|
Somnolence
Somnolence (alternatively sleepiness or drowsiness) is a state of strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods (compare hypersomnia). It has distinct meanings and causes. It can refer to the usual state preceding falling asleep, the condition of being in a drowsy state due to circadian rhythm disorders, or a symptom of other health problems. It can be accompanied by lethargy, weakness and lack of mental agility. Somnolence is often viewed as a symptom rather than a disorder by itself. However, the concept of somnolence recurring at certain times for certain reasons constitutes various disorders, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, shift work sleep disorder, and others; and there are medical codes for somnolence as viewed as a disorder. Sleepiness can be dangerous when performing tasks that require constant concentration, such as driving a vehicle. When a person is sufficiently fatigued, microsleeps may be experienced. In individuals deprived of sleep, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hypersomnia
Hypersomnia is a neurological disorder of excessive time spent sleeping or excessive sleepiness. It can have many possible causes (such as seasonal affective disorder) and can cause distress and problems with functioning. In the fifth edition of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-5), hypersomnolence, of which there are several subtypes, appears under sleep-wake disorders. Hypersomnia is a pathological state characterized by a lack of alertness during the waking episodes of the day.American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The international classification of sleep disorders: diagnostic & coding manual (2nd ed). Westchester, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 2005. It is not to be confused with fatigue, which is a normal physiological state. Daytime sleepiness appears most commonly during situations where little interaction is needed. Since hypersomnia impairs patients' attention levels (wakefulness), quality of life may be impacted as well.Morge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself. Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated with medical conditions including autoimmune disease, organ failure, chronic pain conditions, mood disorders, heart disease, infectious diseases, and post-infectious-disease states. However, fatigue is complex and in up to a third of primary care cases no medical or psychiatric diagnosis is found. Fatigue (in the general usage sense of normal tiredness) often follows prolonged physical or mental activity. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of Cognition, cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ability, can manifest as sleepiness, lethargy, or directed attention fatigue, and can also impair physical performance. Definition Fatigue in a medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microsleep
A microsleep is a sudden temporary episode of sleep or drowsiness which may last for a few seconds where an individual fails to respond to some arbitrary sensory input and becomes unconscious.International Classification of Sleep Disorders, , page 343Poudel, G. R., Innes, C. R., Bones, P. J., Watts, R., & Jones, R. D. (2012) Losing the struggle to stay awake: Divergent thalamic and cortical activity during microsleeps. Human Brain Mapping: 00:000-000 Episodes of microsleep occur when an individual loses and regains awareness after a brief lapse in consciousness, often without warning, or when there are sudden shifts between states of wakefulness and sleep. In behavioural terms, microsleeps may manifest as droopy eyes, slow eyelid-closure, and head nodding. In electrical terms, microsleeps are often classified as a shift in electroencephalography (EEG) during which 4–7 Hz (theta wave) activity replaces the waking 8–13 Hz (alpha wave) background rhythm. Definition So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mood Disorder
A mood disorder, also known as an affective disorder, is any of a group of conditions of mental and behavioral disorder where the main underlying characteristic is a disturbance in the person's mood. The classification is in the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Mood disorders fall into seven groups, including; abnormally elevated mood, such as mania or hypomania; depressed mood, of which the best-known and most researched is major depressive disorder (MDD) (alternatively known as clinical depression, unipolar depression, or major depression); and moods which cycle between mania and depression, known as bipolar disorder (BD) (formerly known as manic depression). There are several subtypes of depressive disorders or psychiatric syndromes featuring less severe symptoms such as dysthymic disorder (similar to MDD, but longer lasting and more persistent, though often milder) and cyclothymic disorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range for total calcium is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia. Those with a mild increase that has developed slowly typically have no symptoms. In those with greater levels or rapid onset, symptoms may include abdominal pain, bone pain, confusion, depression, weakness, kidney stones or an abnormal heart rhythm including cardiac arrest. Most outpatient cases are due to primary hyperparathyroidism and inpatient cases due to cancer. Other causes of hypercalcemia include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, Paget disease, multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN), vitamin D toxicity, familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia and certain medications such as lithium and hydrochlorothiazide. Diagnosis should generally include either a corrected calcium or ionized calcium level and be confirmed aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Non-24-hour Sleep–wake Disorder
Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder (non-24, N24SWD, or N24) is one of several chronic circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSDs). It is defined as a "chronic steady pattern comprising ..daily delays in sleep onset and wake times in an individual living in a society". Symptoms result when the non-entrained ( free-running) endogenous circadian rhythm drifts out of alignment with the light–dark cycle in nature. Although this sleep disorder is more common in blind people, affecting up to 70% of the totally blind, it can also affect sighted people. Non-24 may also be comorbid with bipolar disorder, depression, and traumatic brain injury. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) has provided CRSD guidelines since 2007 with the latest update released in 2015. People with non-24 experience daily shifts in the circadian rhythm such as peak time of alertness, body temperature minimum, metabolism and hormone secretion. These shifts do not align with the natural light–dark cycle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brain Tumor
A brain tumor (sometimes referred to as brain cancer) occurs when a group of cells within the Human brain, brain turn cancerous and grow out of control, creating a mass. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign tumor, benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and metastasis, secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with visual perception, vision, vomiting and cognition, mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness. The cause of most brain tumors is unknown, though up to 4% of brain cancers may be caused by CT scan radiation. Uncommo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasionally photophobia. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, and an inability to tolerate loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid hemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease ( sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
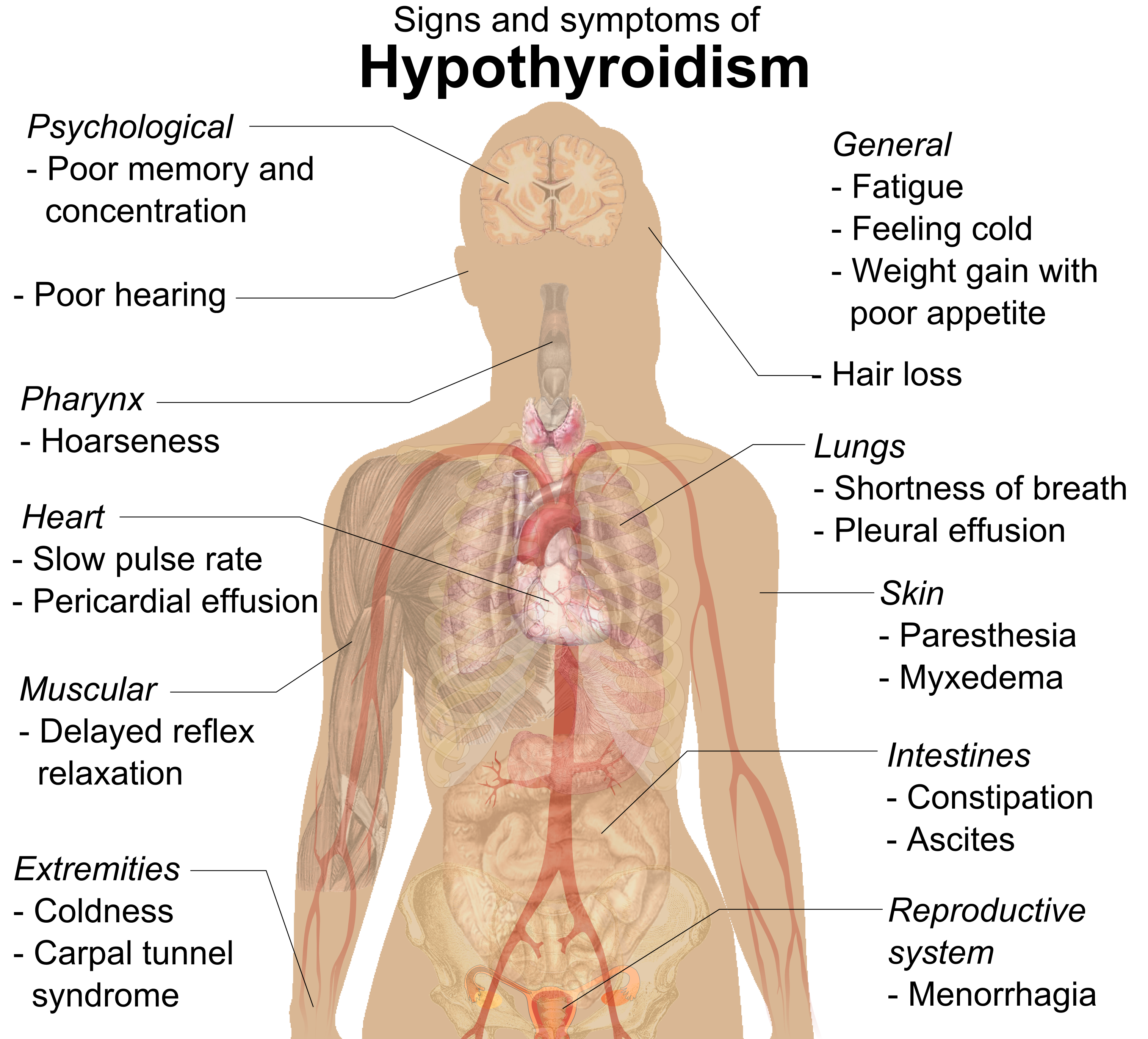
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, Depression (mood), depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in child development, growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, iodine deficiency, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system reacts to the thyroid gland, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with iodine-131, radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the Serum (blood), blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be absent, mild or severe. Mild symptoms include a Altered level of consciousness, decreased ability to think, headaches, nausea, and Balance disorder, poor balance. Severe symptoms include confusion, seizures, and coma; death can ensue. The causes of hyponatremia are typically classified by a person's body fluid status into hypovolemic, low volume, normal volume, or hypervolemic, high volume. Low volume hyponatremia can occur from diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics, and sweating. Normal volume hyponatremia is divided into cases with concentration, dilute urine and concentration, concentrated urine. Cases in which the urine is dilute include adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, and polydipsia, drinking too much water or potomania, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hypermagnesemia
Hypermagnesemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a high level of magnesium in the blood. Symptoms include weakness, confusion, decreased breathing rate, and decreased reflexes. Hypermagnesemia can greatly increase the chances of adverse cardiovascular events. Complications may include low blood pressure and cardiac arrest. It is typically caused by kidney failure or is treatment-induced such as from antacids or supplements that contain magnesium. Less common causes include tumor lysis syndrome, seizures, and prolonged ischemia. Diagnosis is based on a blood level of magnesium greater than 1.1 mmol/L (2.6 mg/dL). It is severe if levels are greater than 2.9 mmol/L (7 mg/dL). Specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes may be present. Treatment involves stopping the magnesium a person is getting. Treatment when levels are very high include calcium chloride, intravenous normal saline with furosemide, and hemodialysis. Hypermagnesemia is uncommon. Rates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |