|
Superluminal Motion
In astronomy, superluminal motion is the apparently faster-than-light motion seen in some radio galaxies, BL Lac objects, quasars, blazars and recently also in some galactic sources called microquasars. Bursts of energy moving out along the relativistic jets emitted from these objects can have a proper motion that appears greater than the speed of light. All of these sources are thought to contain a black hole, responsible for the ejection of mass at high velocities. Light echoes can also produce apparent superluminal motion. Explanation Superluminal motion occurs as a special case of a more general phenomenon arising from the difference between the apparent speed of distant objects moving across the sky and their actual speed as measured at the source. In tracking the movement of such objects across the sky, a calculation of their speed can be determined by a simple distance divided by time formula. If the distance of the object from the Earth is known and the angular sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a Type-cD galaxy, supergiant elliptical galaxy, elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo (constellation), Virgo that contains several trillion stars. One of the List of largest galaxies, largest and most massive galaxies in the local universe, it has a large population of globular clusters—about 15,000 compared with the 150–200 orbiting the Milky Way—and a jet of energetic plasma (physics), plasma that originates at the core and extends at least , traveling at a relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky and a popular target for both amateur and professional astronomers. The French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, and cataloged it as a nebula. M87 is about from Earth and is the second-brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, having many satellite galaxies. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3C 279
3C 279 (also known as 4C–05.55, NRAO 413, and PKS 1253–05) is an OVV quasar, optically violent variable quasar (OVV), which is known in the astronomical community for its variations in the Visible spectrum, visible, Radio frequency, radio and X-ray bands. The quasar was observed to have undergone a period of extreme activity from 1987 until 1991. The Rosemary Hill Observatory (RHO) started observing 3C 279 in 1971, the object was further observed by the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory in 1991, when it was unexpectedly discovered to be one of the brightest gamma ray objects in the sky. It is also one of the brightest and most variable sources in the gamma ray sky monitored by the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. It was used as a calibrator source for Event Horizon Telescope observations of M87* that resulted in the first image of a black hole. Observations * The apparent Superluminal#Astronomical observations, superluminal motion was detected during observations first made in 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minute Of Arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth's circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (abbreviated as arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a minute of arc, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal (base 60) subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Long Baseline Interferometry
Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. The distance between the radio telescopes is then calculated using the time difference between the arrivals of the radio signal at different telescopes. This allows observations of an object that are made simultaneously by many radio telescopes to be combined, emulating a telescope with a size equal to the maximum separation between the telescopes. Data received at each antenna in the array include arrival times from a local atomic clock, such as a hydrogen maser. At a later time, the data are correlated with data from other antennas that recorded the same radio signal, to produce the resulting image. The resolution achievable using interferometry is proportional to the observing frequency. The VLBI technique enables the distance between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Rees
Martin John Rees, Baron Rees of Ludlow, (born 23 June 1942) is a British cosmologist and astrophysicist. He is the fifteenth , appointed in 1995, and was Master of |
Astronomische Nachrichten
''Astronomische Nachrichten'' (''Astronomical Notes''), one of the first international journals in the field of astronomy, was established in 1821 by the German astronomer Heinrich Christian Schumacher. It claims to be the oldest astronomical journal in the world that is still being published. The publication today specializes in articles on solar physics, extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, geophysics, and instrumentation for these fields. All articles are subject to peer review. Early history The journal was founded in 1821 by Heinrich Christian Schumacher,''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'', page 60, v.7 (1895) under the patronage of Christian VIII of Denmark, and quickly became the world's leading professional publication for the field of astronomy. Schumacher edited the journal at the Altona Observatory, then under the administration of Denmark, later part of Prussia, and today part of the German city of Hamburg. Schumacher edited the first 31 issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
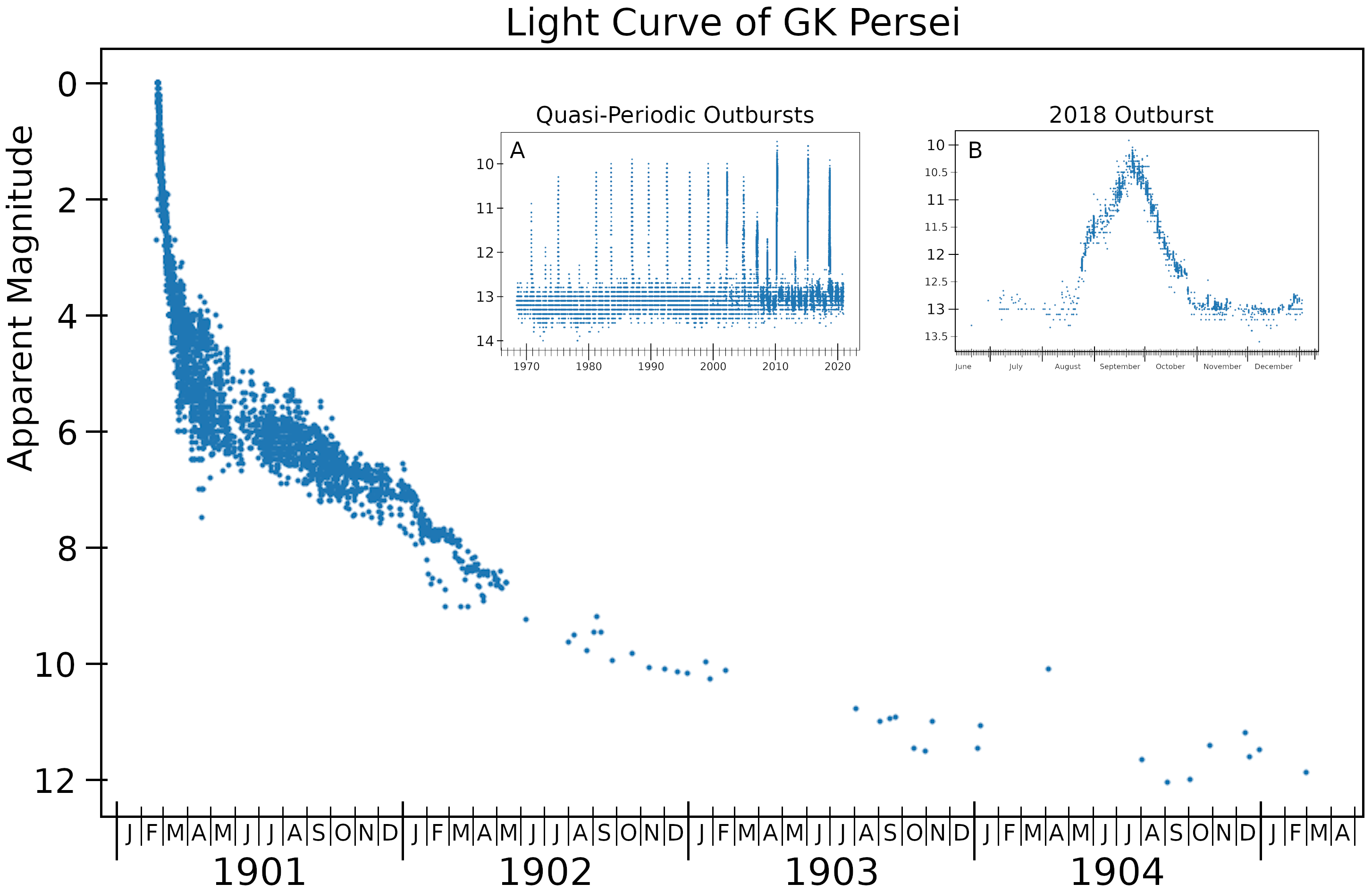
GK Persei
GK Persei (also Nova Persei 1901) was a bright nova first observed on Earth in 1901. It was discovered by Thomas David Anderson, an Edinburgh clergyman, at 02:40 UT on 22 February 1901 when it was at magnitude 2.7. It reached a maximum magnitude of 0.2, the brightest nova of modern times until Nova Aquilae 1918. After fading into obscurity at about magnitude 12 to 13 during the early 20th century, GK Persei began displaying infrequent outbursts of 2 to 3 magnitudes (about 7 to 15 times quiescent brightness). Since about 1980, these outbursts have become quite regular, typically lasting about two months and occurring about every three years. Thus, GK Persei seems to have changed from a classical nova like Nova Aquilae 1918 to something resembling a typical dwarf nova-type cataclysmic variable star. Surrounding GK Persei is the Firework Nebula, a nova remnant first detected in 1902 consisting of an expanding cloud of gas and dust bubbles moving up to 1200 km/s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems, but causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. This type is usually created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. If the orbital period of the system is a few days or less, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to draw accreted matter onto its surface, creating a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmosphere, mostly consisting of hydrogen, is heated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobus Kapteyn
Jacobus Cornelius Kapteyn (19 January 1851 – 18 June 1922) was a Dutch astronomy, astronomer. He carried out extensive studies of the Milky Way. He found that the apparent movement of stars was not randomly distributed but had two preferential directions: the two star streams. This discovery was later reinterpreted as evidence for Galaxy rotation curve, galactic rotation. Kapteyn also suggested that these stellar velocities could be used to find the amount of non-luminous matter in the galaxy, which his student, Jan Oort, measured in 1932, referring to it as "invisible matter". Biography Kapteyn was born in Barneveld (town), Barneveld to Gerrit J. and Elisabeth C. (née Koomans) Kapteyn, and went to the Utrecht University, University of Utrecht to study mathematics and physics in 1868. In 1875, after having finished his thesis, he worked for three years at the Leiden Observatory, before becoming the first Professor of Astronomy and Theoretical Mechanics at the University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |