Guillemin and Andrew V. Schally: pyroGlu-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2 As is standard for peptide representation, the sequence is given from amino terminus to carboxyl terminus; also standard is omission of the designation of chirality, with assumption that all amino acids are in their L- form. The abbreviations are the standard abbreviations for the corresponding proteinogenic amino acids, except for ''pyroGlu'', whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophyseal Portal System
The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain, connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary. Its main function is to quickly transport and exchange hormones between the hypothalamus arcuate nucleus and anterior pituitary gland. The capillaries in the portal system are fenestrated (have many small channels with high vascular permeability) which allows a rapid exchange between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. The main hormones transported by the system include gonadotropin-releasing hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone–releasing hormone, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Structure The blood supply and direction of flow in the hypophyseal portal system has been studied over many years on laboratory animals and human cadaver specimens with injection and vascular corrosion casting methods. Short portal vessels between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anorexigenic
An anorectic is a drug that reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. These substances work by affecting the central nervous system or certain neurotransmitters to create a feeling of fullness or reduce the desire to eat. The understanding of anorexiant effects is crucial in the development of interventions for weight management, eating disorders, and related health concerns. The anorexiant effect can be induced through diverse mechanisms, ranging from hormonal regulation to neural signaling. Ghrelin, leptin, and peptide YY are among the hormones involved in appetite control. Additionally, neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine in the central nervous system contribute significantly to the regulation of food intake. By contrast, an appetite stimulant is referred to as orexigenic. The term is (from the Ancient Greek language, Greek and ), and such drugs are also known as anorexigenic, anorexiant, or appetite suppressant. History Us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexigenic
An orexigenic, or appetite stimulant, is a drug, hormone, or compound that increases appetite and may induce hyperphagia. This can be a medication or a naturally occurring neuropeptide hormone, such as ghrelin, orexin or neuropeptide Y, which increases hunger and therefore enhances food consumption. Usually appetite enhancement is considered an undesirable side effect of certain drugs as it leads to unwanted weight gain, but sometimes it can be beneficial and a drug may be prescribed solely for this purpose, especially when the patient is suffering from severe appetite loss or muscle wasting due to cystic fibrosis, anorexia, old age, cancer or AIDS. There are several widely used drugs which can cause a boost in appetite, including tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tetracyclic antidepressants, natural or synthetic cannabinoids, first-generation antihistamines, most antipsychotics and many steroid hormones. In the United States, no hormone or drug has currently been approved by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus
The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus is a nucleus of the hypothalamus. It is involved in feeding, drinking, body-weight regulation and circadian activity. More specifically, it is a necessary component for the expression of numerous behavioral and physiological circadian rhythms. The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus receives information from neurons and humors involved in feeding regulation, body weight and energy consumption, and then passes this information on to brain regions involved in sleep and wakefulness regulation, body temperature and corticosteroid secretion. Function The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus (DMH) receives its circadian information from the suprachiasmatic nucleus, both directly and via subparaventricular zone, and senses leptin and other feeding cues, but it is also possible that it contains its own feeding-entrained oscillator (FEO). This still has yet to be proven ''in vitro''. The DMH sends information to the ventrolateral preoptic area, locus coeru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventromedial Nucleus
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN, VMH or ventromedial hypothalamus) is a nucleus of the hypothalamus. In 2007, Kurrasch ''et al''. found that the ventromedial hypothalamus is a distinct morphological nucleus involved in terminating hunger, fear, thermoregulation, and sexual activity. This nuclear region is involved in the recognition of the feeling of fullness. Structure It has four subdivisions: * Anterior (VMHa) * Dorsomedial (VMHdm) * Ventrolateral (VMHvl) * Central (VMHc) These subdivisions differ anatomically, neurochemically, and behaviorally. Function The ventromedial nucleus (VMN) is most commonly associated with satiety. Early studies showed that VMN lesions caused over-eating and obesity in rats. However, the interpretation of these experiments was summarily discredited when Gold's research demonstrated that precision lesioning of the VMN did not result in hyperphagia. Nevertheless, numerous studies have shown that the immediacy of hyperphagia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |