|
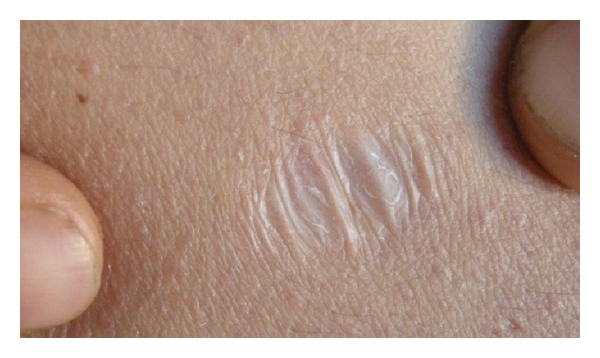
Stria
Stretch marks, also known as striae () or striae distensae, are a form of scarring on the Human skin, skin with an off-color hue. Over time, they may diminish, but will not disappear completely. Striae are caused by tearing of the dermis during periods of rapid growth of the body, such as during puberty or pregnancy, in which they usually form during the Pregnancy#Timeline, last trimester. Usually on the belly, these striae also commonly occur on the breasts, thighs, hips, lower back, and buttocks. Pregnancy-related striae are known as ''striae gravidarum''. Striae may also be influenced by the Hormone, hormonal changes associated with puberty, pregnancy, bodybuilding, or hormone replacement therapy. There is no evidence that creams used during pregnancy prevent stretch marks. Once they have formed, there is no clearly effective treatment, though various methods have been attempted and studied. Signs and symptoms Striae, or "stretch marks", begin as reddish or purple lesions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Spurt
Human height or stature is the distance from the bottom of the feet to the top of the head in a human body, standing erect. It is measured using a stadiometer, in centimetres when using the metric system or SI system, or feet and inches when using United States customary units or the imperial system. In the early phase of anthropometric research history, questions about height measuring techniques for measuring nutritional status often concerned genetic differences. Height is also important because it is closely correlated with other health components, such as life expectancy. Studies show that there is a correlation between small stature and a longer life expectancy. Individuals of small stature are also more likely to have lower blood pressure and are less likely to acquire cancer. The University of Hawaii has found that the "longevity gene" FOXO3 that reduces the effects of aging is more commonly found in individuals of small body size. Short stature decreases the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigmentation
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly insoluble and chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each year. Physical principles Like all materials, the color of pigments arises because they absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarring
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the normal collagen randomised alignment. For example, scars in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face due to facial plethora, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation or loss of menses, with the exact mechanisms of why still unknown. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete Regeneration (biology), regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
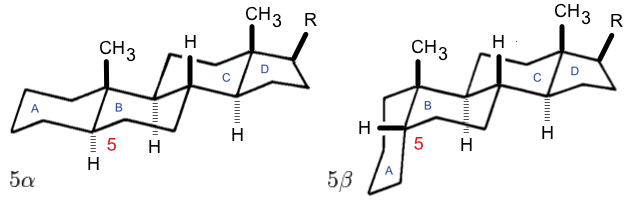
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
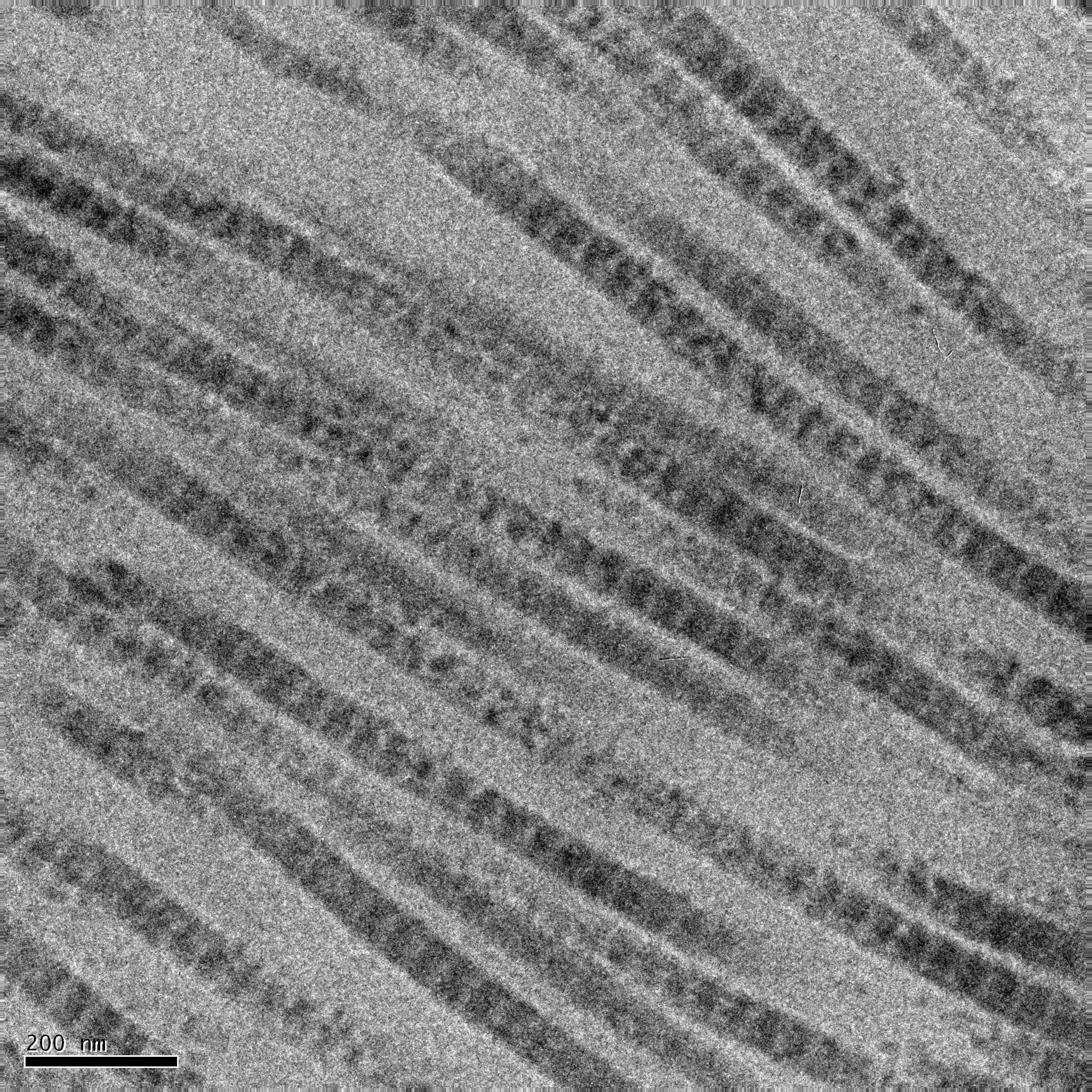
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Vitamin C is vital for collagen synthesis. Depending on the degree of biomineralization, mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the Gut (anatomy), gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes 1% to 2% of muscle tissue and 6% by weight of skeletal muscle. The fibroblast is the most common cell creating collagen in animals. Gelatin, which is used in food and industry, is collagen t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marfan Syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically have hypermobility (joints), exceptionally flexible joints and scoliosis, abnormally curved spines. The most serious complications involve the heart and aorta, with an increased risk of mitral valve prolapse and aortic aneurysm. The lungs, eyes, bones, and the dura mater, covering of the spinal cord are also commonly affected. The severity of the symptoms is variable. MFS is caused by a mutation in ''FBN1'', one of the genes that make fibrillin, which results in abnormal connective tissue. It is an autosomal dominant disorder. In about 75% of cases, it is inherited from a parent with the condition, while in about 25% it is a new mutation. Diagnosis is often based on the Ghent criteria, family history and genetic testing (DNA analysis). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis. The existing classification was last updated in 2017, when a number of rarer forms of EDS were added. EDS occurs due to mutations in one or more particular genes—there are 19 genes that can contribute to the condition. The specific gene affected determines the type of EDS, though the genetic causes of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome are still unknown. Some cases result from a new variation occurring during early development, while others are inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner. Typically, these variations result in defects in the structure or processing of the protein collagen or tenascin. Diagnos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target Organ (anatomy), organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of cells, and disuse or lack of exercise or disease intrinsic to the tissue itself. In medical practice, hormonal and nerve inputs that maintain an organ or body part are said to have ''trophic'' effects. A diminished muscular trophic condition is designated as ''atrophy''. Atrophy is reduction in size of cell, organ or tissue, after attaining its normal mature growth. In contrast, hypoplasia is the reduction in the cellular numbers of an organ, or tissue that has not attained normal maturity. Atrophy is the general physiological process of reabsorption and breakdown of biological tissue, tissues, involving apoptosis. When it occurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
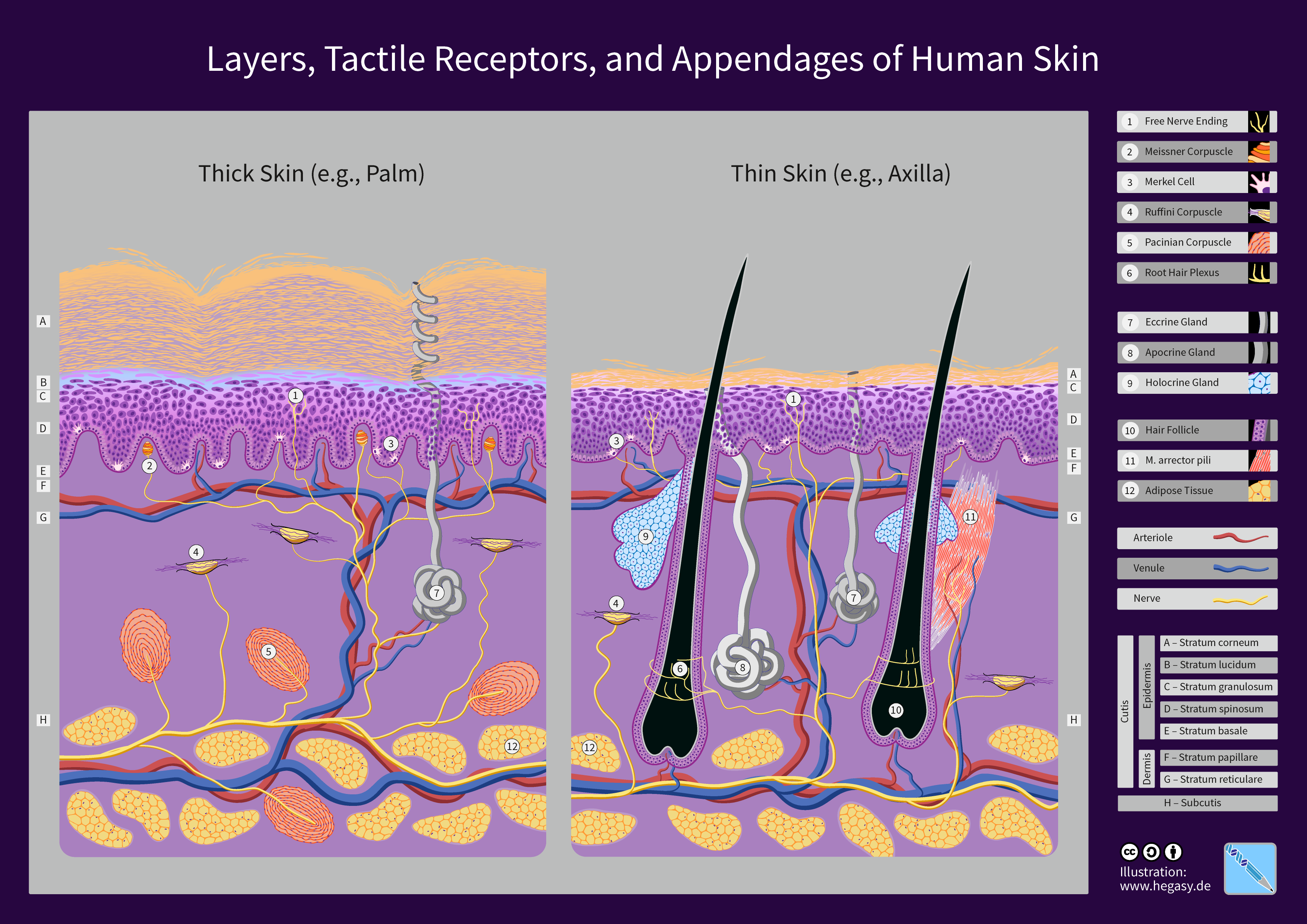
Human Skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue guarding Skeletal muscle, muscles, bones, ligaments and organ (anatomy), internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear Nudity#Evolution of hairlessness, hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#C, ''cutaneous'' literally means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'', skin). Skin plays an important immunity (medical), immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive transepidermal water loss, water loss. Its other functions are Thermal insulation, insulation, thermoregulation, temperature regulation, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and the protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |