|
Superior Olivary Complex
The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that is located in pons, functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system. The SOC is intimately related to the trapezoid body: most of the cell groups of the SOC are dorsal (posterior in primates) to this axon bundle while a number of cell groups are embedded in the trapezoid body. Overall, the SOC displays a significant interspecies variation, being largest in bats and rodents and smaller in primates. Physiology The superior olivary nucleus plays a number of roles in hearing. The #Medial superior olive (MSO), medial superior olive (MSO) is a specialized nucleus that is believed to measure the time difference of arrival of sounds between the ears (the interaural time difference or ITD). The ITD is a major cue for determining the azimuth of sounds, i.e., localising them on the azimuthal plane – t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control and cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine motor skill, fine movement, sense of balance, equilibrium, list of human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
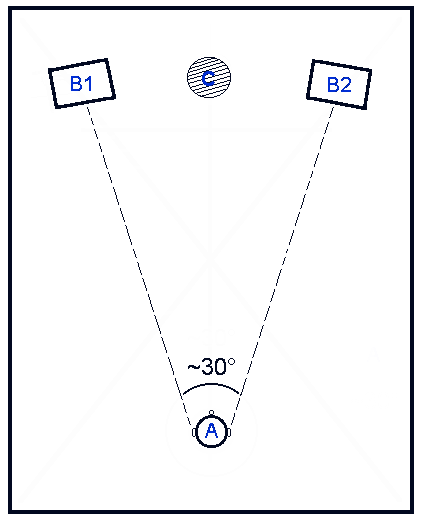
Interaural Level Difference
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. Other animals, such as birds and reptiles, also use them but they may use them differently, and some also have localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the pinna and concha of the exterior ear, and ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Olivary Nucleus
The inferior olivary nucleus (ION) is a structure found in the medulla oblongata underneath the superior olivary nucleus.Gado, Thomas A. Woolsey; Joseph Hanaway; Mokhtar H. (2003). The brain atlas a visual guide to the human central nervous system (2nd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. p. 206. . In vertebrates, the ION is known to coordinate signals from the spinal cord to the cerebellum to regulate motor coordination and learning.Schweighofer N, Lang EJ, Kawato M. Role of the olivo-cerebellar complex in motor learning and control. ''Frontiers in Neural Circuits''. 2013;7:94. . These connections have been shown to be tightly associated, as degeneration of either the cerebellum or the ION results in degeneration of the other. Neurons of the ION are glutamatergic and receive inhibitory input via GABA receptors. There are two distinct GABAα receptor populations that are spatially organized within each neuron present in the ION. The GABAα receptor make-up varies based on where the rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Cochlear Nucleus
In the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), auditory nerve fibers enter the brain via the nerve root in the VCN. The ventral cochlear nucleus is divided into the anterior ventral (anteroventral) cochlear nucleus (AVCN) and the posterior ventral (posteroventral) cochlear nucleus (PVCN). In the VCN, auditory nerve fibers bifurcate, the ascending branch innervates the AVCN and the descending branch innervates the PVCN and then continue to the dorsal cochlear nucleus. The orderly innervation by auditory nerve fibers gives the AVCN a tonotopic organization along the dorsoventral axis. Fibers that carry information from the apex of the cochlea that are tuned to low frequencies contact neurons in the ventral part of the AVCN; those that carry information from the base of the cochlea that are tuned to high frequencies contact neurons in the dorsal part of the AVCN. Several populations of neurons populate the AVCN. Bushy cells receive input from auditory nerve fibers through particularly la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calyx Of Held
The calyx of Held is a particularly large excitatory synapse in the mammalian auditory nervous system, so named after Hans Held who first described it in his 1893 article ''Die centrale Gehörleitung''Held, H. "Die centrale Gehörleitung" Arch. Anat. Physiol. Anat. Abt, 1893 because of its resemblance to the calyx of a flower. Globular bushy cells in the anteroventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN) send axons to the contralateral medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB), where they synapse via these calyces on MNTB principal cells. These principal cells then project to the ipsilateral lateral superior olive (LSO), where they inhibit postsynaptic neurons and provide a basis for interaural level detection (ILD), required for high frequency sound localization. This synapse has been described as the largest in the brain. The related endbulb of Held is also a large axon terminal synapse (15–30 μm in diameter) found in another auditory brainstem structure, namely the anterov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Localization
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. Other animals, such as birds and reptiles, also use them but they may use them differently, and some also have localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the Pinna (anatomy), pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivary Body
The olivary bodies or simply olives (Latin ''oliva'' and ''olivae'', singular and plural, respectively) are a pair of prominent oval structures on either side of the medullary pyramids in the medulla oblongata, medulla, the lower portion of the brainstem. They contain the olivary nuclei. Structure Each olivary body is located on the anterior surface of the medulla lateral to the Pyramid of medulla oblongata, pyramid, from which it is separated by the Anterolateral sulcus of medulla, antero-lateral sulcus and the fibers of the hypoglossal nerve. Behind (Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsally), it is separated from the postero-lateral sulcus by the ventral spinocerebellar fasciculus. In the depression between the upper end of the olive and the pons lies the vestibulocochlear nerve. In humans, it measures about 1.25 cm in length, and between its upper end and the pons there is a slight depression to which the roots of the facial nerve are attached. The exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Colliculus
The inferior colliculus (IC) (Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the Auditory system, auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex.Shore, S. E.: ''Auditory/Somatosensory Interactions''. In: Squire (Ed.): ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience'', Academic Press, 2009, pp. 691–695 The inferior colliculus has three subdivisions: the central nucleus, a dorsal cortex by which it is surrounded, and an external cortex which is located laterally. Its bimodal neurons are implicated in auditory-Somatosensory system, somatosensory interaction, receiving projections from Somatosensory system, somatosensory nuclei. This multisensory integration may underlie a filtering of self-effected sounds from vocalization, chewing, or respiration activities. The inferior colliculi together with the superior colliculi form the eminences of the corpora quadrigemina, and also part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus
The dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN, also known as the "tuberculum acusticum") is a cortex-like structure on the dorso-lateral surface of the brainstem. Along with the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), it forms the cochlear nucleus (CN), where all auditory nerve fibers from the cochlea form their first synapses. Anatomy The DCN differs from the ventral portion of the CN as it not only projects to the central nucleus (a subdivision) of the inferior colliculus (CIC), but also receives efferent innervation from the auditory cortex, superior olivary complex and the inferior colliculus. The cytoarchitecture and neurochemistry of the DCN is similar to that of the cerebellum, an important concept in theories of DCN function. Thus, the DCN is thought to be involved with more complex auditory processing, rather than merely transferring information. The pyramidal cells or giant cells are a major cell grouping of the DCN. These cells are the target of two different input systems. The firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Superior Olive (LSO)
The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that is located in pons, functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system. The SOC is intimately related to the trapezoid body: most of the cell groups of the SOC are dorsal (posterior in primates) to this axon bundle while a number of cell groups are embedded in the trapezoid body. Overall, the SOC displays a significant interspecies variation, being largest in bats and rodents and smaller in primates. Physiology The superior olivary nucleus plays a number of roles in hearing. The medial superior olive (MSO) is a specialized nucleus that is believed to measure the time difference of arrival of sounds between the ears (the interaural time difference or ITD). The ITD is a major cue for determining the azimuth of sounds, i.e., localising them on the azimuthal plane – their degree to the left or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentate Nucleus
The dentate nucleus refer to a pair of deep cerebellar nuclei deep within the white matter of the cerebellum of the brain with a dentate – tooth-like or serrated – edge. The dentate forms the largest pathway between the cerebellum and the remainder of the brain.Sultan, F., Hamodeh, S., & Baizer, J. S. (2010). THE HUMAN DENTATE NUCLEUS: A COMPLEX SHAPE UNTANGLED. rticle Neuroscience, 167(4), 965–968. It is the largest and most lateral of the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, the others being the globose and emboliform nuclei, which together are referred to as the interposed nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus. The dentate nucleus is responsible for the planning, initiation and control of voluntary movements. The dorsal region of the dentate nucleus contains output channels involved in motor function, which is the movement of skeletal muscle, while the ventral region contains output channels involved in nonmotor function, such as conscious thought and visuospatial fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |