|
Sympoliteia
A ''sympoliteia'' (), anglicized as sympolity, was a type of treaty for political organization in ancient Greece. By the time of the Hellenistic period, it occurred in two forms. In mainland Greece, the term was often used for a federal state consisting of individual ''poleis'' (city-states) with shared political institutions and citizenship. Examples of this are the Achaean League and the Aetolian League. The term was also used for the political merger of two or more neighboring ''poleis''. This could eventually, but not necessarily, lead to the disappearance of one of the participating ''poleis''. This second form was especially common in Hellenistic Asia Minor. A ''sympoliteia'' is often contrasted with an '' isopoliteia'', a treaty which granted equal citizenship to the citizens of the participating ''poleis'' but maintained their political independence. Contemporary writers of the Hellenistic period could use the term loosely, Polybius for example used the term ''sympoliteia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isopoliteia
An isopoliteia () was a treaty of equal citizenship rights between the ''poleis'' (city-states) of ancient Greece. This happened through either mutual agreement between cities or through exchange of individual decrees. It was used to cement amicable diplomatic relations. The Aetolian League was a unique case of a larger political entity which granted ''isopoliteia'' treaties. ''Sympoliteia'' goes further, merging the governments of two or more ''poleis''. History There are many examples of this, such as a pact between Miletus and Cyzicus from approximately 330 BC which recorded their eternal friendship. On other occasions the treaties had a limited duration and had to be renewed, such as a treaty between Miletus and Phygela from the end of the fourth century BC, which renewed the ''isopoliteia'' between them. A colony could also be granted an ''isopoliteia'' from its mother city, like Kios obtained it from Miletus in ca. 228 BC.I.Milet. 3.141: English translation a ''atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hellenistic Period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year, which eliminated the last major Hellenistic kingdom. Its name stems from the Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás''), which was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the modern historiographical term ''Hellenistic'' was derived. The term "Hellenistic" is to be distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all the ancient territories of the period that had come under significant Greek influence, particularly the Hellenized Middle East, after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
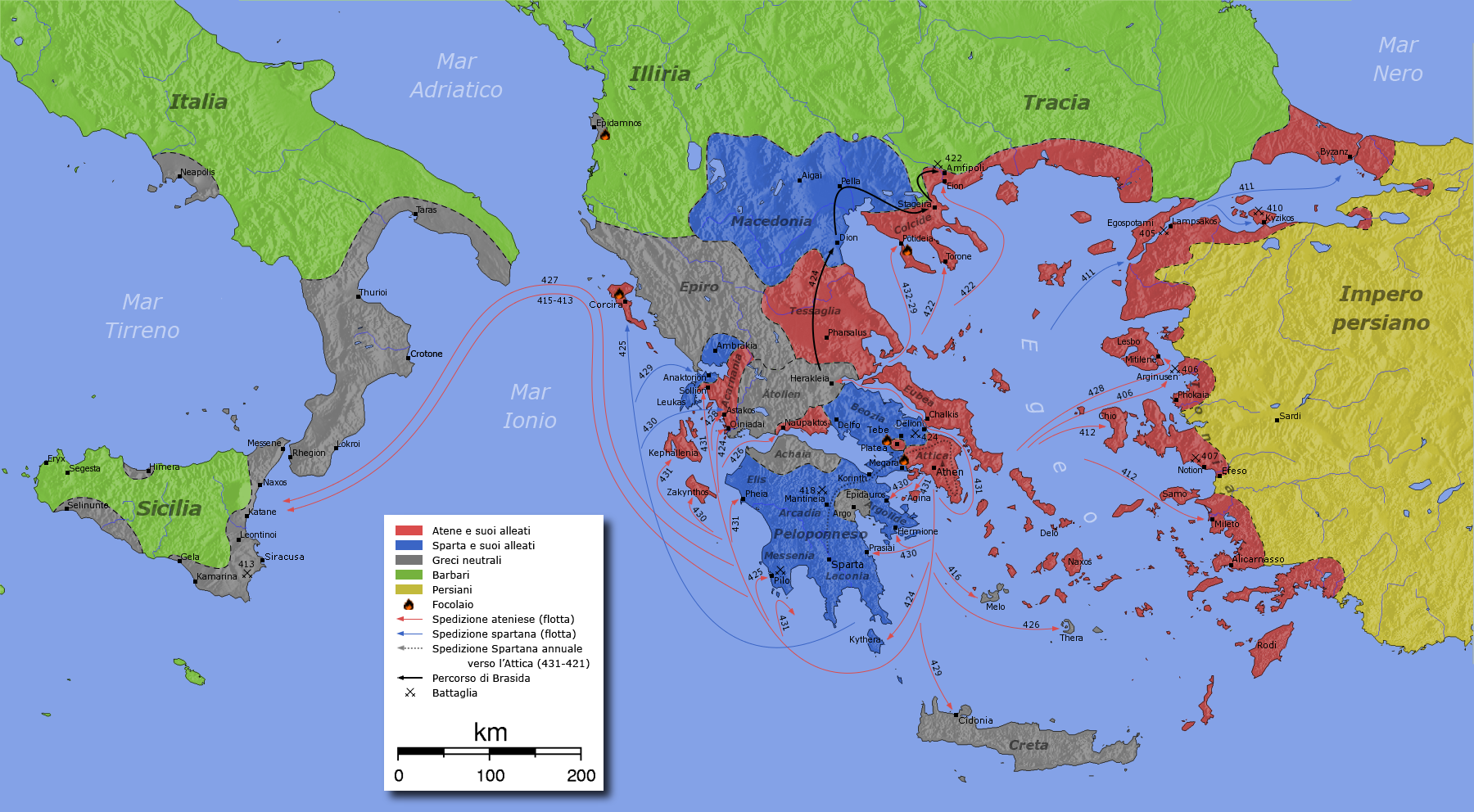
Peloponnesian War - It
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic Greek, demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions of Greece, administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica (region), Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Map Athenian Empire 431 BC-en
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Treaties Of Ancient Greece
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms; however, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties may be bilateral (between two countries) or multilateral (involving more than two countries). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations; the first known example is a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in some form by most major civilizations and became increasingly common and more sophisticated during the early modern era. The early 19th century saw developments in diplomacy, foreign policy, and international law reflected by the widespread use of treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Greek Law
Ancient Greek laws consist of the laws and legal institutions of ancient Greece. The existence of certain general principles of law in ancient Greece is implied by the custom of settling a difference between two Greek states, or between members of a single state, by resorting to external arbitration. The general unity of ancient Greek law shows mainly in the laws of inheritance and adoption, in laws of commerce and contract, and in the publicity uniformly given to legal agreements. While some of its older forms can be studied in the Gortyn code, its influence can be traced in legal documents preserved in Egyptian papyri and it may be recognized at a later period as a consistent whole in its ultimate relations to Roman law in the eastern provinces of the Roman empire, with scholars in the discipline of comparative law comparing Greek law with both Roman law and the primitive institutions of the Germanic nations. Diversity of Greek law Ancient Greece lacked a codified law cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Koinon
''Koinon'' (, pl. Κοινά, ''Koina''), meaning "common thing", in the sense of "public", had many applications, some societal, some governmental. An abstract noun formed from the neuter of the adjective, koinos, "common", the koinon could mean any sort of organization. It had more than one meaning in the governmental sense. Polis One was a polis or its politeia, Latin res publica, "the public thing", or "commonwealth", as seen in the Athenian model. A polis, by definition, is a government of common concern rather than private, making it a republic. The polis also functioned as a federal state with a politeia, or "constitution", which established citizenship. Citizens managed the state through elected magistracies and the assembly. These institutions, claiming supreme political power, directly performed their constitutional duties across executive, judicial, or legislative domains. While political theory had not yet conceptualized the three-branch system common in modern republ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Melos
The siege of Melos occurred in 416 BC during the Peloponnesian War, which was a war fought between Athens and Sparta. Melos is an island in the Aegean Sea roughly east of mainland Greece. Though the Melians had ancestral ties to Sparta, they were neutral in the war. Athens invaded Melos in the summer of 416 BC and demanded that the Melians surrender and pay tribute to Athens or face annihilation. The Melians refused, so the Athenians laid siege to their city. Melos surrendered in the winter, and the Athenians executed the men of Melos and enslaved the women and children. This siege is best remembered for the Melian Dialogue, a dramatization of the negotiations between the Athenians and the Melians before the siege, written by the classical Athenian historian Thucydides. In the negotiations, the Athenians offered no moral justification for their invasion, but instead bluntly told the Melians that Athens needed Melos for its own ends and that the only thing Melians stood to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mytilenean Debate
The Mytilenean Debate (also spelled "Mytilenaean Debate") was an Athenian Assembly concerning reprisals against the city-state of Mytilene, which had attempted unsuccessfully to revolt against Athenian hegemony and gain control over Lesbos during the Peloponnesian War. The debate occurred in 427 BC. In the immediate aftermath of the revolt, the Athenians had decided to execute all Mytilenean men and enslave the women and children, but gathered the next day to reconsider. Thucydides reports the revolt and the resultant debate in book three of his ''History of the Peloponnesian War'', and the opposing viewpoints concerning the warranted retributive justice are reflected in two speeches given by prominent Athenians. The events and speeches serve as an opportunity to explore the political and ideological impact of the war, and provide reflections on democracy and imperial policy. Causes for the revolt Mytilene had joined in alliance with Athens as a member of the Delian League, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League functioned as a dual –offensive and defensive– alliance (''Symmachia (alliance), symmachia'') of autonomous states, similar to its rival association, the Peloponnesian League. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held within the sanctuary of the Temple of Apollo; contemporary authors referred to the organization simply as "the Athenians and their Allies". While Sparta excelled as Greece's greatest power on land, Athens turned to the seas becoming the dominant naval power of the Ancient Greece, Greek world. Following Sparta's withdrawal from the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 BC, recording in detail events in Italy, Iberia, Greece, Macedonia, Syria, Egypt and Africa, and documented the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars among many others. Polybius' ''Histories'' is important not only for being the only Hellenistic historical work to survive in any substantial form, but also for its analysis of constitutional change and the mixed constitution. Polybius' discussion of the separation of powers in government, of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", all influenced Montesquieu's '' The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's '' Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synoecism
Synoecism or synecism ( ; , ''sunoikismos'', ), also spelled synoikism ( ), was originally the amalgamation of villages in Ancient Greece into ''poleis'', or city-states. Etymologically, the word means "dwelling together (''syn'') in the same house (''oikos'')." Subsequently, any act of civic union between polities of any size was described by the word ''synoikismos'', in addition to the Latinized synoecism. Synoecism is opposed to Greek dioecism (διοικισμóς, ''dioikismos''), the creation of independent communities within the territory of a polis. Synoecism is the result of a few major factors, mainly an increase in population density of adjacent settlements, with an incorporation proposed for economic, political or ideological advantages, such as the synoecism of the communities of Attica into Athens, or by imposition of a ruling power, such as the synoecism of Messenia into the newly built city of Messene. Additionally, synoecism may be the result of less active forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |