|
Speech Science
Speech science refers to the study of production, transmission and perception of speech. Speech science involves anatomy, in particular the anatomy of the oro-facial region and neuroanatomy, physiology, and acoustics. Speech production The production of speech is a highly complex motor task that involves approximately 100 orofacial, larynx, laryngeal, pharyngeal muscles, pharyngeal, and muscles of respiration, respiratory muscles. Precise and expeditious timing of these muscles is essential for the production of temporally complex speech sounds, which are characterized by transitions as short as 10 ms between frequency bands and an average speaking rate of approximately 15 sounds per second. Speech production requires airflow from the lungs (respiration (physiology), respiration) to be phonated through the vocal folds of the larynx (phonation) and resonated in the vocal cavities shaped by the jaw, soft palate, lips, tongue and other articulators (articulation (anatomy), articula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, such as informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing; acts may vary in various aspects like enunciation, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, loudness, and Speech tempo, tempo to convey meaning. Individuals may also unintentionally communicate aspects of their social position through speech, such as sex, age, place of origin, physiological and mental condition, education, and experiences. While normally used to facilitate communication with others, people may also use speech without the intent to communicate. Speech may nevertheless express emotions or desires; people Talking to oneself, talk to themselves sometimes in acts that are a development of what some psychologists (e.g., Lev Vygotsky) have maintained is the use of silent spee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
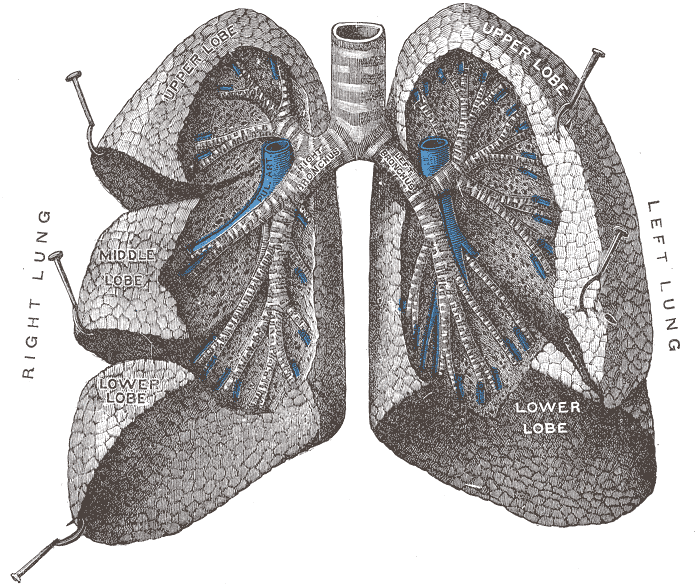
Ventilation (physiology)
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or external respiration, brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where cellular respiration takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
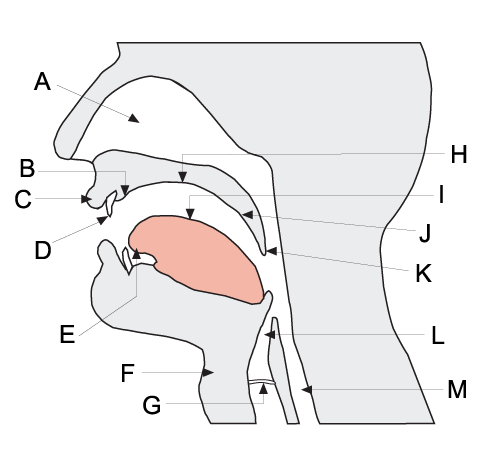
Articulatory Phonetics
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures. Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound. Respiratory sounds can be produced by expelling air from the lungs. However, to vary the sound quality in a way useful for speaking, two speech organs normally move towards each other to contact each other to create an obstruction that shapes the air in a particular fashion. The point of maximum obstruction is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch (music), pitch and sound pressure, volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' (: larynges) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throatʼ. Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a respiratory epithelium, ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The laryngeal cavity, cavity of the larynx extends from its tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Folds
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, the folds are controlled via the recurrent laryngeal nerve, recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve. They are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx. They vibration, vibrate, modulating the flow of air being expelled from the lungs during phonation. The 'true vocal cords' are distinguished from the 'false vocal folds', known as vestibular folds or ''ventricular folds'', which sit slightly superior to the more delicate true folds. These have a minimal role in normal phonation, but can produce deep sonorous tones, screams and growls. The length of the vocal fold at birth is approximately six to eight millimeters and grows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at the front an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trunk (anatomy)
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including human beings), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a human — is usually divided into the ''thoracic'' segment (also known as the upper torso, where the forelimbs extend), the '' abdominal'' segment (also known as the "mid-section" or "midriff"), and the ''pelvic'' and '' perineal'' segments (sometimes known together with the abdomen as the lower torso, where the hindlimbs extend). Anatomy Major organs In humans, most critical organs, with the notable exception of the brain, are housed within the torso. In the upper chest, the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage, and the abdomen contains most of the organs responsible for digestion: the stomach, which breaks down partially digested food via gastric acid; the liver, which respectively produces bile necessary for digestion; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There are two openings of the thoracic cavity, a superior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic inlet and a lower inferior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic outlet. The thoracic cavity includes the tendons as well as the cardiovascular system which could be damaged from injury to the back, spine or the neck. Structure Structures within the thoracic cavity include: * structures of the cardiovascular system, including the heart and great vessels, which include the thoracic aorta, the pulmonary artery and all its branches, the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary veins, and the azygos vein * structures of the respiratory system, including the diaphragm, trachea, bronchi and lungs * structures of the digestive system, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rib Cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration ( diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and therefore has a major ventilatory fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleural Cavity
The pleural cavity, or pleural space (or sometimes intrapleural space), is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient. The serous membrane that covers the surface of the lung is the visceral pleura and is separated from the outer membrane, the parietal pleura, by just the film of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity. The visceral pleura follows the fissures of the lung and the root of the lung structures. The parietal pleura is attached to the mediastinum, the upper surface of the diaphragm, and to the inside of the ribcage. Structure In humans, the left and right lungs are completely separated by the mediastinum, and there is no communication between their pleural cavities. Therefore, in cases of a unilateral pneumothorax, the contralateral lung will remain functioning n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhalation
Inhalation (or inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs. Inhalation of air Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions in some disease states) and does not need conscious control or effort. However, breathing can be consciously controlled or interrupted (within limits). Breathing allows oxygen (which humans and a lot of other species need for survival) to enter the lungs, from where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Other substances – accidental Examples of accidental inhalation includes inhalation of water (e.g. in drowning), smoke, food, vomitus and less common foreign substances (e.g. tooth fragments, coins, batteries, small toy parts, needles). Other substances – deliberate Recreational use Nitrous oxide ("laughing gas") has been used recreationally since 1899 for its ability to induce euphoria, hallucinogenic states and relaxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyle's Law
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an empirical gas laws, gas law that describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a confined gas. Boyle's law has been stated as: The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of substance, amount of gas remain unchanged within a closed system.Levine (1978) p. 12 gives the original definition. Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as: or where is the pressure of the gas, is the volume of the gas, and is a Constant (mathematics), constant for a particular temperature and amount of gas. Boyle's law states that when the temperature of a given mass of confined gas is constant, the product of its pressure and volume is also constant. When comparing the same substance under two different sets of conditions, the law can be expressed as: P_1 V_1 = P_2 V_2. showi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |