|
Spiro Compounds
In organic chemistry, spiro compounds are compounds that have at least two molecular rings with only one common atom. The simplest spiro compounds are bicyclic (having just two rings), or have a bicyclic portion as part of the larger ring system, in either case with the two rings connected through the defining single common atom. The one common atom connecting the participating rings distinguishes spiro compounds from other bicyclics: from ''isolated ring compounds'' like biphenyl that have no connecting atoms, from ''fused ring compounds'' like decalin having two rings linked by two adjacent atoms, and from ''bridged ring compounds'' like norbornane with two rings linked by two non-adjacent atoms.For all four categories, see The specific chapters can be found aan respectively, same access date. For the description featuring adjacent atoms for all but the isolated category, see Clayden, op. cit. Spiro compounds may be fully carbocyclic (all carbon) or heterocyclic (hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
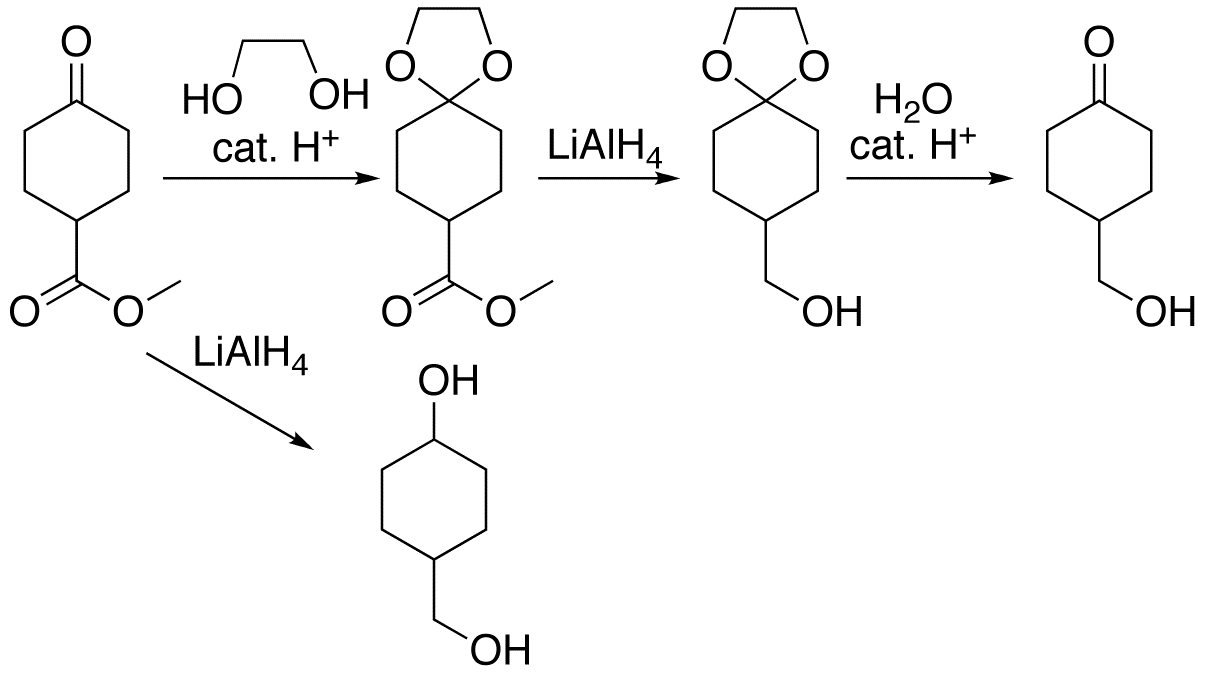
Ketal Synthesis V
In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity . Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other (a "symmetric acetal") or not (a "mixed acetal"). Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry. The term ketal is sometimes used to identify structures associated with ketones (both R groups organic fragments rather than hydrogen) rather than aldehydes and, historically, the term acetal was used specifically for the aldehyde-related cases (having at least one hydrogen in place of an R on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiropentadiene
Spiropentadiene, or bowtiediene, is a hydrocarbon with formula C5H4. The simplest spiro-connected cycloalkene, it is very unstable—decomposing even below −100 °C—due to its high bond strain and does not occur in nature. Its synthesis was reported in 1991. Synthesis Spiropentadiene was synthesised from bistrimethylsilylpropynone 1 by reaction with p-toluenesulfonylhydrazide to tosylhydrazone 2 followed by treatment with sodium cyanoborohydride to allene 3 and followed by two successive reactions with chlorocarbene generated from methyllithium and dichloromethane to spiro compound 5. Spiropentadiene was trapped in a liquid nitrogen trap after reaction with TBAF in a double elimination reaction. : Derivatives The derivative dichlorospiropentadiene has been reported. An all-silicon derivative (Si5 frame, (tBuMe2Si)3Si side groups) is also known. In contrast to the carbon parent this compound is stable with a melting point of 216 to 218 °C. The angle betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. Production Cyclohexanone is produced by the oxidation of cyclohexane in air, typically using cobalt catalysts: :C6H12 + O2 → (CH2)5CO + H2O This process forms cyclohexanol as a by-product, and this mixture, called "KA Oil" for ketone-alcohol oil, is the main feedstock for the production of adipic acid. The oxidation involves radicals and the hydroperoxide C6H11O2H as an intermediate. In some cases, purified cyclohexanol, obtained by hydration of cyclohexene, is the precursor. Alternatively, cyclohexanone can be produced by the partia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithiol
In organic chemistry, a dithiol is a type of organosulfur compound with two thiol () functional groups. Their properties are generally similar to those of monothiols in terms of solubility, odor, and volatility. They can be classified according to the relative location of the two thiol groups on the organic backbone. File:C6H4(SH)2.svg, Benzene-1,2-dithiol, the parent aromatic dithiol File:1,3-Propandithiol Structural Formula V1.svg, Propane-1,3-dithiol File:Meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic-acid-2D-skeletal-A-configurations-labelled.png, The drug meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid File:Dimercaprol.svg, Dimercaprol ("British anti-Lewisite"), an early antidote for arsenic poisoning File:Dihydrolipoic-acid-2D-skeletal.png, Dihydrolipoic acid, a vitamin File:Dithiothreitol.png, Dithiothreitol, a reagent in protein biochemistry Geminal dithiols Geminal dithiols have the formula RR'C(SH)2. They are derived from aldehydes and ketones by the action of hydrogen sulfide. Their stability con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Society Reviews
''Chemical Society Reviews'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society of Chemistry, for review articles on topics of current interest in chemistry. Its predecessors were ''Quarterly Reviews, Chemical Society'' (1947–1971) and ''Royal Institute of Chemistry, Reviews'' (1968–1971); it maintained its current title since 1971. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 54.564. The current editor-in-chief (Chair of Editorial Board) is Douglas Stephan. ''Chemical Society Reviews'' publishes occasional themed issues on new and emerging areas of research in the chemical sciences. These issues are edited by a guest editor who is a specialist in their field. Since 2005, ''Chemical Society Reviews'' has published reviews on topics of broad appeal, termed "social interest" reviews, such as articles on art conservation, forensics, and automotive fuels. The journal is abstracted and indexed in PubMed/MEDLINE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spironolactone
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood pressure, low blood potassium that does not improve with supplementation, early puberty in boys, acne and excessive hair growth in women, and as a part of transgender hormone therapy in transfeminine people. Spironolactone is taken by mouth. Common side effects include electrolyte abnormalities, particularly high blood potassium, nausea, vomiting, headache, rashes, and a decreased desire for sex. In those with liver or kidney problems, extra care should be taken. Spironolactone has not been well studied in pregnancy and should not be used to treat high blood pressure of pregnancy. It is a steroid that blocks the effects of the hormones aldosterone and testosterone and has some estrogen-like effects. Spironolactone belongs to a cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science News
''Science News (SN)'' is an American bi-weekly magazine devoted to articles about new scientific and technical developments, typically gleaned from recent scientific and technical journals. History ''Science News'' has been published since 1922 by Society for Science & the Public, a non-profit organization founded by E. W. Scripps in 1920. American chemist Edwin Slosson served as the publication's first editor. From 1922 to 1966, it was called ''Science News Letter''. The title was changed to ''Science News'' with the March 12, 1966 issue (vol. 89, no. 11). Tom Siegfried was the editor from 2007 to 2012. In 2012, Siegfried stepped down, and Eva Emerson became the Editor in Chief of the magazine. In 2017, Eva Emerson stepped down to become the editor of a new digital magazine, Annual Reviews. On February 1, 2018 Nancy Shute became the Editor in Chief of the magazine. In April 2008, the magazine changed from a weekly format to the current biweekly format, and the website w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Products
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis (both semisynthesis and total synthesis) and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients. Within the field of organic chemistry, the definition of natural products is usually restricted to organic compounds isolated from natural sources that are produced by the pathways of primary or secondary metabolism. Within the field of medicinal chemistry, the definition is often further restricted to secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites (or specialized metabolite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicyclic
In chemistry, a bicyclic molecule () is a molecule that features two joined rings. Bicyclic structures occur widely, for example in many biologically important molecules like α-thujene and camphor. A bicyclic compound can be carbocyclic (all of the ring atoms are carbons), or heterocyclic (the rings' atoms consist of at least two elements), like DABCO. Moreover, the two rings can both be aliphatic (''e.g.'' decalin and norbornane), or can be aromatic (''e.g.'' naphthalene), or a combination of aliphatic and aromatic (''e.g.'' tetralin). Three modes of ring junction are possible for a bicyclic compound: * In spirocyclic compounds, the two rings share only one single atom, the spiro atom, which is usually a quaternary carbon. An example of a spirocyclic compound is the photochromic switch spiropyran. * In fused/condensed bicyclic compounds, two rings share two adjacent atoms. In other words, the rings share one covalent bond, ''i.e.'' the so-called bridgehead atoms are di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Synthesis
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis (or combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses, the process is reproducible and reliable. A chemical synthesis involves one or more compounds (known as '' reagents'' or ''reactants'') that will experience a transformation when subjected to certain conditions. Various reaction types can be applied to formulate a desired product. This requires mixing the compounds in a reaction vessel, such as a chemical reactor or a simple round-bottom flask. Many reactions require some form of processing (" work-up") or purification procedure to isolate the final product. The amount produced by chemical synthesis is known as the ''reaction yield''. Typically, yields are expressed as a mass in grams (in a laboratory setting) or as a percentage of the total theoretical quantity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |