|
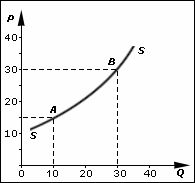
Supply Curve
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or to an individual. Supply can be in produced goods, labour time, raw materials, or any other scarce or valuable object. Supply is often plotted graphically as a supply curve, with the price per unit on the vertical axis and quantity supplied as a function of price on the horizontal axis. This reversal of the usual position of the dependent variable and the independent variable is an unfortunate but standard convention. The supply curve can be either for an individual seller or for the market as a whole, adding up the quantity supplied by all sellers. The quantity supplied is for a particular time period (e.g., the tons of steel a firm would supply in a year), but the units and time are often omitted in theoretical presentations. In the goods market, supply is the amount of a product per un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply
Supply may refer to: *The amount of a resource that is available **Supply (economics), the amount of a product which is available to customers **Materiel, the goods and equipment for a military unit to fulfill its mission *Supply, as in confidence and supply, the provision of funds for government expenditure *Narcissistic supply, the way in which a narcissistic individual requires affirmation, approval, and admiration from others in the same way as the infant requires an external supply of food Places *Supply, North Carolina, an unincorporated community *Supply, Virginia, an unincorporated community Ships * HMS ''Supply'', eight ships of the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom * HMAS ''Supply'', two ships of the Royal Australian Navy * USS ''Supply'', four ships of the United States Navy People with the name *Supply Belcher (1751–1836), early American composer of the First New England School Entertainment * "Supplies" (song), by Justin Timberlake, from his 2018 album ''Man of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Markets
A financial market is a market in which people trade financial securities and derivatives at low transaction costs. Some of the securities include stocks and bonds, raw materials and precious metals, which are known in the financial markets as commodities. The term "market" is sometimes used for what are more strictly ''exchanges'', organizations that facilitate the trade in financial securities, e.g., a stock exchange or commodity exchange. This may be a physical location (such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), London Stock Exchange (LSE), JSE Limited (JSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) or an electronic system such as NASDAQ. Much trading of stocks takes place on an exchange; still, corporate actions (merger, spinoff) are outside an exchange, while any two companies or people, for whatever reason, may agree to sell the stock from the one to the other without using an exchange. Trading of currencies and bonds is largely on a bilateral basis, although some bonds trade o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shutdown (economics)
A firm will choose to implement a shutdown of production when the revenue received from the sale of the goods or services produced cannot even cover the variable costs of production. In that situation, the firm will experience a higher loss when it produces, compared to not producing at all. Technically, shutdown occurs if average revenue is below average variable cost at the profit-maximizing positive level of output. Producing anything would not generate enough revenue to offset the associated variable costs; producing some output would add further costs in excess of revenues to the costs inevitably being incurred (the fixed costs). By not producing, the firm loses only the fixed costs. Explanation The goal of a firm is to maximize profits or minimize losses. The firm can achieve this goal by following two rules. First, the firm should operate, if at all, at the level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Second, the firm should shut down rather than operate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Cost
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented, the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it refers to the rate of change of total cost as output is increased by an infinitesimal amount. As Figure 1 shows, the marginal cost is measured in dollars per unit, whereas total cost is in dollars, and the marginal cost is the slope of the total cost, the rate at which it increases with output. Marginal cost is different from average cost, which is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. At each level of production and time period being considered, marginal cost includes all costs that vary with the level of production, whereas costs that do not vary with production are fixed. For example, the marginal cost of producing an automobile will include the costs of labor and parts needed for the additional automobile but not the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply And Demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a Market (economics), market. It postulates that, Ceteris paribus, holding all else equal, in a perfect competition, competitive market, the unit price for a particular Good (economics), good, or other traded item such as Labour supply, labor or Market liquidity, liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In macroeconomics, as well, the AD–AS model, aggregate demand-aggregate supply model has been used to depict how the quantity of real GDP, total output and the aggregate price level may be determined in equilibrium. Graphical representations Supply schedule A supply schedule, depicted graphically as a supply cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
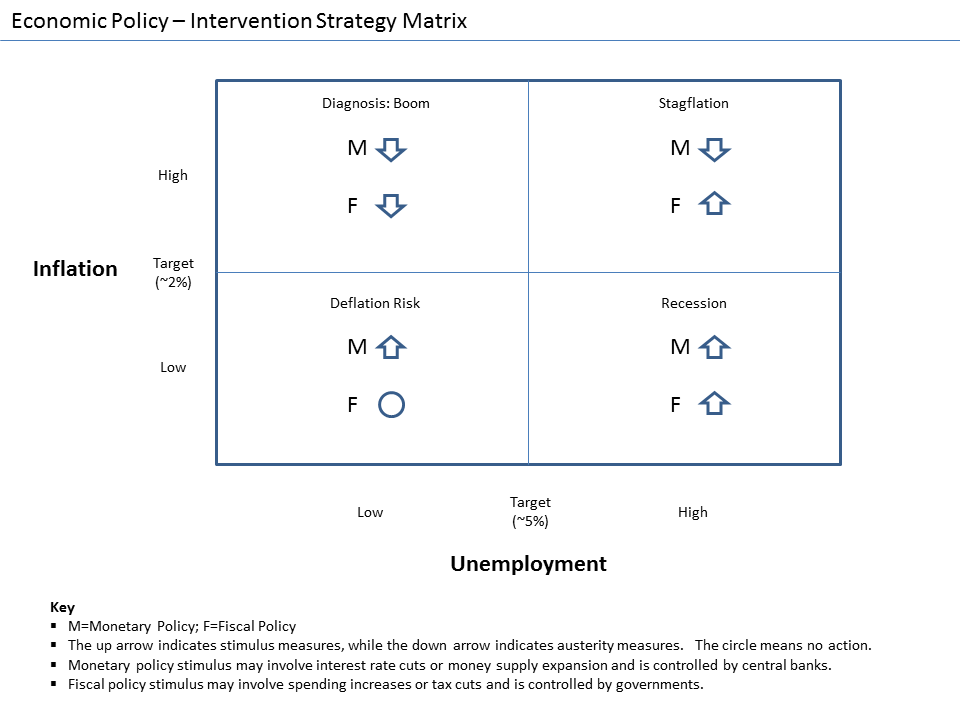
Economic Interventionism
Economic interventionism, sometimes also called state interventionism, is an economic policy position favouring government intervention in the market process with the intention of correcting market failures and promoting the general welfare of the people. An economic intervention is an action taken by a government or international institution in a market economy in an effort to impact the economy beyond the basic regulation of fraud, enforcement of contracts, and provision of public goods and services. Economic intervention can be aimed at a variety of political or economic objectives, such as promoting economic growth, increasing employment, raising wages, raising or reducing prices, promoting income equality, managing the money supply and interest rates, increasing profits, or addressing market failures. The term ''intervention'' is typically used by advocates of ''laissez-faire'' and free market capitalism, and assumes that, on a philosophical level, the state and econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item is a function of an item's perceived necessity, price, perceived quality, convenience, available alternatives, purchasers' disposable income and tastes, and many other options. Factors influencing demand Innumerable factors and circumstances affect a consumer's willingness or to buy a good. Some of the common factors are: The price of the commodity: The basic demand relationship is between potential prices of a good and the quantities that would be purchased at those prices. Generally, the relationship is negative, meaning that an increase in price will induce a decrease in the quantity demanded. This negative relationship is embodied in the downward slope of the consumer demand curve. The assumption of a negative relationship is reaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technological Progress
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to economic deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Product Pricing
In microeconomics, joint product pricing is the firm's problem of choosing prices for joint products, which are two or more products produced from the same process or operation, each considered to be of value. Pricing for joint products is more complex than pricing for a single product. To begin with, there are two demand curves. The characteristics of each could be different. Demand for one product could be greater than for the other. Consumers of one product could be more price elastic than consumers of the other (and therefore more sensitive to changes in the product's price). To complicate things further, both products, because they are produced jointly, share a common marginal cost curve. There are also complexities in the production function. Their production could be linked in the sense that they are bi-products (referred to as ''complements in production'') or in the sense that they can be produced by the same inputs (referred to as ''substitutes in production''). Further, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Of Production
In economics, factors of production, resources, or inputs are what is used in the production process to produce output (economics), output—that is, goods and service (economics), services. The utilized amounts of the various inputs determine the quantity of output according to the relationship called the production function. There are four ''basic'' resources or factors of production: land, labour, capital and entrepreneur (or enterprise). The factors are also frequently labeled "producer goods or services" to distinguish them from the goods or services purchased by consumers, which are frequently labeled "consumer goods". There are two types of factors: ''primary'' and ''secondary''. The previously mentioned primary factors are land, labour and capital. Materials and energy are considered secondary factors in classical economics because they are obtained from land, labour, and capital. The primary factors facilitate production but neither becomes part of the product (as with raw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Of Production
In economics, factors of production, resources, or inputs are what is used in the production process to produce output (economics), output—that is, goods and service (economics), services. The utilized amounts of the various inputs determine the quantity of output according to the relationship called the production function. There are four ''basic'' resources or factors of production: land, labour, capital and entrepreneur (or enterprise). The factors are also frequently labeled "producer goods or services" to distinguish them from the goods or services purchased by consumers, which are frequently labeled "consumer goods". There are two types of factors: ''primary'' and ''secondary''. The previously mentioned primary factors are land, labour and capital. Materials and energy are considered secondary factors in classical economics because they are obtained from land, labour, and capital. The primary factors facilitate production but neither becomes part of the product (as with raw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Supply
The law of supply is a fundamental principle of economic theory which states that, keeping other factors constant, an increase in price results in an increase in quantity supplied. In other words, there is a direct relationship between price and quantity: quantities respond in the same direction as price changes. This means that producers are willing to offer more of a product for sale on the market at higher prices by increasing production as a way of increasing profits. In short, the law of supply is a positive relationship between quantity supplied and price and is the reason for the upward slope of the supply curve. Some heterodox economists, such as Steve Keen and Dirk Ehnts, dispute the law of supply, arguing that the supply curve for mass produced goods is often downward-sloping: as production increases, unit prices go down, and conversely, if demand is very low, unit prices go up. This corresponds to economies of scale. Definition To know law of supply, we should kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |