|
Solubilizer
Micellar solubilization (solubilization) is the process of incorporating the solubilizate (the component that undergoes solublization) into or onto micelles. Solublization may occur in a system consisting of a solvent, an association colloid (a colloid that forms micelles), and at least one other solubilizate. Usage of the term Solubilization is distinct from dissolution (chemistry), dissolution because the resulting fluid is a colloidal dispersion involving an association colloid. This suspension is distinct from a true Solution (chemistry), solution, and the amount of the solubilizate in the micellar system can be different (often higher) than the regular solubility of the solubilizate in the solvent. In non-chemical literature and in everyday language, the term "solubilization" is sometimes used in a broader meaning as "to bring to a solution or (non-sedimentation, sedimenting) suspension" by any means, e.g., leaching (chemistry), leaching by a reaction with an acid. Applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
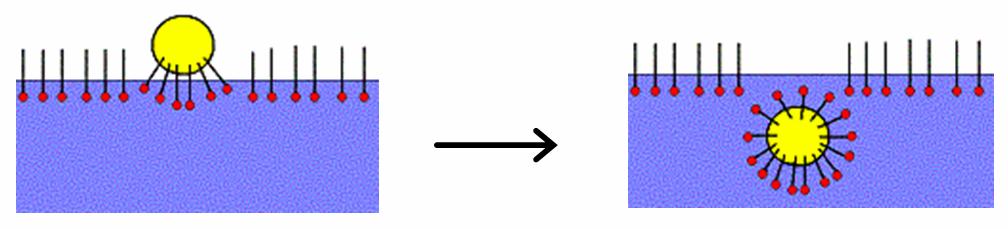
Micelle
A micelle () or micella () (plural micelles or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension (also known as associated colloidal system). A typical micelle in water forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the micelle centre. This phase is caused by the packing behavior of single-tail lipids in a bilayer. The difficulty filling all the volume of the interior of a bilayer, while accommodating the area per head group forced on the molecule by the hydration of the lipid head group, leads to the formation of the micelle. This type of micelle is known as a normal-phase micelle (oil-in-water micelle). Inverse micelles have the head groups at the centre with the tails extending out (water-in-oil micelle). Micelles are approximately spherical in shape. Other phases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels. The term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture (although a narrower sense of the word ''suspension'' is distinguished from colloids by larger particle size). A colloid has a dispersed phase (the suspended particles) and a continuous phase (the medium of suspension). The dispersed phase particles have a diameter of approximately 1 nanometre to 1 micrometre. Some colloids are translucent because of the Tyndall effect, which is the scattering of light by particles in the colloid. Other colloids may be opaque or have a slight color. Colloidal suspensions are the subject of interface and colloid science. This field of study was introduced in 1845 by Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolution (chemistry)
Solvation (or dissolution) describes the interaction of a solvent with dissolved molecules. Both ionized and uncharged molecules interact strongly with a solvent, and the strength and nature of this interaction influence many properties of the solute, including solubility, reactivity, and color, as well as influencing the properties of the solvent such as its viscosity and density. If the attractive forces between the solvent and solute particles are greater than the attractive forces holding the solute particles together, the solvent particles pull the solute particles apart and surround them. The surrounded solute particles then move away from the solid solute and out into the solution. Ions are surrounded by a concentric shell of solvent. Solvation is the process of reorganizing solvent and solute molecules into solvation complexes and involves bond formation, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. Solvation of a solute by water is called hydration. Solubility of solid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solution (chemistry)
In chemistry, a solution is a special type of homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. In such a mixture, a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. If the attractive forces between the solvent and solute particles are greater than the attractive forces holding the solute particles together, the solvent particles pull the solute particles apart and surround them. These surrounded solute particles then move away from the solid solute and out into the solution. The mixing process of a solution happens at a scale where the effects of chemical polarity are involved, resulting in interactions that are specific to solvation. The solution usually has the state of the solvent when the solvent is the larger fraction of the mixture, as is commonly the case. One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term "aqueous solution" is used when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be " miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. M. Diepen (1966): "Gas—Gas Equilibria". ''Journal of Chemical Physics'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the forces acting on them: these forces can be due to gravity, centrifugal acceleration, or electromagnetism. Settling is the falling of suspended particles through the liquid, whereas sedimentation is the final result of the settling process. In geology, sedimentation is the deposition of sediments which results in the formation of sedimentary rock. The term is broadly applied to the entire range of processes that result in the formation of sedimentary rock, from initial erosion through sediment transport and settling to the lithification of the sediments. However, the strict geological definition of sedimentation is the mechanical deposition of sediment particles from an initial suspension in air or water. Sedimentation may pertain to ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaching (chemistry)
Leaching is the process of a solute becoming detached or extracted from its carrier substance by way of a solvent. Leaching is a naturally occurring process which scientists have adapted for a variety of applications with a variety of methods. Specific extraction methods depend on the soluble characteristics relative to the sorbent material such as concentration, distribution, nature, and size. Leaching can occur naturally seen from plant substances (inorganic and organic), solute leaching in soil, and in the decomposition of organic materials. Leaching can also be applied affectedly to enhance water quality Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through tr ... and contaminant removal, as well as for disposal of hazardous waste products such as fly ash, or Rare-earth element, rare ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laundry
Laundry refers to the washing of clothing and other textiles, and, more broadly, their drying and ironing as well. Laundry has been part of history since humans began to wear clothes, so the methods by which different cultures have dealt with this universal human need are of interest to several branches of scholarship. Laundry work has traditionally been highly gendered, with the responsibility in most cultures falling to women (formerly known as laundresses or washerwomen). The Industrial Revolution gradually led to mechanized solutions to laundry work, notably the washing machine and later the tumble dryer. Laundry, like cooking and child care, is still done both at home and by commercial establishments outside the home. The word "laundry" may refer to the clothing itself, or to the place where the cleaning happens. An individual home may have a laundry room; a utility room includes but is not restricted to the function of washing clothes. An apartment building or student hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washing
Washing is a method of cleaning, usually with water and soap or detergent. Washing and then rinsing both body and clothing is an essential part of good hygiene and health. Often people use soaps and detergents to assist in the emulsification of oils and dirt particles so they can be washed away. The soap can be applied directly, or with the aid of a washcloth. People wash themselves, or bathe periodically for religious ritual or therapeutic purposes or as a recreational activity. In Europe, some people use a bidet to wash their external genitalia and the anal region after using the toilet, instead of using toilet paper. The bidet is common in predominantly Catholic countries where water is considered essential for anal cleansing. More frequent is washing of just the hands, e.g. before and after preparing food and eating, after using the toilet, after handling something dirty, etc. Hand washing is important in reducing the spread of germs. Also common is washing the face, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more soluble in hard water, because the polar sulfonate (of detergents) is less likely than the polar carboxylate (of soap) to bind to calcium and other ions found in hard water. Definitions The word ''detergent'' is derived from the Latin adjective ''detergens'', from the verb ''detergere'', meaning to wipe or polish off. Detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. However, conventionally, detergent is used to mean synthetic cleaning compounds as opposed to ''soap'' (a salt of the natural fatty acid), even though soap is also a detergent in the true sense. In domestic contexts, the term ''detergent'' refers to household cleaning products such as ''laundry detergent'' or '' dish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |