|
Taijiquan
is a Chinese martial art. Initially developed for combat and self-defense, for most practitioners it has evolved into a sport and form of exercise. As an exercise, tai chi is performed as gentle, low-impact movement in which practitioners perform a series of deliberate, flowing motions while focusing on deep, slow breaths. Often referred to as "meditation in motion", tai chi aims to concentrate and balance the body's purported (vital energy), providing benefits to mental and physical health. Many forms of tai chi are practiced, both traditional and modern. While the precise origins are not known, the earliest documented practice is from Chen-style tai chi, Chen Village and Zhaobao tai chi, Zhabao Village in Henan on the North China Plain, a region where centuries of rebellions, invasions, and adverse economic and social conditions nurtured the development of a wide range of martial arts, including those of the Shaolin Monastery on Mount Song at the western edge of the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen-style Tai Chi
The Chen-style tai chi ( zh, s=陳氏太极拳, p=Chén shì tàijíquán) is a Northern Wushu (sport), Chinese martial art and the original form of tai chi. Chen (surname), Chen-style is characterized by silk reeling, alternating fast and slow motions, and bursts of power (''fa jin''). Traditionally, tai chi is practiced as a martial art but has expanded into other domains of practice such as health or performances. Some argue that Chen-style tai chi has preserved and emphasized the martial efficacy to a greater extent. History Origin theories It is not clear how the Chen family actually came to practise their unique martial style and contradictory "histories" abound. What is known is that the other four tai chi styles (Yang, Sun, Wu and Wu (Hao)) trace their teachings back to Chen village in the early 1800s. The Chen family were originally from Hongtong County in Shanxi. In the 13th or 14th century, later documents claim that the head of the Chen family, Chen Bu (), migra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Fake
Chen Fake ( zh, c=陳發科, w=Ch'en Fa-k'e; 1887–1957), courtesy name Chen Fusheng ( zh, c=福生, labels=no), was a Chinese martial arts, Chinese martial artist who taught Chen-style tai chi. He was born and raised in Chen Family Village (Chenjiagou, 陳家溝) in Henan province. In 1928, Chen Fake relocated to Beijing to teach his family's heritage, Chen-style tai chi. After successfully defeating numerous challengers, Chen garnered a following of students, including several renowned martial artists. As a martial artist rather than a scholar, Chen Fake did not leave behind a written record of his accomplishments. His life story was recounted and preserved by his sons and students, most notably Hong Junsheng. By the time of his death in 1957, Chen had firmly established the global practice of Chen-style tai chi, creating a martial arts tradition that continues to thrive. Background Early life Chen Fake was born in 1887 in Chen Village, located in Wen County, Henan, Wen co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheng Man-ch'ing
Cheng Man-ch'ing or Zheng Manqing (29 July 1902 - 26 March 1975) was a Chinese expert of tai chi, Chinese medicine, and the so-called three perfections: calligraphy, painting and poetry. He was born in Yongjia (present-day Wenzhou), Zhejiang Province, during the Qing dynasty. Cheng died March 26, 1975; his grave is near the city of Taipei in Taiwan. Because of his skills in the '' 3 Perfections'' or "Excellences" – considered to be among some of the traditional skills and pastimes of a Confucian scholar – plus medicine and tai chi, he was often referred to as the "Master of Five Excellences." Because he had been a college professor, his students in the USA called him "Professor Cheng." Early years Cheng's father died when Cheng was very young. Around the age of nine, Cheng was struck on the head by a falling object, and was in a coma for a short while. He recuperated slowly, and was apprenticed to a well-known artist, Wang Xiangchan 汪香禪, in hopes that simple jobs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Luchan
Yang Luchan ( zh, c=杨露禅, w=Yang Lu-ch'an, p=Yáng Lùchán), also known as Yang Fukui (1799–1872), was an influential Chinese practitioner and teacher of the internal style tai chi martial art. He is known as the founder of Yang-style tai chi, the most popular and widely practised tai chi style in the world today. History Yang Luchan's family was a poor farming/worker class from Hebei Province, Guangping Prefecture, Yongnian County. Yang would follow his father in planting the fields and, as a teenager, held temporary jobs. One period of temporary work was spent doing odd jobs at the Taihetang Chinese pharmacy located in the west part of Yongnian City, opened by Chen Dehu of the Chen Village in Huaiqing Prefecture, Wen County, Henan. As a child, Yang liked martial arts and studied Changquan, gaining a certain level of skill. One day Yang reportedly witnessed one of the partners of the pharmacy utilizing a style of martial art that he had never before seen to easily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Chengfu
Yang Chengfu (1883–1936) was one of the best known teachers of Yang-style tai chi Chinese martial art. He helped develop the art into its modern form. His students would go on to found successful martial arts schools of their own and helped spread Yang-style tai chi around the world. Biography Yang Chengfu was born into the famous Yang family of tai chi practitioners, the son of Yang Jianhou and grandson of Yang Luchan. With his older brother Yang Shaohou and colleagues Wu Jianquan and Sun Lutang, he was among the first teachers to offer tai chi instruction to the general public at the Beijing Physical Culture Research Institute from 1914 until 1928. He moved to Shanghai in 1928. Chengfu is known for having "smoothed" out the somewhat more vigorous training routine he learned from his family as well as emphasising a "large frame" ( zh, c=大架, p=dà jià, labels=no) with expansive movements in stepping and using large circular motions with the arms. His smooth, evenly pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Martial Art
Chinese martial arts, commonly referred to with umbrella terms Kung fu (term), kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (sport), wushu (), are Styles of Chinese martial arts, multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to common traits, identified as "families" of martial arts. Examples of such traits include ''Shaolin kung fu, Shaolinquan'' () physical exercises involving Five Animals, All Other Animals () mimicry or training methods inspired by Chinese philosophies, Old Chinese philosophies, religions and legends. Styles that focus on qi manipulation are called ''Internal martial arts, internal'' (; ), while others that concentrate on improving muscle and cardiovascular fitness are called ''Styles of Chinese martial arts#External styles, external'' (; ). Geographical associations, as in ''northern'' (; ) and ''Nanquan (martial art), southern'' (; ), is another popular classification method. Ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Wangting
Chen Wangting (1580–1660), courtesy name Chen Zouting, was a Ming dynasty military officer who may have founded Chen-style tai chi, one of the five major styles of the popular Chinese martial art. He reputedly devised his style of tai chi after his retirement following the fall of the Ming dynasty. Military career During the Ming dynasty, Chen served as Commander of the Wen County garrison, and was distinguished for his protection of merchant caravans in Henan and Shandong. After the Ming dynasty ended and the reign of the Qing dynasty began, Chen's military career was effectively over, and he retired to the family settlement. Influence on tai chi Whether or not Chen invented the earliest form of tai chi is in dispute. Traditional folklore and many lineages name the semi-mythical figure of Zhang Sanfeng, a Taoist monk, as the progenitor of the art. Two widely documented theories of Chen's martial arts work exist: the first is that he learnt his arts from Wang Zongyue, Jian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Sanfeng
Zhang Sanfeng (also spelled Zhang San Feng, Chang San-Feng) refers to a legendary Chinese Taoist who many believe invented the Chinese martial art tai chi. However, other sources point to earlier versions of tai chi predating Sanfeng. He is purported to have achieved immortality. History There are conflicting accounts of where Zhang Sanfeng was born. According to the History of Ming, he was born in Liaoning in late Song and lived up to 212 years. In 2014, the local government of Shaowu, Fujian province, claimed that he was born in their city. His given name was Tong (通) and his courtesy name was Junbao (). He specialised in Confucian and Taoist studies, scholarly and literary arts. During the reign of Emperor Shizu in the Yuan dynasty, he was nominated as a candidate to join the civil service and held office as the Magistrate of Boling County (博陵縣; around present-day Dingzhou, Baoding, Hebei). While touring around the mountainous regions near present-day Baoji, Shaa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Jianquan
Wu Jianquan ( zh, c=吴鉴泉, w=Wu Chien-ch‘üan, p=Wú Jiànquán; 1870–1942) was a famous teacher and founder of the ''neijia'' martial art of Wu-style tai chi in late Imperial and early Republican China. Biography Wu Jianquan was taught martial arts by his father, Wu Quanyou, a senior student of Yang Luchan, and Yang Banhou. Both Wu Jianquan and his father were hereditary Manchu cavalry officers of the Yellow Banner as well as the Imperial Guards Brigade, yet the Wu family were to become patriotic supporters of Sun Yat-sen. At the time of the establishment of the Chinese Republic in 1912, China was in turmoil, besieged for many years economically and even militarily by several foreign powers, so Wu Jianquan and his colleagues Yang Shaohou, Yang Chengfu and Sun Lutang promoted the benefits of tai chi training on a national scale. They subsequently offered classes at the Beijing Physical Culture Research Institute to as many people as possible, starting in 1914. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoism
Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dào, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', 'path', or 'technique', generally understood in the Taoist sense as an enigmatic process of transformation Ultimate reality, ultimately underlying reality. Taoist thought has informed the development of various practices within the Taoist tradition and beyond, including forms of Taoist meditation, meditation, Chinese astrology, astrology, qigong, feng shui, and Neidan, internal alchemy. A common goal of Taoist practice is self-cultivation, a deeper appreciation of the Tao, and more harmonious existence. Taoist ethics vary, but generally emphasize such virtues as ''wu wei, effortless action'', ziran, ''naturalness'', ''pu (Taoism), simplicity'', and the Three Treasures (Taoism), three treasures of compassion, frugality, and humility. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
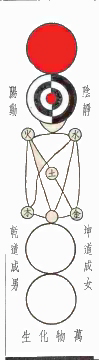
Yin And Yang
Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary and at the same time opposing forces that interact to form a dynamic system in which the whole is greater than the assembled parts and the parts are as important for the cohesion of the whole. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of primordial qi or material energy, organized into the cycles of yin and yang, force and motion leading to form and matter. "Yin" is retractive, passive and contractive in nature, while "yang" is repelling, active and expansive in principle; this dichotomy in some form, is seen in all things in nature—patterns of change and difference. For example, biological, psychological and seasonal cycles, the historical evolution of landscapes over days, weeks, years to eons. The origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiji (philosophy)
In Chinese philosophy, ''taiji'' () is a cosmological state of the universe and its affairs on all levels—including the mutually reinforcing interactions between the two opposing forces of yin and yang (a dualistic monism), as well as that among the Three Treasures, the four cardinal directions, and the Five Elements—which together ultimately bring about the myriad things, each with their own nature. The concept of ''taiji'' has reappeared throughout the technological, religious, and philosophical history of the Sinosphere, finding concrete application in techniques developed in acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine. Etymology ''Taiji'' () is a compound of ''tai'' ( 'great', 'supreme') and ''ji'' ( 'pole', 'extremity'). Used together, ''taiji'' may be understood as 'source of the world'. Common English translations of ''taiji'' in the cosmological sense include "Supreme Ultimate", "Supreme Pole", and "Great Absolute". Core concept Scholars Zhang and Ryden e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |