|
Strangelet
A strangelet (pronounced ) is a hypothetical particle consisting of a bound state of roughly equal numbers of up, down, and strange quarks. An equivalent description is that a strangelet is a small fragment of strange matter, small enough to be considered a particle. The size of an object composed of strange matter could, theoretically, range from a few femtometers across (with the mass of a light nucleus) to arbitrarily large. Once the size becomes macroscopic (on the order of metres across), such an object is usually called a strange star. The term "strangelet" originates with Edward Farhi and Robert Jaffe in 1984. It has been theorized that strangelets can convert matter to strange matter on contact. Strangelets have also been suggested as a dark matter candidate. Theoretical possibility Strange matter hypothesis The known particles with strange quarks are unstable. Because the strange quark is heavier than the up and down quarks, it can spontaneously decay, via the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strange Matter
Strange matter (or strange quark matter) is quark matter containing strange quarks. In extreme environments, strange matter is hypothesized to occur in the core of neutron stars, or, more speculatively, as isolated droplets that may vary in size from femtometers ( strangelets) to kilometers, as in the hypothetical strange stars. At high enough density, strange matter is expected to be color superconducting. Ordinary matter, also referred to as atomic matter, is composed of atoms, with nearly all matter concentrated in the atomic nuclei. Nuclear matter is a liquid composed of neutrons and protons, and they are themselves composed of up and down quarks. Quark matter is a condensed form of matter composed entirely of quarks. When quark matter does not contain strange quarks, it is sometimes referred to as non-strange quark matter. Context In particle physics and astrophysics, the term 'strange matter' is used in two different contexts, one broader and the other more speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strange Quark
The strange quark or s quark (from its symbol, s) is the third lightest of all quarks, a type of elementary particle. Strange quarks are found in subatomic particles called hadrons. Examples of hadrons containing strange quarks include kaons (), strange D mesons (), Sigma baryons (), and other strange particles. According to the IUPAP, the symbol s is the official name, while "strange" is to be considered only as a mnemonic. The name sideways has also been used because the s quark (but also the other three remaining quarks) has an isospin, I value of 0 while the u ("up") and d ("down") quarks have values of + and − respectively. Along with the charm quark, it is part of the generation (physics), second generation of matter. It has an electric charge of elementary charge, ''e'' and a bare mass of . Like all quarks, the strange quark is an elementary particle, elementary fermion with Spin (physics), spin spin-1/2, , and experiences all four fundamental interactions: gravit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothetical Particle
This is a list of known and hypothesized microscopic particles in particle physics, condensed matter physics and cosmology. Standard Model elementary particles Elementary particles are particles with no measurable internal structure; that is, it is unknown whether they are composed of other particles. They are the fundamental objects of quantum field theory. Many families and sub-families of elementary particles exist. Elementary particles are classified according to their Spin (physics), spin. Fermions have half-integer spin while bosons have integer spin. All the elementary particles of the Standard Model have been experimentally observed, including the Higgs boson in 2012. Many other hypothetical elementary particles, such as the graviton, have been proposed, but not observed experimentally. Fermions Fermions are one of the two fundamental classes of particles, the other being bosons. Fermion particles are described by Fermi–Dirac statistics and have quantum numbers de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Witten
Edward Witten (born August 26, 1951) is an American theoretical physics, theoretical physicist known for his contributions to string theory, topological quantum field theory, and various areas of mathematics. He is a professor emeritus in the school of natural sciences at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, Princeton. Witten is a researcher in string theory, quantum gravity, supersymmetry, supersymmetric quantum field theories, and other areas of mathematical physics. Witten's work has also significantly impacted pure mathematics. In 1990, he became the first physicist to be awarded a Fields Medal by the International Mathematical Union, for his mathematical insights in physics, such as his 1981 proof of the positive energy theorem in general relativity, and his interpretation of the Vaughan Jones, Jones invariants of knots as Feynman integrals. He is considered the practical founder of M-theory.Duff 1998, p. 65 Early life and education Witten was born on A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
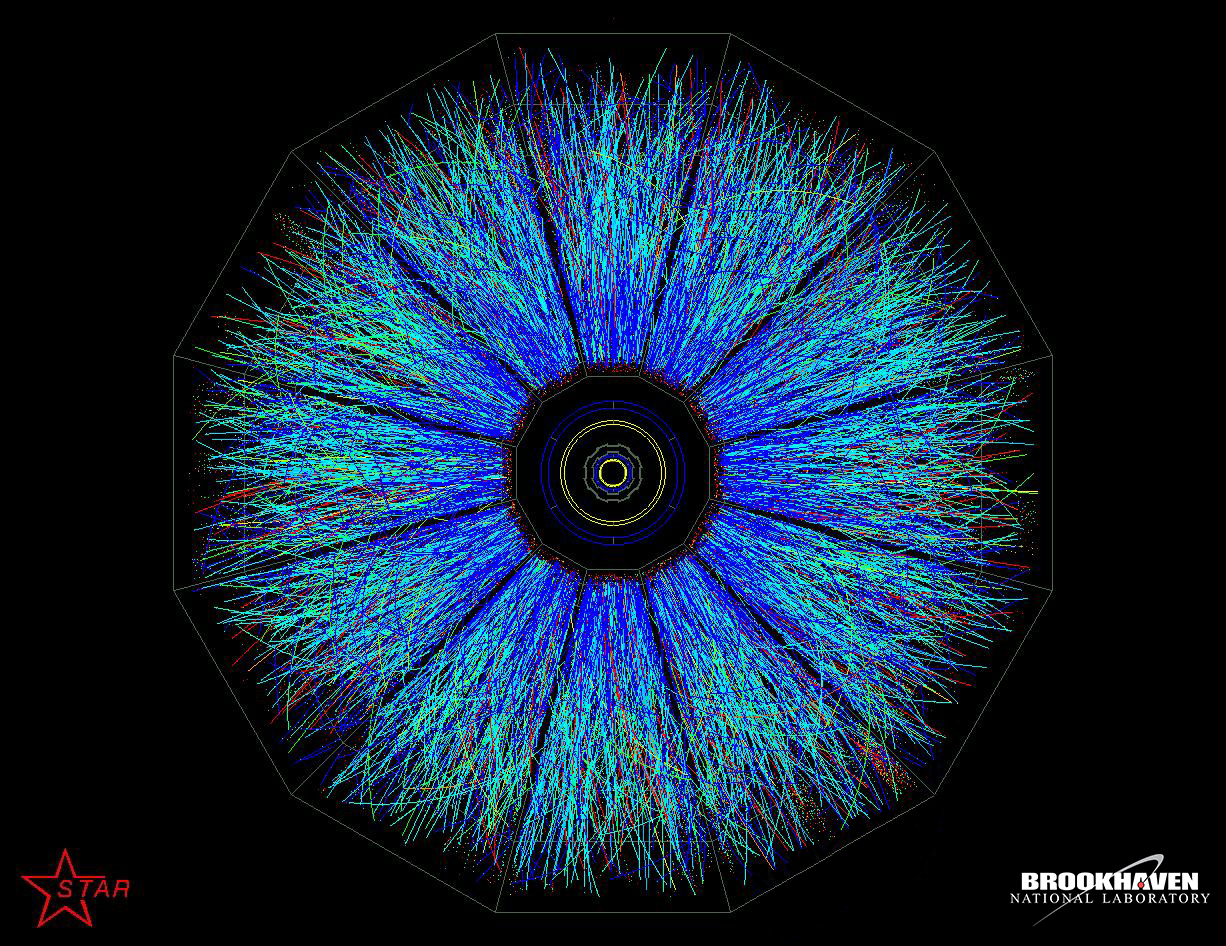
STAR Detector
The STAR detector (for Solenoidal Tracker at RHIC) is one of the four experiments at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) in Brookhaven National Laboratory, United States. The primary scientific objective of STAR is to study the formation and characteristics of the quark–gluon plasma (QGP), a state of matter believed to exist at sufficiently high energy densities. Detecting and understanding the QGP allows physicists to understand better the Universe in the seconds after the Big Bang, when the presently-observed symmetries (and asymmetries) of the Universe were established. Unlike other physics experiments where a theoretical prediction can be tested directly by a single measurement, STAR must make use of a variety of simultaneous studies in order to draw strong conclusions about the QGP. This is due both to the complexity of the system formed in the high-energy nuclear collision and the unexplored landscape of the physics studied. STAR therefore consists of several types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider
The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC ) is the first and one of only two operating heavy- ion colliders, and the only spin-polarized proton collider ever built. Located at Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) in Upton, New York, and used by an international team of researchers, it is the only operating particle collider in the US. By using RHIC to collide ions traveling at relativistic speeds, physicists study the primordial form of matter that existed in the universe shortly after the Big Bang. By colliding spin-polarized protons, the spin structure of the proton is explored. RHIC is as of 2019 the second-highest-energy heavy-ion collider in the world, with nucleon energies for collisions reaching 100 GeV for gold ions and 250 GeV for protons. As of November 7, 2010, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has collided heavy ions of lead at higher energies than RHIC. The LHC operating time for ions (lead–lead and lead–proton collisions) is limited to about one month per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases (see Composition below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Ray
In astroparticle physics, an ultra-high-energy cosmic ray (UHECR) is a cosmic ray with an energy greater than 1 EeV (1018 electronvolts, approximately 0.16 joules), far beyond both the rest mass and energies typical of other cosmic ray particles. The origin of these highest energy cosmic rays is not known. These particles are extremely rare; between 2004 and 2007, the initial runs of the Pierre Auger Observatory (PAO) detected 27 events with estimated arrival energies above , that is, about one such event every four weeks in the area surveyed by the observatory. Observational history The first observation of a cosmic ray particle with an energy exceeding (16 J) was made by John Linsley and Livio Scarsi at the Volcano Ranch experiment in New Mexico in 1962. Cosmic ray particles with even higher energies have since been observed. Among them was the Oh-My-God particle observed by the University of Utah's Fly's Eye experiment on the evening of 15 October 1991 over Dugway P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Monopole
In particle physics, a magnetic monopole is a hypothetical particle that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). A magnetic monopole would have a net north or south "magnetic charge". Modern interest in the concept stems from high-energy physics, particle theories, notably the grand unified theory, grand unified and superstring theory, superstring theories, which predict their existence. The known elementary particles that have electric charge are electric monopoles. Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets is not caused by magnetic monopoles, and indeed, there is no known experimental or observational evidence that magnetic monopoles exist. A magnetic monopole is not necessarily an elementary particle, and models for magnetic monopole production can include (but are not limited to) Spin (physics), spin-0 monopoles or spin-1 massive vector mesons. The term "magnetic monopole" only refers to the nature of the particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk are deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the study of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type of quantum field theory called a non-abelian gauge theory, with symmetry group special unitary group, SU(3). The QCD analog of electric charge is a property called ''color''. Gluons are the force carriers of the theory, just as photons are for the electromagnetic force in quantum electrodynamics. The theory is an important part of the Standard Model of particle physics. A large body of Quantum chromodynamics#Experimental tests, experimental evidence for QCD has been gathered over the years. QCD exhibits three salient properties: * Color confinement. Due to the force between two color charges remaining constant as they are separated, the energy grows until a quark–antiquark pair is mass–energy equivalence, spontaneously produced, turning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension (physics), tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. Gerridae, water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to Cohesion (chemistry), cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |