|
Tamponade
Tamponade () is the closure or blockage (as of a wound or body cavity) by or as if by a tampon, especially to stop bleeding. Tamponade is a useful method of stopping a hemorrhage. This can be achieved by applying an absorbent dressing directly into a wound, thereby absorbing excess blood and creating a blockage, or by applying direct pressure with a hand or a tourniquet. Not to be confused with a tamponade that occurs as a result of health problems. For example: cardiac tamponade is a condition where fluid collects in the pericardial sac increasing pressure within the pericardium which in turn prevents the ventricles from expanding fully significantly reducing the efficiency of the heart. It is considered a medical emergency and if left unchecked is fatal. Bladder tamponade is obstruction of the urinary bladder outlet due to heavy blood clot formation within it. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
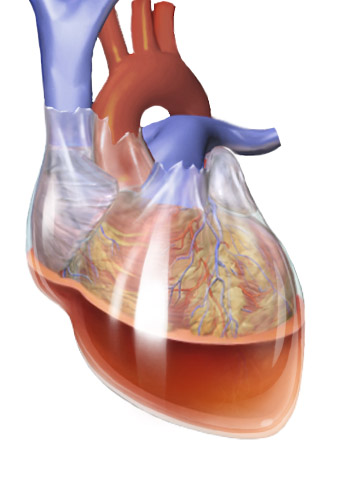
Cardiac Tamponade
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is a compression of the heart due to pericardial effusion (the build-up of pericardial fluid in the pericardium, sac around the heart). Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically include those of obstructive shock including shortness of breath, weakness, lightheadedness, and cough. Other symptoms may relate to the underlying cause. Common causes of cardiac tamponade include cancer, kidney failure, chest trauma, myocardial infarction, and pericarditis. Other causes include connective tissue disease, connective tissues diseases, hypothyroidism, aortic rupture, autoimmune disease, and complications of cardiac surgery. In Africa, tuberculosis is a relatively common cause. Diagnosis may be suspected based on hypotension, low blood pressure, jugular venous distension, or quiet heart sounds (together known as Beck's triad (cardiology), Beck's triad). A pericardial rub may be present in cases due to inflammation. The dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Wax
Bone wax as a sterile preparation for surgeryBone wax is a waxy substance used to help mechanically control bleeding from bone surfaces during surgical procedures. It is generally made of beeswax with a softening agent such as paraffin or petroleum jelly and is smeared across the bleeding edge of the bone, blocking the holes and causing immediate bone hemostasis through a tamponade effect. Bone wax is most commonly supplied in sterile sticks, and usually requires softening before it can be applied. History A note by Victor Horsley published in the British Medical Journal in 1892 described a formulation of "antiseptic wax" having seven parts beeswax, one part almond oils, and 1% salicylic acid. The material was useful for controlling bleeding when pressed into the pores and channels of cut or damaged bone. The wax was sterilized by boiling and kept istoppered bottles This material soon became the standard of care for bleeding control in bone for general orthopedics, craniomaxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix ''peri-'' (περί) 'around' and the suffix ''-cardion'' (κάρδιον) 'heart'. Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfluoropropane
Octafluoropropane (C3F8) is the perfluorocarbon counterpart to the hydrocarbon propane. This non-flammable and non-toxic synthetic substance has applications in semiconductor production and medicine. It is also an extremely potent greenhouse gas. Manufacture Octafluoropropane can be produced either by electrochemical fluorination or by the Fowler process using cobalt fluoride. Applications In the electronics industry, octafluoropropane is mixed with oxygen and used as a plasma etching material for SiO2 layers in semiconductor applications, as oxides are selectively etched versus their metal substrates. In medicine, octafluoropropane may compose the gas cores of microbubble contrast agents used in contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Octafluoropropane microbubbles reflect sound waves well and are used to improve the ultrasound signal backscatter. It is used in eye surgery, such as pars plana vitrectomy procedures where a retina hole or tear is repaired. The gas provides a long-term ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorragic Effusion
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by the rupture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tampon
A tampon is a menstrual product designed to absorb blood and vaginal secretions by insertion into the vagina during menstruation. Unlike a pad, it is placed internally, inside of the vaginal canal. Once inserted correctly, a tampon is held in place by the vagina and expands as it soaks up menstrual blood. As tampons also absorb the vagina's natural lubrication and bacteria in addition to menstrual blood, they can increase the risk of toxic shock syndrome by changing the normal pH of the vagina and increasing the risk of infections from the bacterium ''Staphylococcus aureus''. TSS is a rare but life-threatening infection that requires immediate medical attention. The majority of tampons sold are made of blends of rayon and cotton, along with synthetic fibers. Some tampons are made out of organic cotton. Tampons are available in several absorbency ratings. Several countries regulate tampons as medical devices. In the United States, they are considered to be a Class II medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourniquet
A tourniquet is a device that is used to apply pressure to a limb or extremity in order to create ischemia or stopping the flow of blood. It may be used in emergencies, in surgery, or in post-operative rehabilitation. A simple tourniquet can be made from a stick and a rope, but the use of makeshift tourniquets has been reduced over time due to their ineffectiveness compared to a commercial and professional tourniquet. This may stem the flow of blood, but side effects such as soft tissue damage and nerve damage may occur. History During Alexander the Great’s military campaigns in the fourth century BC, tourniquets were used to stanch the bleeding of wounded soldiers. Romans used them to control bleeding, especially during amputations. These tourniquets were narrow straps made of bronze, using only leather for comfort. In 1718, French surgeon Jean Louis Petit developed a screw device for occluding blood flow in surgical sites. Before this invention, the ''tourniquet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
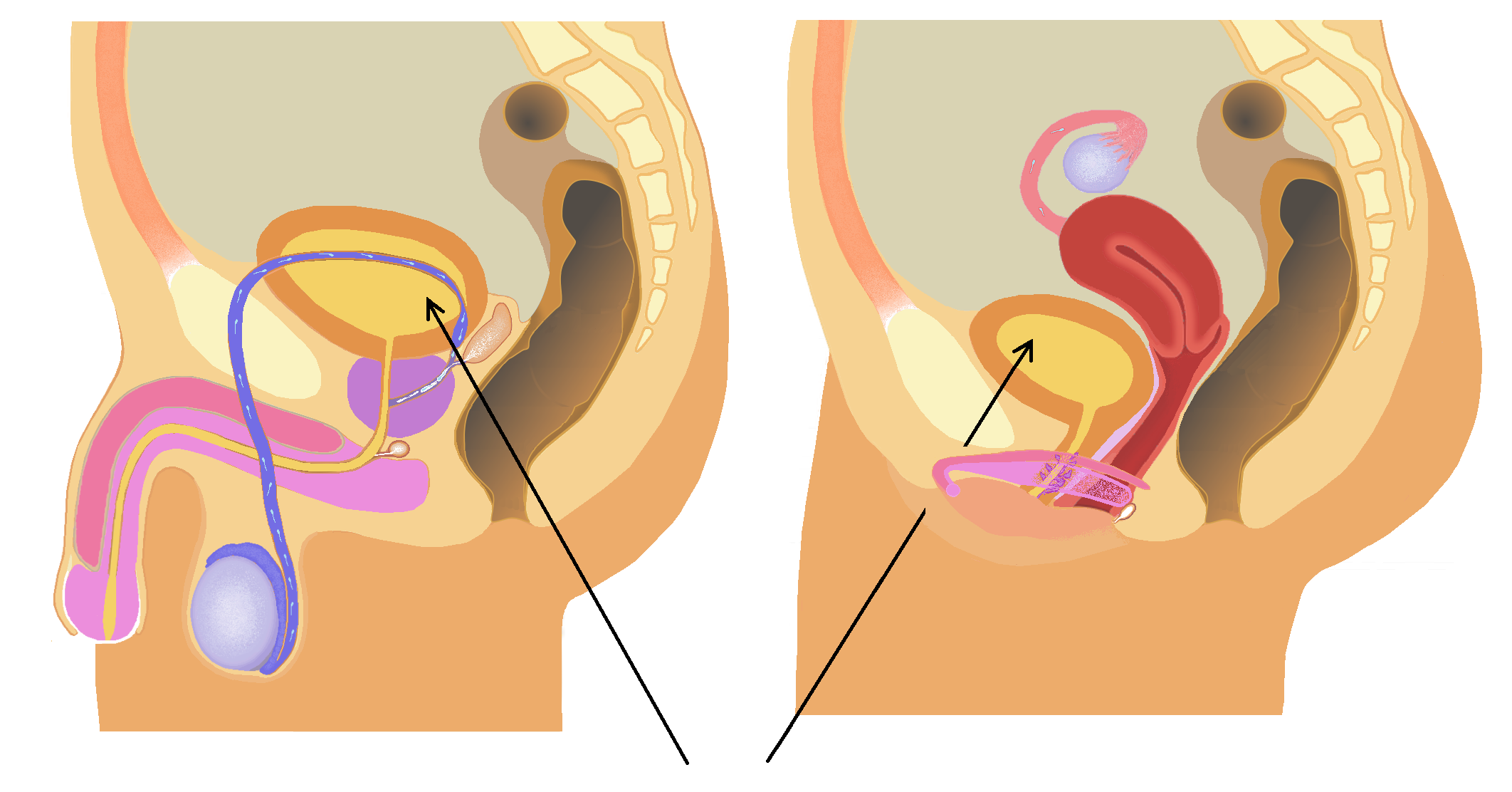
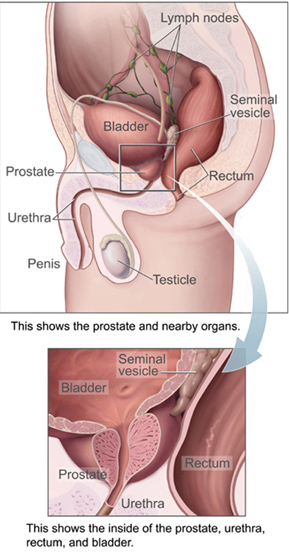
Bladder Tamponade
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward toward the up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis in or out of the circulatory system. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to stop and prevent further bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when a clot obstructs blood flow through a healthy blood vessel in the circulatory system. In the microcirculation consisting of the very small and smallest blood vessels the capillaries, tiny thrombi known as microclots can obstruct the flow of blood in the capillaries. This can cause a number of problems particularly affecting the alveoli in the lungs of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |