|
Subsidies For Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuel subsidies are energy subsidies on fossil fuels. Under a narrow definition, fossil fuel subsidies totalled around $1.5 trillion in 2022. Under more expansive definition, they totalled around $7 trillion. They may be tax breaks on consumption, such as a lower sales tax on natural gas for residential heating; or subsidies on production, such as tax breaks on exploration for oil. Or they may be free or cheap negative externalities; such as air pollution or climate change due to burning gasoline, diesel and jet fuel. Some fossil fuel subsidies are via electricity generation, such as subsidies for coal-fired power stations. Eliminating fossil fuel subsidies would reduce the health risks of air pollution, and would greatly reduce global carbon emissions thus helping to limit climate change. , policy researchers estimate that substantially more money is spent on fossil fuel subsidies than on environmentally harmful agricultural subsidies or environmentally harmful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Fuel
Jet fuel or aviation turbine fuel (ATF, also abbreviated avtur) is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by Gas turbine, gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial aviation are Jet A and Jet A-1, which are produced to a standardized international specification. The only other jet fuel commonly used in civilian turbine-engine powered aviation is Jet B, which is used for its enhanced cold-weather performance. Jet fuel is a mixture of a variety of hydrocarbons. Because the exact composition of jet fuel varies widely based on petroleum source, it is impossible to define jet fuel as a ratio of specific hydrocarbons. Jet fuel is therefore defined as a performance specification rather than a chemical compound. Furthermore, the range of molecular mass between hydrocarbons (or different carbon numbers) is defined by the requirements for the product, such as the freezing point or smoke point. Keros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Institute For Sustainable Development
The International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) is an independent think tank founded in 1990 working to shape and inform international policy on sustainable development governance. The institute has three offices in Canada - Winnipeg, Ottawa, and Toronto, and one office in Geneva, Switzerland. It has over 150 staff and associates working in over 30 countries. IISD is a registered charitable organization in Canada. History and organization In 1988 at the United Nations General Assembly, then-Canadian Prime Minister Brian Mulroney announced plans to "establish a centre which will promote internationally the concept of environmentally sustainable development," to be headquartered in Winnipeg. The new centre would be part of Canada's contribution to preparations for what became the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), also known as the Rio Earth Summit. Two years later in 1990, IISD was formally set up, following the signature of an agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Prices
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation expected, required, or given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, especially when the product is a service rather than a physical good, the price for the service may be called something else such as "rent" or "tuition". Prices are influenced by production costs, supply of the desired product, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted in currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices could be quoted as quantities of other goods or services, this sort of barter exchange is rarely seen. Prices are sometimes quoted in terms of vouchers su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Costs
Health economics is a branch of economics concerned with issues related to Health care efficiency, efficiency, effectiveness, value and behavior in the production and consumption of health and healthcare. Health economics is important in determining how to improve health outcomes and lifestyle patterns through interactions between individuals, healthcare providers and clinical settings. Health economists study the functioning of healthcare systems and health-affecting behaviors such as smoking, diabetes, and obesity. One of the biggest difficulties regarding healthcare economics is that it does not follow normal rules for economics. Price and quality are often hidden by the third-party payer system of insurance companies and employers. Additionally, Quality-adjusted life year, QALYs (Quality Adjusted Life Years), one of the most commonly used measurements for treatments, is very difficult to measure and relies upon assumptions that are often unreasonable. A seminal 1963 arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption (as opposed to household energy insecurity). Access to cheaper energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerability, vulnerabilities. International energy relations have contributed to the globalization of the world leading to energy security and energy vulnerability at the same time. Renewable energy, Renewable resources and significant opportunities for Efficient energy use, energy efficiency and Energy transition, transitions exist over wide geographical areas, in contrast to other energy sources, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Rapid deployment of wind power and solar power and energy efficiency, and technological diversification of energy sources, would result in significant energy security. Threats The m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. The 31 member countries and 13 association countries of the IEA represent 75% of global energy demand. The IEA was set up under the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis to respond to physical disruptions in global oil supplies, provide data and statistics about the global Petroleum industry, oil market and Energy industry, energy sector, promote energy savings and conservation, and establish international technical collaboration. Since its founding, the IEA has also coordinated use of the oil reserves that its members are required to hold. By regularly underestimating the role of renewable energies and overestimating the growth of nuclear energy, the IEA promotes the nuclear industry. In subsequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Subsidies
A subsidy, subvention or government incentive is a type of government expenditure for individuals and households, as well as businesses with the aim of stabilizing the economy. It ensures that individuals and households are viable by having access to essential goods and services while giving businesses the opportunity to stay afloat and/or competitive. Subsidies not only promote long term economic stability but also help governments to respond to economic shocks during a recession or in response to unforeseen shocks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Subsidies take various forms— such as direct government expenditures, tax incentives, soft loans, price support, and government provision of goods and services. For instance, the government may distribute direct payment subsidies to individuals and households during an economic downturn in order to help its citizens pay their bills and to stimulate economic activity. Here, subsidies act as an effective financial aid issued when the ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Subsidy
An agricultural subsidy (also called an agricultural incentive) is a government incentive paid to agribusinesses, agricultural organizations and farms to supplement their income, manage the supply of agricultural products, and influence the cost and supply of such commodities. Examples of such commodities include: wheat, feed grains (grain used as fodder, such as maize or corn, sorghum, barley and oats), cotton, milk, rice, peanuts, sugar, tobacco, oilseeds such as soybeans and meat products such as beef, pork, and lamb and mutton. A 2021 study by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization found $540 billion was given to farmers every year between 2013 and 2018 in global subsidies. The study found these subsidies are harmful in a number of ways. In under-developed countries, they encourage consumption of low-nutrition staples, such as rice. Subsidies also encourage deforestation; and they also drive inequality because smallholder farmers (many of whom are women) are excluded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, replacing fossil fuels with sustainable energy, clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and carbon sequestration, removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100, significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C. Solar energy and wind power can replace fossil fuels at the lowest cost compared to other renewable energy options.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
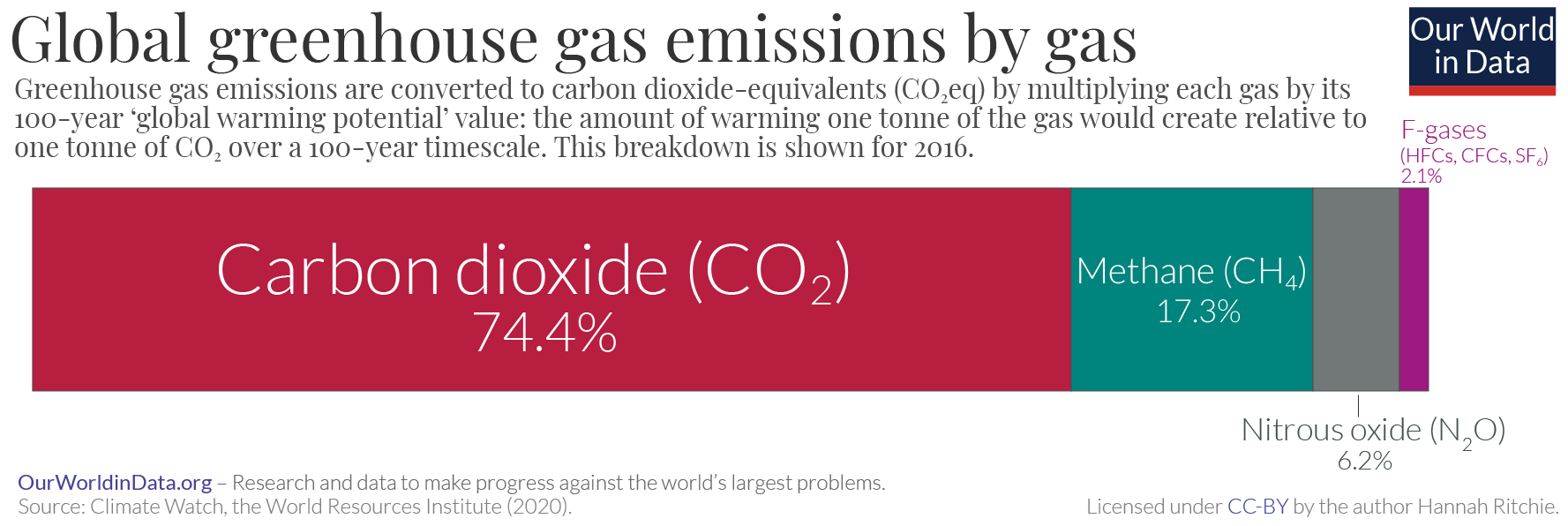
Carbon Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development. The World Bank is the collective name for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and International Development Association (IDA), two of five international organizations owned by the World Bank Group. It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference. After a slow start, its first loan was to France in 1947. In its early years, it primarily focused on rebuilding Europe. Over time, it focused on providing loans to developing world countries. In the 1970s, the World Bank re-conceptualized its mission of facilitating development as being oriented around poverty reduction. For the last 30 years, it has included NGOs and environmental groups in its loan portfolio. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |