|
Safranin
Safranin (Safranin O or basic red 2) is a biological stain used in histology and cytology. Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring cell nuclei red. This is the classic counterstain in both Gram stains and endospore staining. It can also be used for the detection of cartilage, mucin and mast cell granules. Safranin typically has the chemical structure shown at right (sometimes described as dimethyl safranin). There is also trimethyl safranin, which has an added methyl group in the ''ortho-'' position (see Arene substitution pattern) of the lower ring. Both compounds behave essentially identically in biological staining applications, and most manufacturers of safranin do not distinguish between the two. Commercial safranin preparations often contain a blend of both types. Safranin is also used as redox indicator in analytical chemistry. Safranines Safranines are the azonium compounds of symmetrical 2,8-dimethyl-3,7-diaminophenazine. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific ( DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel electrophoresis. Light microscopes are us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Stain
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884. Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. Gram-positive cells have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in the cell wall that retains the primary stain, crystal violet. Gram-negative cells have a thinner peptidoglycan layer that allows the crystal violet to wash out on addition of ethanol. They are stained pink or red by the counterstain, commonly safranin or fuchsine. Lugol's iodine solution is always added after addition of crystal violet to strengthen the bonds of the stain with the cell membrane. Gram staining is almost always the first step in the preliminary identification of a bacterial organism. While Gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauveine
Mauveine, also known as aniline purple and Perkin's mauve, was one of the first synthetic dyes. It was discovered serendipitously by William Henry Perkin in 1856 while he was attempting to synthesise the phytochemical quinine for the treatment of malaria. It is also among the first chemical dyes to have been mass-produced. Chemistry Mauveine is a mixture of four related aromatic compounds differing in number and placement of methyl groups. Its organic synthesis involves dissolving aniline, ''p''-toluidine, and ''o''-toluidine in sulfuric acid and water in a roughly 1:1:2 ratio, then adding potassium dichromate. Mauveine A () incorporates 2 molecules of aniline, one of ''p''-toluidine, and one of ''o''-toluidine. Mauveine B () incorporates one molecule each of aniline, ''p''-toluidine, and two of ''o''-toluidine. In 1879, Perkin showed mauveine B related to safranines by oxidative/ reductive loss of the ''p''-tolyl group. In fact, safranine is a 2,8-dimethyl phenaziniu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone to oxidation: while freshly purified aniline is an almost colorless oil, exposure to air results in gradual darkening to yellow or red, due to the formation of strongly colored, oxidized impurities. Aniline can be diazotized to give a diazonium salt, which can then undergo var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
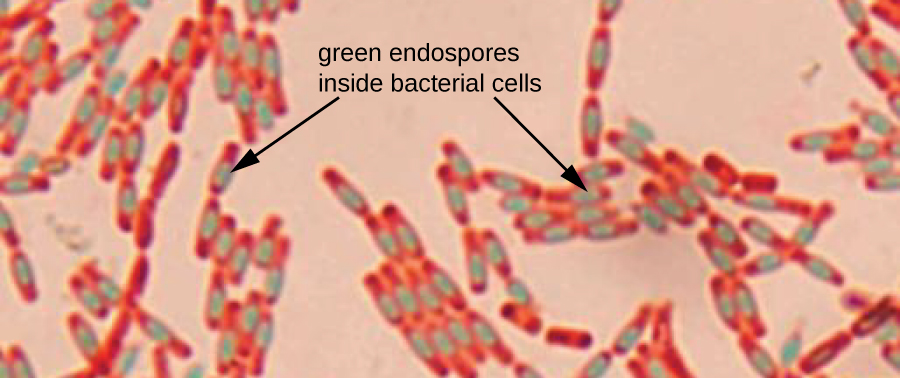
Endospore Staining
Endospore staining is a technique used in bacteriology to identify the presence of endospores in a bacterial sample. Within bacteria, endospores are protective structures used to survive extreme conditions, including high temperatures making them highly resistant to chemicals. Endospores contain little or no ATP which indicates how dormant they can be. Endospores contain a tough outer coating made up of keratin which protects them from nucleic DNA as well as other adaptations. Endospores are able to regerminate into vegetative cells, which provides a protective nature that makes them difficult to stain using normal techniques such as simple staining and gram staining. Special techniques for endospore staining include the Schaeffer–Fulton stain and the Moeller stain. History Endospores were first studied in 1876 by scientists Cohn and Koch. It was found that endospores could not be stained using simple stains such as methylene blue, safranin, and carbol fuchsin. These scientis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox Indicator
A redox indicator (also called an oxidation-reduction indicator) is an indicator which undergoes a definite color change at a specific electrode potential. The requirement for fast and reversible color change means that the oxidation-reduction equilibrium for an indicator redox system needs to be established very quickly. Therefore, only a few classes of organic redox systems can be used for indicator purposes. There are two common classes of redox indicators: * metal complexes of phenanthroline and bipyridine. In these systems, the metal changes oxidation state. * organic redox systems such as methylene blue. In these systems, a proton participant in the redox reaction. Therefore, sometimes redox indicators are also divided into two general groups: independent or dependent on pH. The most common redox indicator are organic compounds. Redox Indicator example: The molecule 2,2'- Bipyridine is a redox Indicator. In solution, it changes from light blue to red at an electrode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterstain
A counterstain is a stain with colour contrasting to the principal stain, making the stained structure easily visible using a microscope. Examples include the malachite green counterstain to the fuchsine stain in the Gimenez staining technique and the eosin counterstain to haematoxylin in the H&E stain. In Gram staining, crystal violet stains only Gram-positive bacteria, and safranin counterstain is applied which stains all cells, allowing the identification of Gram-negative bacteria as well. An alternative method uses dilute carbofluozide. Counterstains are sometimes used to separate animals from organic detritus In biology, detritus () is dead particulate organic material, as distinguished from dissolved organic material. Detritus typically includes the bodies or fragments of bodies of dead organisms, and fecal material. Detritus typically hosts comm ... in microbiology studies. References Staining {{pathology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lustre (mineralogy)
Lustre (British English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally implies radiance, gloss, or brilliance. A range of terms are used to describe lustre, such as ''earthy'', ''metallic'', ''greasy'', and ''silky''. Similarly, the term ''vitreous'' (derived from the Latin for glass, ''vitrum'') refers to a glassy lustre. A list of these terms is given below. Lustre varies over a wide continuum, and so there are no rigid boundaries between the different types of lustre. (For this reason, different sources can often describe the same mineral differently. This ambiguity is further complicated by lustre's ability to vary widely within a particular mineral species). The terms are frequently combined to describe intermediate types of lustre (for example, a "vitreous greasy" lustre). Some minerals exhibit unu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is Salt, table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic compound, inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic chemistry, organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic ion, monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic ion, polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |