|
Superresolution
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that improve the image resolution, resolution of an digital imaging, imaging system. In optical SR the diffraction-limited, diffraction limit of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital image sensor, imaging sensors is enhanced. In some radar and sonar imaging applications (e.g. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), high-resolution computed tomography), space (mathematics), subspace decomposition-based methods (e.g. MUSIC (algorithm), MUSIC) and compressed sensing-based algorithms (e.g., SAMV (algorithm), SAMV) are employed to achieve SR over standard periodogram algorithm. Super-resolution imaging techniques are used in general image processing and in super-resolution microscopy. Basic concepts Because some of the ideas surrounding super-resolution raise fundamental issues, there is need at the outset to examine the relevant physical and information-theoretical principles: * Diffraction limit: T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super-resolution Microscopy
Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have Optical resolution, resolutions higher than those imposed by the Diffraction-limited system, diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techniques rely on the Electromagnetic radiation#Near and far fields, near-field (photon-tunneling microscopy as well as those that use the Superlens, Pendry Superlens and near field scanning optical microscopy) or on the Near and far field, far-field. Among techniques that rely on the latter are those that improve the resolution only modestly (up to about a factor of two) beyond the diffraction-limit, such as confocal microscopy with closed pinhole or aided by computational methods such as deconvolution or detector-based pixel reassignment (e.g. re-scan microscopy, pixel reassignment), the 4Pi Microscope, 4Pi microscope, and structured-illumination microscopy technologies such as SIM and Vertico SMI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUSIC (algorithm)
MUSIC (multiple sIgnal classification) is an algorithm used for frequency estimation and radio direction finding.Schmidt, R.O,Multiple Emitter Location and Signal Parameter Estimation" IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagation, Vol. AP-34 (March 1986), pp. 276–280. History In many practical signal processing problems, the objective is to estimate from measurements a set of constant parameters upon which the received signals depend. There have been several approaches to such problems including the so-called maximum likelihood (ML) method of Capon (1969) and Burg's maximum entropy (ME) method. Although often successful and widely used, these methods have certain fundamental limitations (especially bias and sensitivity in parameter estimates), largely because they use an incorrect model (e.g., AR rather than special ARMA) of the measurements. Pisarenko (1973) was one of the first to exploit the structure of the data model, doing so in the context of estimation of parameters of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly ''resolved''. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes (e.g. lines per mm, lines per inch), to the overall size of a picture (lines per picture height, also known simply as lines, TV lines, or TVL), or to angular subtense. Instead of single lines, line pairs are often used, composed of a dark line and an adjacent light line; for example, a resolution of 10 lines per millimeter means 5 dark lines alternating with 5 light lines, or 5 line pairs per millimeter (5 LP/mm). Photographic lens are most often quoted in line pairs per millimeter. Types The resolution of digital cameras can be described in many different ways. Pixel count The term ''resolution'' is often considered eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principles Of Optics
''Principles of Optics'', colloquially known as ''Born and Wolf'', is an optics textbook written by Max Born and Emil Wolf that was initially published in 1959 by Pergamon Press. After going through six editions with Pergamon Press, the book was transferred to Cambridge University Press who issued an expanded seventh edition in 1999. A 60th anniversary edition was published in 2019 with a foreword by Sir Peter Knight (physicist), Peter Knight. It is considered a classic book, classic science book and one of the most influential optics books of the twentieth century. Background In 1933, Springer Science+Business Media, Springer published Max Born's book ''Optik'', which dealt with all optical phenomena for which the methods of classical physics, and Maxwell's equations in particular, were applicable. In 1950, with encouragement from Sir Edward Victor Appleton, Edward Appleton, the principal of Edinburgh University, Born decided to produce an updated version of ''Optik'' in Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
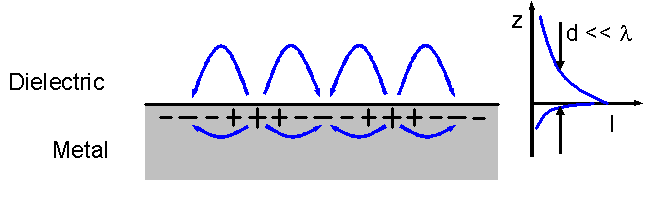
Evanescent Waves
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evanescent" – hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moiré Pattern
In mathematics, physics, and art, moiré patterns ( , , ) or moiré fringes are large-scale wave interference, interference patterns that can be produced when a partially opaque grating, ruled pattern with transparent gaps is overlaid on another similar pattern. For the moiré interference pattern to appear, the two patterns must not be completely identical, but rather displaced, rotated, or have slightly different pitch. Moiré patterns appear in many situations. In printing, the printed pattern of dots can interfere with the image. In television and digital photography, a pattern on an object being photographed can interfere with the shape of the light sensors to generate unwanted artifacts. They are also sometimes created deliberately; in micrometer (device), micrometers, they are used to amplify the effects of very small movements. In physics, its manifestation is wave interference like that seen in the double-slit experiment and the Beat (acoustics), beat phenomenon in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Illumination Superresolution
Structuring, also known as smurfing in banking jargon, is the practice of executing financial transactions such as making bank deposits in a specific pattern, calculated to avoid triggering financial institutions to file reports required by law, such as the United States' Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Internal Revenue Code section 6050I (relating to the requirement to file Form 8300). Structuring may be done in the context of money laundering, fraud, and other financial crimes. Legal restrictions on structuring are concerned with limiting the size of domestic transactions for individuals. Definition Structuring is the act of parceling what would otherwise be a large financial transaction into a series of smaller transactions to avoid scrutiny by regulators and law enforcement. Typically each of the smaller transactions is executed in an amount below some statutory limit that normally does not require a financial institution to file a report with a government agency. Criminal enterp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture Synthesis
Aperture synthesis or synthesis imaging is a type of interferometry that mixes signals from a collection of telescopes to produce images having the same angular resolution as an instrument the size of the entire collection. At each separation and orientation, the lobe-pattern of the interferometer produces an output which is one component of the Fourier transform of the spatial distribution of the brightness of the observed object. The image (or "map") of the source is produced from these measurements. Astronomical interferometers are commonly used for high-resolution optical astronomy, optical, infrared astronomy, infrared, submillimetre astronomy, submillimetre and radio astronomy observations. For example, the Event Horizon Telescope project derived the first image of a black hole using aperture synthesis. Technical issues Aperture synthesis is possible only if both the amplitude and the phase (waves), phase of the incoming signal are measured by each telescope. For radio fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark-field Microscopy
Dark-field microscopy, also called dark-ground microscopy, describes microscopy methods, in both light and electron microscopy, which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. Consequently, the field around the specimen (i.e., where there is no specimen to scatter the beam) is generally dark. In optical microscopes a darkfield condenser lens must be used, which directs a cone of light away from the objective lens. To maximize the scattered light-gathering power of the objective lens, oil immersion is used and the numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens must be less than 1.0. Objective lenses with a higher NA can be used but only if they have an adjustable diaphragm, which reduces the NA. Often these objective lenses have a NA that is variable from 0.7 to 1.25. Light microscopy applications In optical microscopy, dark-field describes an illumination technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained samples. It works by illuminating the sample with light that wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (logic), formally) of that which may be sensed, or their abstractions. Any natural process that is not completely random and any observable pattern in any Media (communication), medium can be said to convey some amount of information. Whereas digital signals and other data use discrete Sign (semiotics), signs to convey information, other phenomena and artifacts such as analog signals, analogue signals, poems, pictures, music or other sounds, and current (fluid), currents convey information in a more continuous form. Information is not knowledge itself, but the meaning (philosophy), meaning that may be derived from a representation (mathematics), representation through interpretation. The concept of ''information'' is relevant or connected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark-field Microscopy
Dark-field microscopy, also called dark-ground microscopy, describes microscopy methods, in both light and electron microscopy, which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. Consequently, the field around the specimen (i.e., where there is no specimen to scatter the beam) is generally dark. In optical microscopes a darkfield condenser lens must be used, which directs a cone of light away from the objective lens. To maximize the scattered light-gathering power of the objective lens, oil immersion is used and the numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens must be less than 1.0. Objective lenses with a higher NA can be used but only if they have an adjustable diaphragm, which reduces the NA. Often these objective lenses have a NA that is variable from 0.7 to 1.25. Light microscopy applications In optical microscopy, dark-field describes an illumination technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained samples. It works by illuminating the sample with light that wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Frequencies
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, spatial frequency is a characteristic of any structure that is periodic across position in space. The spatial frequency is a measure of how often sinusoidal components (as determined by the Fourier transform) of the structure repeat per unit of distance. The SI unit of spatial frequency is the reciprocal metre (m−1), (11 pages) although cycle (rotational unit), cycles per (c/m) is also common. In image-processing applications, spatial frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |