|
Stretch Reflexes
The stretch reflex (myotatic reflex), or more accurately ''muscle stretch reflex'', is a muscle contraction in response to stretching a muscle. The function of the reflex is generally thought to be maintaining the muscle at a constant length but the response is often coordinated across multiple muscles and even joints. The older term ''deep tendon reflex'' is now criticized as misleading. Tendons have little to do with the response, and some muscles with stretch reflexes have no tendons. Rather, muscle spindles detect a stretch and convey the information to the central nervous system. As an example of a spinal reflex, it results in a fast response that involves an afferent signal into the spinal cord and an efferent signal out to the muscle. The stretch reflex can be a monosynaptic reflex which provides automatic regulation of skeletal muscle length, whereby the signal entering the spinal cord arises from a change in muscle length or velocity. It can also include a polysynaptic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
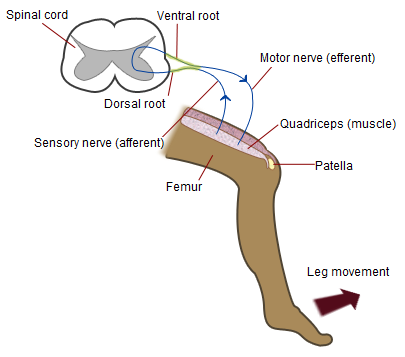
Patellar Tendon Reflex Arc
The patella (: patellae or patellas), also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds, and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles. In humans, the patella is the largest sesamoid bone (i.e., embedded within a tendon or a muscle) in the body. Babies are born with a patella of soft cartilage which begins to ossify into bone at about four years of age. Structure The patella is a sesamoid bone roughly triangular in shape, with the apex of the patella facing downwards. The apex is the most Inferior (anatomy), inferior (lowest) part of the patella. It is pointed in shape, and gives attachment to the patellar ligament. The front and back surfaces are joined by a thin margin and towards centre by a thicker margin. The tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle attaches to the base of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaw Jerk Reflex
The jaw jerk reflex, or masseter reflex, is a stretch reflex used to test the status of a patient's trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) and to help distinguish an upper cervical cord compression from lesions that are above the foramen magnum. The mandible—or lower jaw—is tapped at a downward angle just below the lips at the chin while the mouth is held slightly open. In response, the masseter muscles will jerk the mandible upwards. Normally this reflex is absent or very slight. However, in individuals with upper motor neuron lesions the jaw jerk reflex can be quite pronounced. The jaw jerk reflex can be classified as a dynamic stretch reflex. As with most other reflexes, the response to the stimulus is monosynaptic, with sensory neurons of the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus sending axons to the trigeminal motor nucleus, which in turn innervates the masseter. This reflex is used to judge the integrity of the upper motor neurons projecting to the trigeminal motor nucleus. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus. Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs via neural pathways in the nervous system called reflex arcs. A stimulus initiates a neural signal, which is carried to a synapse. The signal is then transferred across the synapse to a motor neuron, which evokes a target response. These neural signals do not always travel to the brain, so many reflexes are an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought. Many reflexes are fine-tuned to increase organism survival and self-defense. This is observed in reflexes such as the startle reflex, which provides an automatic response to an unexpected stimulus, and the feline righting reflex, which reorients a cat's body when falling to ensure safe landing. The simplest type of reflex, a short-latency reflex, has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other Sensory nervous system, sensory systems, such as Visual perception, the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Motor Neuron Lesion
An upper motor neuron lesion (also known as pyramidal insufficiency) Is an injury or abnormality that occurs in the neural pathway above the anterior horn cell of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. Conversely, a lower motor neuron lesion affects nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord or the cranial motor nuclei to the relevant muscle(s). Upper motor neuron lesions occur in the brain or the spinal cord as the result of stroke, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, cerebral palsy, atypical parkinsonisms, multiple system atrophy, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Symptoms Changes in muscle performance can be broadly described as the upper motor neuron syndrome. These changes vary depending on the site and the extent of the lesion, and may include: * Muscle weakness. known as 'pyramidal weakness' *Sloth sign. Decreased control of active movement, particularly slowness * Spasticity, a velocity-dependent change in muscle tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clasp-knife Response
Clasp-knife response is a Golgi tendon reflex with a rapid decrease in resistance when attempting to flex a joint, usually during a neurological examination. It is one of the characteristic responses of an upper motor neuron lesion. It gets its name from the resemblance between the motion of the limb and the sudden closing of a claspknife after sufficient pressure is applied. Cause When a joint is passively flexed, the resisting force comes from the stretch reflex (or sometimes called tendon reflex) resulting from the extensor muscle being stretched. In upper motor neuron lesions, muscle tonus may increase and resistance of muscle to stretch increases. However, if sufficient force is applied, limb resistance suddenly decreases, presumably mediated by the Golgi tendon reflex (also call autogenic inhibition). Mechanism This reflex is observed in patients with upper motor neuron lesions. It was frequently attributed to the action of the golgi tendon organ, likely because of early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonus
Clonus is a set of involuntary and rhythmic muscular contractions and relaxations. Clonus is a sign of certain neurological conditions, particularly associated with upper motor neuron lesions involving descending motor pathways, and in many cases is accompanied by spasticity (another form of hyperexcitability). Unlike small spontaneous twitches known as fasciculations (usually caused by lower motor neuron pathology), clonus causes large motions that are usually initiated by a reflex. Studies have shown clonus beat frequency to range from three to eight Hz on average, and may last a few seconds to several minutes depending on the patient's condition. Signs Clonus is most commonly found at the ankle, specifically with a dorsiflexion/plantarflexion movement (up and down). Some case studies have also reported clonus in the finger, toe, and laterally in the ankle (as opposed to the typical up and down motion). * Ankle (medial gastrocnemius) * Patella ( knee cap) * Triceps su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jendrassik Maneuver
The Jendrassik maneuver is a medical maneuver wherein the patient clenches the teeth, flexes both sets of fingers into a hook-like form, and interlocks those sets of fingers together. The tendon below the patient's knee is then hit with a reflex hammer to elicit the patellar reflex. The elicited response is compared with the reflex result of the same action when the maneuver is not in use. Often a larger reflex response will be observed when the patient is occupied with the maneuver: "A weak or apparently missing reflex could be triggered by afferent activity resulting from such muscle tension. This is the true explanation for the maneuver, not a diversion of the patient’s attention – a misconception that can be heard even today." This effect was first observed in the late 19th century by Hungarian physician Ernő Jendrassik, after whom it was named. This maneuver is particularly useful in that even if the patient is aware of the maneuver's purpose, it still functions prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankle Jerk Reflex
The ankle jerk reflex, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs when the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed. It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it. A positive result would be the jerking of the foot towards its plantar surface. Being a deep tendon reflex, it is monosynaptic. It is also a stretch reflex. These are monosynaptic spinal segmental reflexes. When they are intact, integrity of the following is confirmed: cutaneous innervation, motor supply, and cortical input to the corresponding spinal segment. Root value This reflex is mediated by the S1 spinal segment of the spinal cord. Procedure and components Ankle of the patient is relaxed. It is helpful to support the ball of the foot at least somewhat to put some tension in the Achilles tendon, but don’t completely dorsiflex the ankle. A small strike is given on the Achilles tendon using a rubber hammer to elicit the resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patellar Reflex
The patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord. Many animals, most significantly humans, have been seen to have the patellar reflex, including dogs, cats, horses, and other mammalian species. Mechanism Striking of the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer just below the patella stretches the muscle spindle in the quadriceps muscle. This produces a signal which travels back to the spinal cord and synapses (without interneurons) at the level of L3 or L4 in the spinal cord, completely independent of higher centres. From there, an alpha motor neuron conducts an efferent impulse back to the quadriceps femoris muscle, triggering contraction. This contraction, coordinated with the relaxation of the antagonistic flexor hamstring muscle causes the leg to kick. There is a latency of around 18 ms between stretch of the patellar tendon and the beginning of contraction of the quadriceps femori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceps Reflex
The triceps reflex, a deep tendon reflex, is a reflex that elicits involuntary contraction of the triceps brachii muscle. It is sensed and transmitted by the radial nerve. The reflex is tested as part of the neurological examination to assess the sensory and motor pathways within the C7 and C8 spinal nerves. Testing The test can be performed by tapping the triceps tendonA tendon is a strip or sheet of connective tissue that transmits the force generated by the contraction of muscle to the bone by attaching with it. Thus, in simple words, a tendon attaches a muscle to a bone with the sharp end of a reflex hammer while the forearm is hanging loose at a right angle to the arm. A sudden contraction of the triceps muscle causes extension,A straightening at the elbow joint) of the forearm and indicates a normal reflex. Reflex arc The arc involves the stretch receptors in the triceps tendon, from where the information travels along the radial nerve, through the C7/C8 nerve roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Digitorum Reflex
The extensor digitorum reflex is tested as part of the neurological examination to assess the sensory and motor pathways within the C6 and C7 spinal nerves. It is also known as Braunecker-Effenberg reflex, or BER. Testing The test is performed by tapping the extensor digitorum muscle while the fingers are light or half flexed. A sudden contraction of the musculus extensor digitorum and extension of the fingers indicate a normal reflex. Absence of reflex An absence of reflex can be an indicator for radiculopathy within the C6 and C7 or neuropathy within the deep branch of the radial nerve. References External links * Extensor-Digitorum-ReflexApplying the Extensor Digitorum Reflex to Neurological Examination {{DEFAULTSORT:Extensor Digitorum Reflex Reflexes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |