|
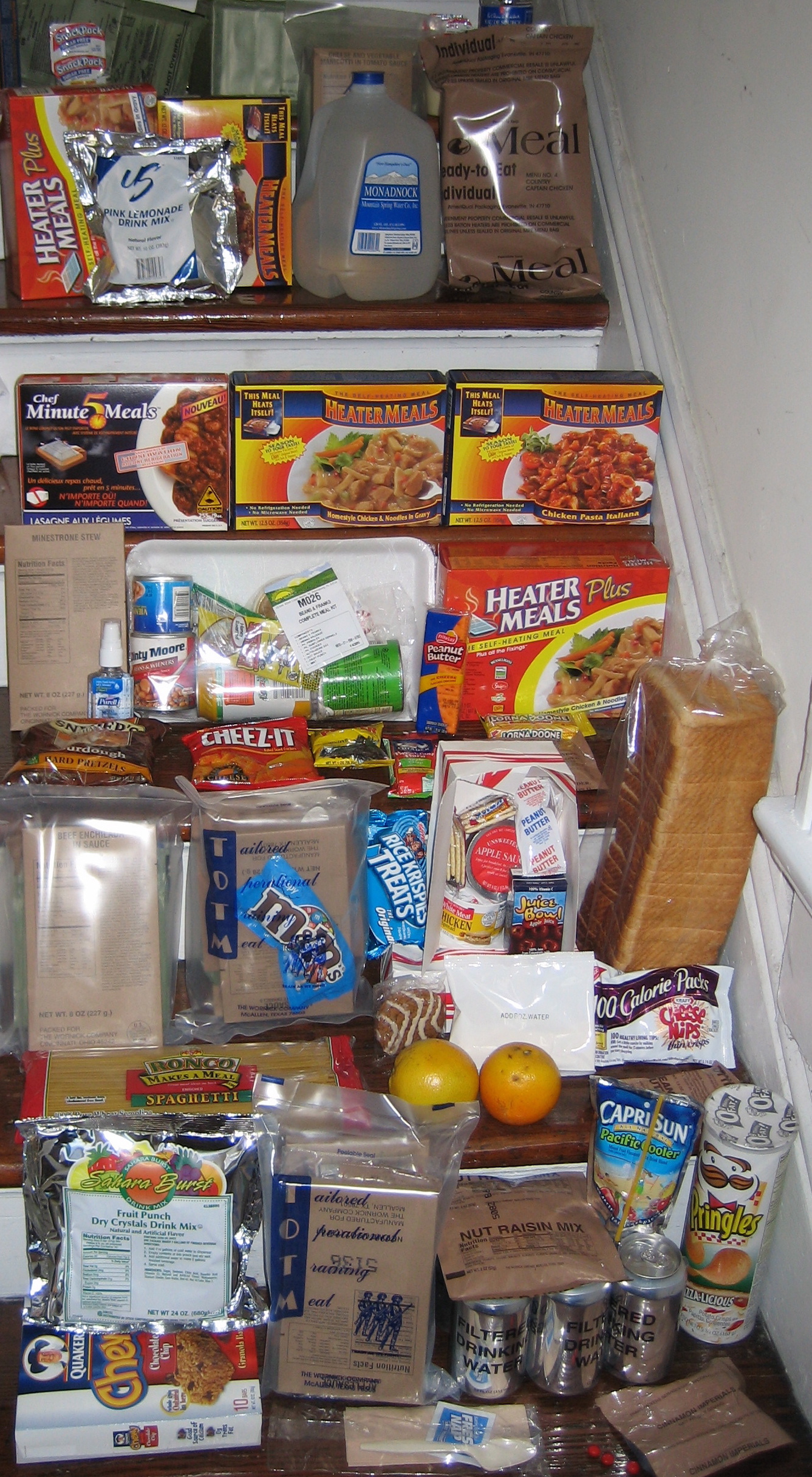
Space Food
Space food is a type of food product created and processed for consumption by astronauts during missions to outer space. Such food has specific requirements to provide a balanced diet and adequate nutrition for individuals working in space while being easy and safe to store, prepare and consume in the machinery-filled weightless environments of crewed spacecraft. Space food is commonly freeze-dried to minimize weight and ensure long shelf life. Before eating, it is rehydrated. Unmodified food such as items of fruit, and even a sandwich, have been brought into space. Packaging varies including tubes, cans, and sealed plastic packages. In recent years, space food has been used by various nations engaging in space programs as a way to share and show off their cultural identity and facilitate intercultural communication. Although astronauts consume a wide variety of foods and beverages in space, the initial idea from The Man in Space Committee of the Space Science Board in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Irradiation
Food irradiation (sometimes American English: radurization; British English: radurisation) is the process of exposing food and food packaging to ionizing radiation, such as from gamma rays, x-rays, or electron beams. Food irradiation improves food safety and extends product shelf life (preservation) by effectively destroying organisms responsible for spoilage and foodborne illness, inhibits sprouting or ripening, and is a means of controlling insects and invasive pests. In the United States, consumer perception of foods treated with irradiation is more negative than those processed by other means. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) have performed studies that confirm irradiation to be safe.World Health Organization. Safety and Nutritional Adequacy of Irradiated Food. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1994 In order for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scone
A scone ( or ) is a traditional British and Irish baked good, popular in the United Kingdom and Ireland. It is usually made of either wheat flour or oatmeal, with baking powder as a leavening agent, and baked on sheet pans. A scone is often slightly sweetened and occasionally Glaze (cooking technique), glazed with egg wash. The scone is a basic component of the cream tea. It differs from teacakes and other types of sweets that are made with Baker's yeast, yeast. Scones were chosen as Republic of Ireland, Ireland's representative for Café Europe during the Austrian presidency of the European Union in 2006, while the United Kingdom chose shortbread. Lexicology The pronunciation of the word within the English-speaking world varies, with some pronouncing it (rhymes with "gone"), and others (rhymes with "tone"). The dominant pronunciation differs by area. Pronunciation rhyming with "tone" is strongest in the English Midlands and Republic of Ireland, Ireland, though it seems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Spoilage
Food spoilage is the process whereby food becomes unsuitable to ingest by a person; it is a matter of food safety. Bacteria and various fungi are the causes of spoilage, and can create serious consequences for consumers, but there are preventive measures that can be taken. The precise cause of the process is due to many outside factors as a side-effect of the type of product it is, as well as how the product is packaged and stored. Food spoilage is the reason for food preservation, to extend shelf life. Processed meat, Meat is processed, Frozen food, food is frozen, and Canning, food is canned. Due to spoilage, one-third of the world's food produced for human consumption is lost every year. Bacteria Some bacteria are responsible for the spoilage of food. When bacteria breaks down the food, acids and other waste products are generated in the process. While the bacteria itself may or may not be harmful, the waste products may be unpleasant to taste or may even be harmful to one's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in Jain literature authored in 6th-century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Microorganisms are extremely diverse, representing most unicellular organisms in all three domains of life: two of the three domains, Archaea and Bacteria, only contain microorganisms. The third domain, Eukaryota, includes all multicellular o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of disease, germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or Transmission (medicine), transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granola Bar
Granola is a food consisting of rolled oats, nuts, seeds, honey or other sweeteners such as brown sugar, and sometimes puffed rice, that is usually baked until crisp, toasted and golden brown. The mixture is stirred while baking to avoid burning and to maintain a loose breakfast cereal consistency. Dried fruit, such as raisins and dates, and confections such as chocolate are sometimes added. Granola is often eaten in combination with yogurt, honey, fresh fruit (such as bananas, strawberries or blueberries), milk or other forms of cereal. It also serves as a topping for various pastries, desserts or ice cream. Muesli is similar to granola, except that it is traditionally neither sweetened nor baked. Granola is sometimes taken when hiking, camping, or backpacking because it is nutritious, lightweight, high in calories, and easy to store (properties that make it similar to trail mix and muesli). Manufacturers also add honey, corn syrup, or maple syrup to it and compress i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cookie
A cookie is a sweet biscuit with high sugar and fat content. Cookie dough is softer than that used for other types of biscuit, and they are cooked longer at lower temperatures. The dough typically contains flour, sugar, egg, and some type of oil or fat. It may include other ingredients such as raisins, oats, chocolate chips, or nuts. Cookie texture varies from crisp and crunchy to soft and chewy, depending on the exact combination of ingredients and methods used to create them. People in the United States and Canada typically refer to all sweet biscuits as "cookies". People in most other English-speaking countries call crunchy cookies "biscuits" but may use the term "cookies" for chewier biscuits and for certain types, such as chocolate-chip cookies. Cookies are often served with beverages such as milk, coffee, or tea and sometimes dunked, which releases more flavour by dissolving the sugars, while also softening their texture. Factory-made cookies are sold in grocery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nut (fruit)
A nut is a fruit consisting of a hard or tough nutshell protecting a kernel which is usually edible. In general usage and in a culinary sense, many dry seeds are called nuts, but in a botanical context, "nut" implies that the shell does not open to release the seed (Dehiscence (botany), indehiscent). Most seeds come from fruits that naturally free themselves from the shell, but this is not the case in nuts such as hazelnuts, chestnuts, and acorns, which have hard shell walls and originate from a compound ovary. Definition A seed is the mature fertilised ovule of a plant; it consists of three parts, the embryo which will develop into a new plant, stored food for the embryo, and a protective seed coat. Botany, Botanically, a nut is a fruit with a woody pericarp developing from a syncarpous gynoecium. Nuts may be contained in an Bract#Involucral bracts, involucre, a cup-shaped structure formed from the flower bracts. The involucre may be scaly, spiny, leafy or tubular, depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shelf-stable Food
Shelf-stable food (sometimes ambient food) is food of a type that can be safely stored at room temperature in a sealed container. This includes foods that would normally be stored refrigerated, but which have been processed so that they can be safely stored at room or ambient temperature for a usefully long shelf life. Various food preservation and packaging techniques are used to extend a food's shelf life. Decreasing the amount of available water in a product, increasing its acidity, or irradiating or otherwise sterilizing the food and then sealing it in an air-tight container are all ways of depriving bacteria of suitable conditions in which to thrive. All of these approaches can extend a food's shelf life, often without unacceptably changing its taste or texture. For some foods, alternative ingredients can be used. Common oils and fats become rancid relatively quickly if not refrigerated; replacing them with hydrogenated oils delays the onset of rancidity, increasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beef Jerky
Jerky is lean trimmed meat strips which are dehydrated to prevent spoilage and seasoned to varying degrees. Normally, this drying includes the addition of salt to prevent microbial growth through osmosis. The word "jerky" derives from the Quechua word ''ch'arki'' which means "dried, salted meat". Modern manufactured jerky is often marinated, prepared with a seasoned spice rub or liquid, or smoked with low heat (usually under ). Store-bought jerky commonly includes sweeteners such as brown sugar. Jerky is ready to eat, needs no additional preparation, and can be stored for months without refrigeration. A proper protein-to-moisture content is required in the final cured product to ensure maximum shelf-life. Many products that are sold as jerky consist of highly processed, chopped, and formed meat rather than traditional sliced whole-muscle meat. These products may contain more fat, but moisture content, as in the whole-muscle product, must meet a 0.75 to 1 moisture-to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |