|
Superplume
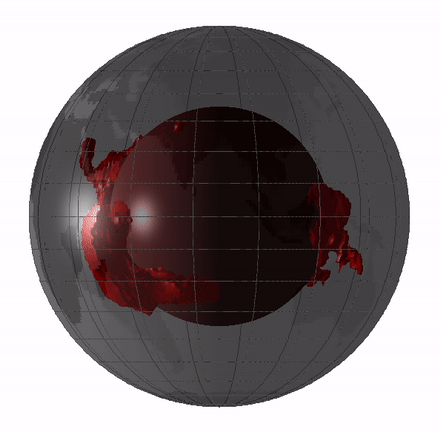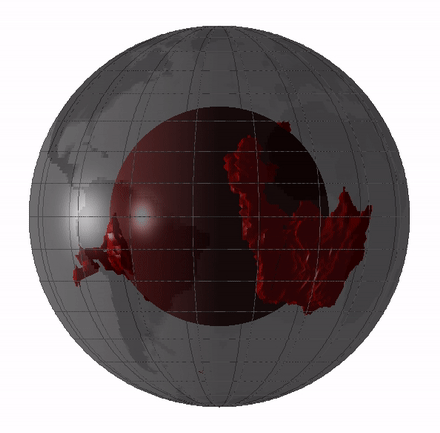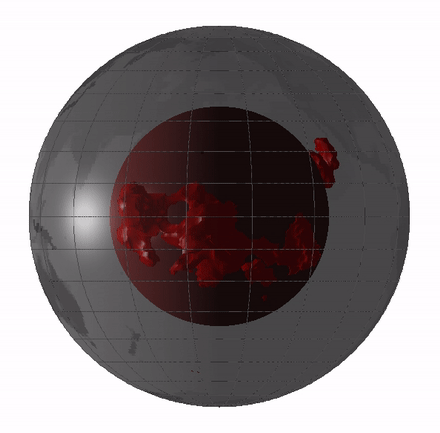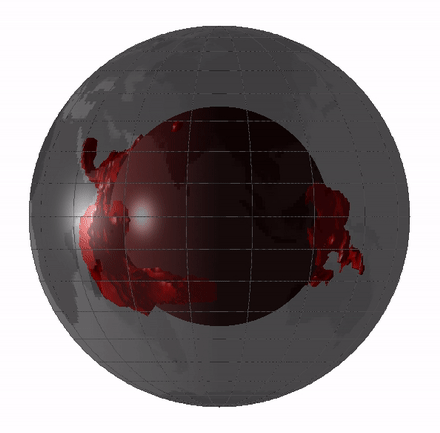
Large low-shear-velocity provinces (LLSVPs), also called large low-velocity provinces (LLVPs) or superplumes, are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost mantle, the region surrounding the outer core deep inside the Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow shear wave velocities and were discovered by seismic tomography of deep Earth. There are two main provinces: the African LLSVP and the Pacific LLSVP, both extending laterally for thousands of kilometers and possibly up to 1,000 kilometres vertically from the core–mantle boundary. These have been named Tuzo and Jason respectively, after Tuzo Wilson and W. Jason Morgan, two geologists acclaimed in the field of plate tectonics. The Pacific LLSVP is across and underlies four hotspots on Earth's crust that suggest multiple mantle plumes underneath. These zones represent around 8% of the volume of the mantle, or 6% of the entire Earth. Other names for LLSVPs and their superstructures include superswells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superswell
A superswell is a large area of anomalously high topography and shallow ocean regions. These areas of anomalous topography are byproducts of large upwelling of mantle material from the core–mantle boundary, referred to as superplumes. Two present day superswells have been identified: the African superswell and the South Pacific superswell. In addition to these, the Darwin Rise in the south central Pacific Ocean is thought to be a paleosuperswell, showing evidence of being uplifted compared to surrounding ancient ocean topography. Superplume Data shows a dramatic increase in crustal production from 125–120 to 70 Ma, largely in East Pacific Rise areas, although the marked increase in production rates of crustal material was also seen in the Gondwana ridges, as well as in oceanic plateaus. This period of increased crustal production is interpreted as a superplume event. This "pulse" of increased crustal production peaked soon after the initial plume (between 120 Ma and 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LLSVP
Large low-shear-velocity provinces (LLSVPs), also called large low-velocity provinces (LLVPs) or superplumes, are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost Earth's mantle, mantle, the region surrounding the Earth's outer core, outer core deep inside the Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow S-wave, shear wave velocities and were discovered by seismic tomography of deep Earth. There are two main provinces: the African LLSVP and the Pacific LLSVP, both extending laterally for thousands of kilometers and possibly up to 1,000 kilometres vertically from the core–mantle boundary. These have been named Tuzo and Jason respectively, after Tuzo Wilson and W. Jason Morgan, two geologists acclaimed in the field of plate tectonics. The Pacific LLSVP is across and underlies four Hotspot (geology), hotspots on Earth's Crust (geology), crust that suggest multiple mantle plumes underneath. These zones represent around 8% of the volume of the mantle, or 6% of the entire Earth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspots, such as Hawaii or Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan and Siberian Traps. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries. Concepts Mantle plumes were first proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 and further developed by W. Jason Morgan in 1971 and 1972. A mantle plume is posited to exist where super-heated material forms ( nucleates) at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle. Rather than a continuous stream, plumes should be viewed as a series of hot bubbles of material. Reaching the brittle upper Earth's crust they form diapirs. These diapirs are "hotspots" in the crust. In particular, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Convection
Mantle convection is the very slow creep of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carry heat from the interior to the planet's surface. Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface. The Earth's lithosphere rides atop the asthenosphere, and the two form the components of the upper mantle. The lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that are continuously being created or consumed at plate boundaries. Accretion occurs as mantle is added to the growing edges of a plate, associated with seafloor spreading. Upwelling beneath the spreading centers is a shallow, rising component of mantle convection and in most cases not directly linked to the global mantle upwelling. The hot material added at spreading centers cools down by conduction and convection of heat as it moves away from the spreading centers. At the consumption edges of the plate, the material has thermally contracted to become dense, and it sinks under its own weight i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core–mantle Boundary
The core–mantle boundary (CMB) of Earth lies between the planet's silicate mantle and its liquid iron–nickel outer core, at a depth of below Earth's surface. The boundary is observed via the discontinuity in seismic wave velocities at that depth due to the differences between the acoustic impedances of the solid mantle and the molten outer core. P-wave velocities are much slower in the outer core than in the deep mantle while S-waves do not exist at all in the liquid portion of the core. Recent evidence suggests a distinct boundary layer directly above the CMB possibly made of a novel phase of the basic perovskite mineralogy of the deep mantle named post-perovskite. Seismic tomography studies have shown significant irregularities within the boundary zone and appear to be dominated by the African and Pacific Large low-shear-velocity provinces (LLSVP). The uppermost section of the outer core is thought to be about 500–1,800 K hotter than the overlying mantle, creating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
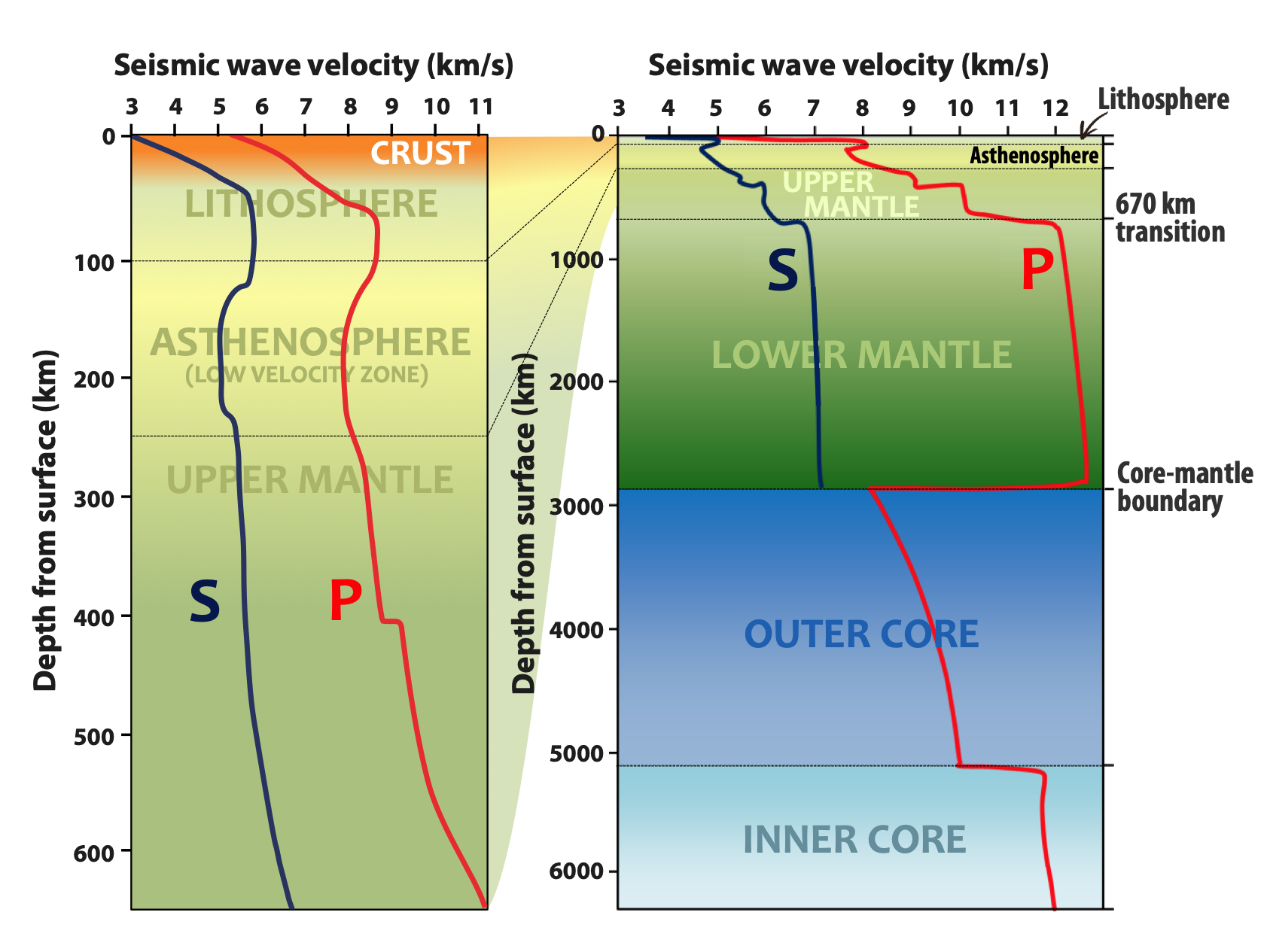
Seismic Wave
A seismic wave is a mechanical wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth or another planetary body. It can result from an earthquake (or generally, a quake), volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy. Seismic waves are studied by seismologists, who record the waves using seismometers, hydrophones (in water), or accelerometers. Seismic waves are distinguished from seismic noise (ambient vibration), which is persistent low-amplitude vibration arising from a variety of natural and anthropogenic sources. The propagation velocity of a seismic wave depends on density and elasticity of the medium as well as the type of wave. Velocity tends to increase with depth through Earth's crust and mantle, but drops sharply going from the mantle to Earth's outer core. Earthquakes create distinct types of waves with different velocities. When recorded by a seismic observatory, their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-low Velocity Zone
Ultra low velocity zones (ULVZs) are patches on the core-mantle boundary that have extremely low seismic velocities. The zones are mapped to be hundreds of kilometers in diameter and tens of kilometers thick. Their shear wave velocities can be up to 30% lower than surrounding material. The composition and origin of the zones remain uncertain. The zones appear to correlate with edges of the African and Pacific large low-shear-velocity provinces (LLSVPs) as well as the location of hotspots. Discovery and constraints ULVZs are discovered by the delay and scattering of body waves that reflect and diffract on or are refracted by the core-mantle boundary. Different body waves types give different constraints on the dimensions or velocity contrasts of the ULVZ. Even though ULVZs are discovered in places, it remains difficult to map out their extent and constrain their density and velocity. Usually trade-offs between various parameters exist. In general though, ULVZs appear to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Tide
Earth tide (also known as solid-Earth tide, crustal tide, body tide, bodily tide or land tide) is the displacement of the solid earth's surface caused by the gravity of the Moon and Sun. Its main component has meter-level amplitude at periods of about 12 hours and longer. The largest body tide constituents are semi- diurnal, but there are also significant diurnal, semi-annual, and fortnightly contributions. Though the gravitational force causing earth tides and ocean tides is the same, the responses are quite different. Tide raising force The larger of the periodic gravitational forces is from the Moon but that of the Sun is also important. The images here show lunar tidal force when the Moon appears directly over 30° N (or 30° S). This pattern remains fixed with the red area directed toward (or directly away from) the Moon. Red indicates upward pull, blue downward. If, for example the Moon is directly over 90° W (or 90° E), the red areas are centred on the western northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth And Planetary Science Letters
''Earth and Planetary Science Letters'' (EPSL) is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on physical, chemical and mechanical processes of the Earth and other planets, including extrasolar ones. Topics covered range from deep planetary interiors to atmospheres. The journal was established in 1966 and is published by Elsevier. The co-editors-in-chief are Tristan Horner, Yemane Asmerom, Jean-Philippe Avouac, James Badro, Huiming Bao, Rosemary Hickey-Vargas, Andrew Jacobson, Carolina Lithgow-Bertelloni, Olivier Mousis, Chiara Maria Petrone, Fang-Zhen Teng, Hans Thybo, Alexander Webb. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Atlantic Anomaly
The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) is an area where Earth's inner Van Allen radiation belt comes closest to Earth's surface, dipping down to an altitude of . This leads to an increased flux of energetic particles in this region and exposes orbiting satellites (including the ISS) to higher-than-usual levels of ionizing radiation. The effect is caused by the non- concentricity of Earth with its magnetic dipole and has been observed to be increasing in intensity recently. The SAA is the near-Earth region where Earth's magnetic field is weakest relative to an idealized Earth-centered dipole field. Definition The area of the SAA is confined by the intensity of Earth's magnetic field at less than 32,000 nanotesla at sea level, which corresponds to the dipolar magnetic field at ionospheric altitudes. However, the field itself varies in intensity as a gradient. Position and shape The Van Allen radiation belts are symmetric about the Earth's magnetic axis, which is tilted with respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |