|
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system, the rotor. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system. Design Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from a printed circuit board (PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy. One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairpin Technology
Hairpin technology is a winding technology for stators in electric motors and generators and is also used for traction applications in electric vehicles. In contrast to conventional winding technologies, the hairpin technology is based on solid, flat copper bars which are inserted into the stator stack. These copper bars, also known as hairpins, consist of enameled copper wire bent into a U-shape, similar to the geometry of hairpins. In addition to hairpins with U-shape, there are two other variants of bar windings, the so-called I-pin technology and the concept of continuous hairpin windings. I-Pins are straight copper wire elements that are inserted into the stator slots. Unlike Hairpins, these Pins are not bent prior to insertion into stack. However, contacting is necessary on both sides of the stator. In the concept of continuous hairpin windings, so-called winding mats are produced and afterwards inserted into the stack from the inner diameter. Hairpin stators are most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque Converter
A torque converter is a device, usually implemented as a type of fluid coupling, that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the prime mover to the automatic gear train, which then drives the load. It is thus usually located between the engine's flexplate and the transmission. The equivalent device in a manual transmission is the mechanical clutch. A torque converter serves to increase transmitted torque when the output rotational speed is low. In the fluid coupling embodiment, it uses a fluid, driven by the vanes of an input impeller, and directed through the vanes of a fixed stator, to drive an output turbine in such a manner that torque on the output is increased when the output shaft is rotating more slowly than the input shaft, thus providing the equivalent of an adaptive reduction gear. This is a feature beyond what a simple fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motors
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate Laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may also be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be brushed or brushless, single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase, axial or radial flux, and may be air-cooled or liquid-cooled. Standardized electric motors provide power for industrial use. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stator Of A 3-phase Induction Motor
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system, the rotor. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system. Design Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from a printed circuit board (PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy. One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stator Machine Triphasée
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system, the rotor. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system. Design Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from a printed circuit board (PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy. One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stator And Rotor By Zureks
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, Siren (alarm), sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial Flagellum, flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system, the Rotor (electric), rotor. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating Armature (electrical), armature; in a Electric generator, generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system. Design Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from a printed circuit board (PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy. One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mud Motor
A mud motor (or drilling motor) is a progressive cavity positive displacement pump (PCPD) placed in the drill string to provide additional power to the bit while drilling. The PCPD pump uses drilling fluid (commonly referred to as drilling mud, or just mud) to create eccentric motion in the power section of the motor which is transferred as concentric power to the drill bit. The mud motor uses different rotor and stator configurations to provide optimum performance for the desired drilling operation, typically increasing the number of lobes and length of power assembly for greater horsepower. In certain applications, compressed air, or other gas, can be used for mud motor input power. Normal rotation of the bit while using a mud motor can be from 60 rpm to over 100 rpm. Basic principle Based on the principle developed by René Moineau, the theory states that a helical rotor with one or more lobes will rotate eccentrically when the stator contains more lobes than the rotor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary switch, electrical switch in certain types of electric motors and electrical generators that periodically reverses the Current (electricity), current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. It consists of a cylinder composed of multiple metal contact segments on the rotating armature (electrical engineering), armature of the machine. Two or more electrical contacts called "brush (electric), brushes" made of a soft conductive material like carbon press against the commutator, making sliding contact with successive segments of the commutator as it rotates. The windings (coils of wire) on the armature (electrical engineering), armature are connected to the commutator segments. Commutators are used in direct current (DC) machines: dynamos (DC generators) and many DC motors as well as universal motors. In a motor the commutator applies electric current to the windings. By reversing the current direction in the rotating windings each half turn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
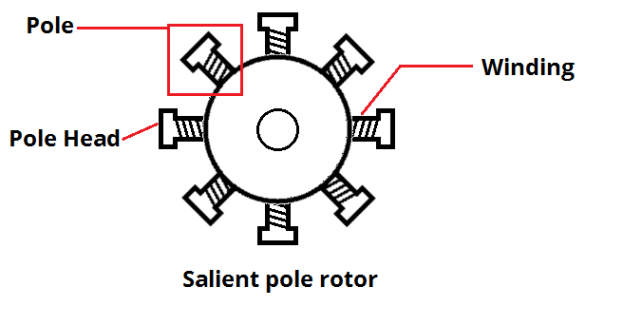
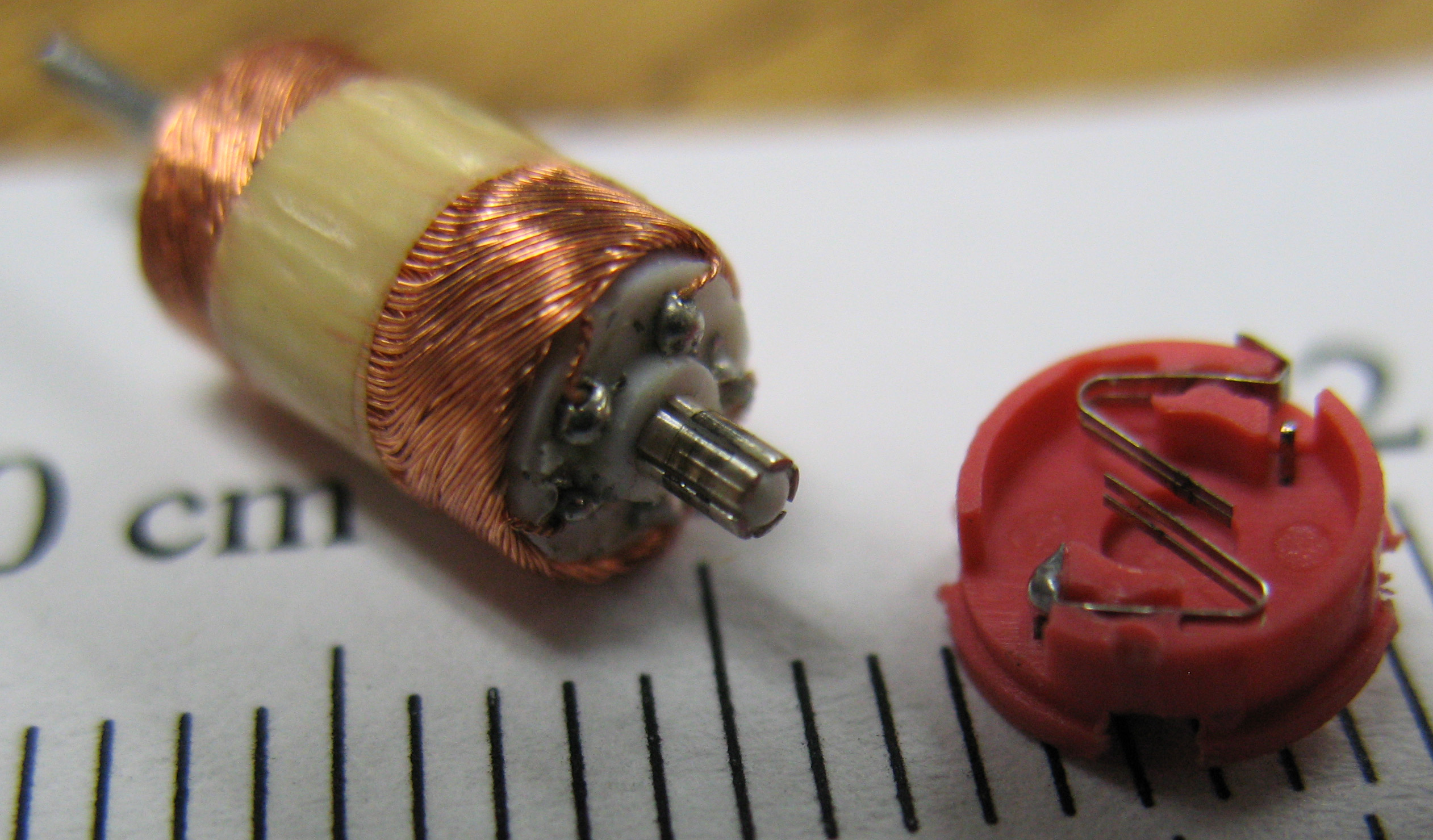
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is a moving component of an electromagnetic system in the electric motor, electric generator, or alternator. Its rotation is due to the interaction between the windings and magnetic fields which produces a torque around the rotor's axis.Staff. "Understanding Alternators. What Is an Alternator and How Does It Work." N.p., n.d. Web. 24 November 2014 . Early development An early example of electromagnetic rotation was the first rotary machine built by Ányos Jedlik with electromagnets and a commutator, in 1826-27. Other pioneers in the field of electricity include Hippolyte Pixii who built an alternating current generator in 1832, and William Ritchie's construction of an electromagnetic generator with four rotor coils, a commutator and brushes, also in 1832. Development quickly included more useful applications such as Moritz Hermann Jacobi's motor that could lift 10 to 12 pounds with a speed of one foot per second, about 15 watts of mechanical power in 1834. In 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |