|
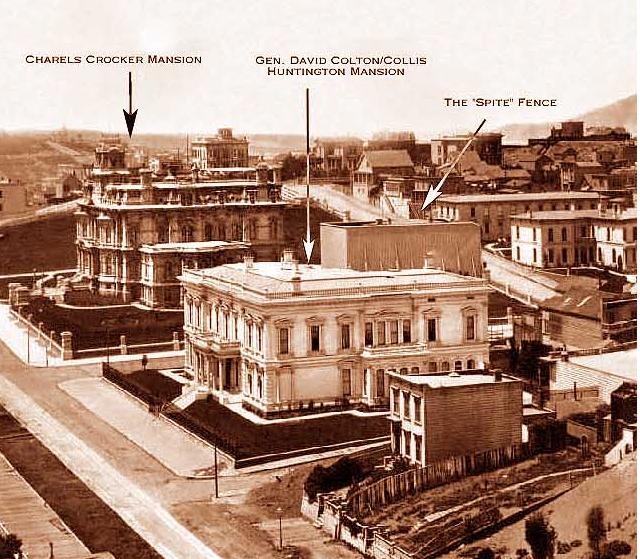
Spite Fence
In property law, a spite fence is an overly tall fence or a row of trees, bushes, or hedges, constructed or planted between adjacent lots by a property owner (with no legitimate purpose), who is annoyed with or wishes to annoy a neighbor, or who wishes to completely obstruct the view between lots. Several U.S. states and local governments have regulations to prohibit spite fences, or related regulations such as those establishing a maximum allowed height for fences. In the United Kingdom, the terms spite wall or blinder wall (as in, to blind the view of a neighbor) are more commonly used. Law Courts have said, " der American rule... one may not erect a structure for the sole purpose of annoying his neighbor. Many courts hold that a spite fence which serves no useful purpose may give rise to an action for both injunctive relief and damages." Sundowner, Inc. v. King is a classic spite fence case. In this case from Idaho, the defendant King, bought a motel from the plaintiff (Bush ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Spite Wall, Stankelt Road, Silverdale (geograph 3230069)
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''English alphabet#Letter names, a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, ''English articles, a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marino Crescent
Marino Crescent () is a Georgian crescent of 26 houses at the junction of Marino, Fairview and Clontarf in Dublin 3, Ireland. It is the only Georgian crescent in Dublin. History The crescent was built by Charles Ffolliott in 1792 as a spite wall to block the view of Dublin Bay from the now demolished Marino House and its better-known folly, the Casino at Marino, which was much coveted by its owner, James Caulfeild, 1st Earl of Charlemont . The terrace was built with red brick front finishes in a similar method to Mountjoy Square and Merrion Square however, owing to the fashion of the time the fronts were plastered over during the Regency period and all of the facades remain in the same state as of 2020. All of the houses are three-storey over basement properties and all are two-bay with the exception of the two largest central houses, numbers 13 and 14, which are three-bay. Number 26 was demolished in the 1980s to make way for a faux Georgian block of apartments known as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right To Light
Right to light is a form of easement in English law that gives a long-standing owner of a building with windows a right to maintain an adequate level of illumination. The right was traditionally known as the doctrine of "ancient lights". A right to light can also be granted expressly by deed, or granted implicitly, for example under the rule in '' Wheeldon v. Burrows'' (1879). In England, the rights to ancient lights are most usually acquired under the Prescription Act 1832. In American common law the doctrine died out during the 19th century, and is generally no longer recognized. Japanese law provides for a comparable concept known as . Rights In effect, the owner of a building with windows that have received natural daylight for 20 years or more is entitled to forbid any construction or other obstruction on adjacent land that would block the light so as to deprive them of adequate illumination through those windows. The owner may build more or larger windows but cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nail House
A holdout is a property that did not become part of a larger real estate development, usually because the owner refused to sell their property. There are many examples of holdouts worldwide. Examples Macy's headquarters at Macy's Herald Square in New York City, for example, does not cover the whole block because of a holdout named the Million Dollar Corner on the corner of Broadway and West 34th Street (in Herald Square). Now decorated as a Macy's shopping bag, the building received its name from the fact that it sold for a million dollars in 1911, an unprecedented sum at the time. One mile () north of Macy's Herald Square is 30 Rockefeller Center, which has slight setbacks at its corners of 49th and 50th Streets on Sixth Avenue due to two buildings at those corners. The owner of 1258 Sixth Avenue—John F. Maxwell, grandson of the original owner—outright refused to sell to John D. Rockefeller Jr. during the construction of Rockefeller Center. While Rockefeller was success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Rights
In real estate, air rights are the property interest in the "space" above the Earth's surface. Generally speaking, owning or renting land or a building includes the right to use and build in the space above the land without interference by others. This legal concept is encoded in the Latin phrase ''Cuius est solum, eius est usque ad coelum et ad inferos'' ("''Whoever owns the soil, it is theirs up to Heaven and down to Hell''."), which appears in medieval Roman law and is credited to 13th-century glossator Accursius; it was notably popularized in common law in ''Commentaries on the Laws of England'' (1766) by William Blackstone; see Cuius est solum, eius est usque ad coelum et ad inferos#Origins, origins of phrase for details. In the 20th century, the splitting of air-rights from the underlying property became an important issue for property development, particularly for skyscrapers in some crowded cities. Air travel Property rights defined by points on the ground once ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric Megalith, megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connecting horizontal lintel stones, held in place with mortise and tenon joints, a feature unique among contemporary monuments. Inside is a ring of smaller bluestones. Inside these are free-standing trilithons, two bulkier vertical sarsens joined by one lintel. The whole monument, now ruinous, is aligned towards the sunrise on the summer solstice and sunset on the winter solstice. The stones are set within Earthwork (archaeology), earthworks in the middle of the densest complex of Neolithic British Isles, Neolithic and Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred ''tumuli'' (burial mounds). Stonehenge was constructed in several phases beginning about 3100 BC and continuing until about 1600 B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
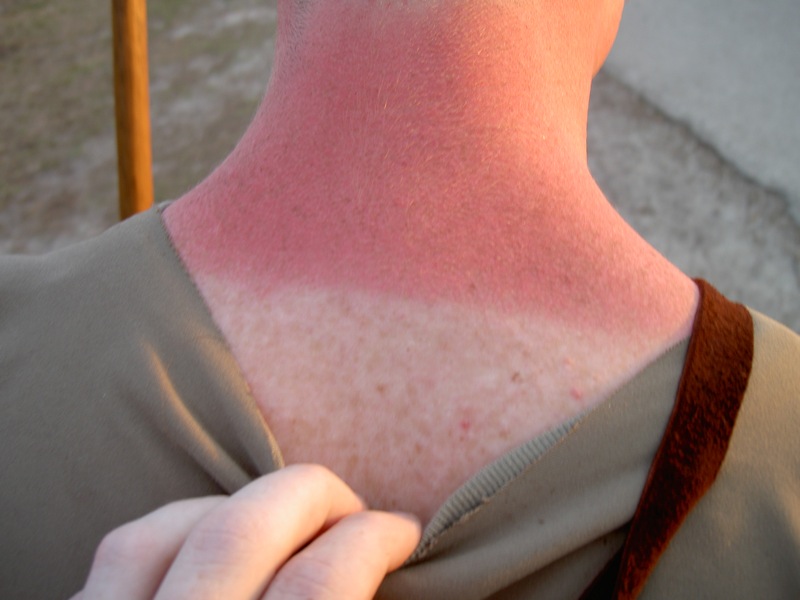
Redneck
''Redneck'' is a derogatory term mainly applied to white Americans perceived to be crass and unsophisticated, closely associated with rural whites of the southern United States.Harold Wentworth, and Stuart Berg Flexner, ''Dictionary of American Slang'' (1975) p. 424. Its meaning possibly stems from the sunburn found on farmers' necks dating back to the late 19th century. Authors Joseph Flora and Lucinda MacKethan describe the stereotype as follows: :''Redneck'' is a derogatory term currently applied to some lower-class and working-class southerners. The term, which came into common usage in the 1930s, is derived from the redneck's beginnings as a "yeoman farmer" whose neck would burn as he or she toiled in the fields. These yeoman farmers settled along the Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina coasts. Its modern usage is similar in meaning to ''Cracker (pejorative), cracker'' (especially regarding Texas, Georgia, and Florida), ''hillbilly'' (especially regarding Appalac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooper, Utah
Hooper ( ) is a city in Weber County, Utah, Weber County, Utah, United States, first called Muskrat Springs and later Hooperville for Captain William Henry Hooper, an early Utah delegate to Congress. The population was 9,087 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, up from the 2010 United States Census, 2010 figure of 6,932. Prior to the city's incorporation on November 30, 2000, Hooper was an unincorporated census-designated place (CDP). Hooper is part of the Ogden, Utah, Ogden–Clearfield, Utah, Clearfield, Utah Ogden-Clearfield metropolitan area, Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Hooper was settled in 1854, and become a township in 1997 (about 15 years after a failed vote to incorporate). Over the next several years "it became evident that the township board could make plans and suggestions, but had no official power," so a vote to incorporate passed on May 2, 2000, with the city being officially incorporated on November 30, 2000. Geography According to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Kuklick
Bruce Kuklick ( ; born March 3, 1941, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) is an American historian. He currently serves as the Nichols Professor of American History at the University of Pennsylvania, specializing in diplomatic and intellectual history of the United States and the history of philosophy The history of philosophy is the systematic study of the development of philosophical thought. It focuses on philosophy as rational inquiry based on argumentation, but some theorists also include myth, religious traditions, and proverbial lor .... He has written several books on those subjects, including ''Black Philosopher, White Academy: The Career of William Fontaine'', which was described as "a biography of Fontaine is as good a story as that life itself." Selected publications * American policy and the Division of Germany: the clash with Russia over Reparations', 1972 * ''Puritans in Babylon – the Ancient Near East & American Intellectual Life 1880–1930: The Ancient Nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connie Mack
Cornelius McGillicuddy (December 22, 1862 – February 8, 1956), better known as Connie Mack, was an American professional baseball catcher, manager, and team owner. Mack holds records for the most wins (3,731), losses (3,948), ties (76), and games managed (7,755) in Major League Baseball (MLB) history. His victory total is 847 more than the second-highest: Tony La Russa's 2,884 wins. Mack's lead in career losses is even greater, with 1,449 more than La Russa's 2,499. Mack also has 17 more ties than the next-closest manager, Clark Griffith, who has 59. Mack managed the Philadelphia Athletics for its first 50 seasons of play, starting in 1901; was at least part-owner from 1901 to 1954; and retired after the 1950 season at age 87. He was the first American League manager to lead a team to 100 wins, doing so in 1910, 1911, 1929, 1930, and 1931; his five 100-win seasons are second-most in MLB history, with only two other managers surpassing him. He was the first manager to win th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 1,603,797 in the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city is the urban core of the Philadelphia metropolitan area (sometimes called the Delaware Valley), the nation's Metropolitan statistical area, seventh-largest metropolitan area and ninth-largest combined statistical area with 6.245 million residents and 7.379 million residents, respectively. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Americans, English Quakers, Quaker and advocate of Freedom of religion, religious freedom, and served as the capital of the Colonial history of the United States, colonial era Province of Pennsylvania. It then played a historic and vital role during the American Revolution and American Revolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |