|
Software Metrics
In software engineering and Software development, development, a software metric is a standard of measure of a degree to which a software system or process possesses some property. Even if a metric is not a measurement (metrics are functions, while measurements are the numbers obtained by the application of metrics), often the two terms are used as synonyms. Since Quantitative research, quantitative measurements are essential in all sciences, there is a continuous effort by computer science practitioners and theoreticians to bring similar approaches to software development. The goal is obtaining objective, reproducible and quantifiable measurements, which may have numerous valuable applications in schedule and budget planning, cost estimation, quality assurance, testing, software debugging, software Program optimization, performance optimization, and optimal personnel task assignments. Common software measurements Common software measurements include: * ABC Software Metric * Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principles and computer programming expertise to develop software systems that meet user needs. The terms ''programmer'' and ''coder'' overlap ''software engineer'', but they imply only the construction aspect of a typical software engineer workload. A software engineer applies a software development process, which involves defining, Implementation, implementing, Software testing, testing, Project management, managing, and Software maintenance, maintaining software systems, as well as developing the software development process itself. History Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was recognized as a separate field of engineering. The development of software engineering was seen as a struggle. Problems included software that was over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function Point
The function point is a "unit of measurement" to express the amount of business functionality an information system (as a product) provides to a user. Function points are used to compute a functional size measurement (FSM) of software. The cost (in dollars or hours) of a single unit is calculated from past projects. Standards There are several recognized standards and/or public specifications for sizing software based on Function Point. 1. ISO Standards * FiSMA: ISO/IEC 29881:2010 Information technology – Systems and software engineering – FiSMA 1.1 functional size measurement method. * IFPUG: ISO/IEC 20926:2009 Software and systems engineering – Software measurement – IFPUG functional size measurement method. * Mark-II: ISO/IEC 20968:2002 Software engineering – Ml II Function Point Analysis – Counting Practices Manual * Nesma: ISO/IEC 24570:2018 Software engineering – Nesma functional size measurement method version 2.3 – Definitions and counting guidelines for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Sizing
Software sizing or software size estimation is an activity in software engineering that is used to determine or estimate the size of a software application or component in order to be able to implement other software project management activities (such as estimating or tracking). Size is an inherent characteristic of a piece of software just like weight is an inherent characteristic of a tangible material. Background Software sizing is different from software effort estimation. Sizing estimates the probable size of a piece of software while effort estimation predicts the effort needed to build it. The relationship between the size of software and the effort required to produce it is called productivity. For example, if a software engineer has built a small web-based calculator application, we can say that the project effort was 280 man-hours. However, this does not give any information about the size of the ''software product'' itself. Conversely, we can say that the application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schedule (project Management)
In project management, a schedule is a listing of a project's milestones, activities, and deliverables. Usually dependencies and resources are defined for each task, then start and finish dates are estimated from the resource allocation, budget, task duration, and scheduled events. A schedule is commonly used in the project planning and project portfolio management parts of project management. Elements on a schedule may be closely related to the work breakdown structure (WBS) terminal elements, the Statement of work, or a Contract Data Requirements List. Overview In many industries, such as engineering and construction, the development and maintenance of the project schedule is the responsibility of a full-time scheduler or team of schedulers, depending on the size and the scope of the project. The techniques of scheduling are well developed but inconsistently applied throughout industry. Standardization and promotion of scheduling best practices are being pursued by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Pass Yield
First-pass yield (FPY), also known as throughput yield (TPY), is defined as the number of units coming out of a process divided by the number of units going into that process over a specified period of time. Example Consider the following: You have a process that is divided into four sub-processes: A, B, C and D. Assume that you have 100 units entering process A. To calculate first time yield (FTY) you would: #Calculate the yield (number out of step/number into step) of each step. #Multiply these together. For example: (# units leaving the process as good parts) / (# units put into the process) = FTY *100 units enter A and 90 leave as good parts. The FTY for process A is 90/100 = 0.9000 *90 units go into B and 80 leave as good parts. The FTY for process B is 80/90 = 0.8889 *80 units go into C and 75 leave as good parts. The FTY for C is 75/80 = 0.9375 *75 units go into D and 70 leave as good parts. The FTY for D is 70/75 = 0.9333 The total first time yield is equal to FTYofA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycle Time (software)
In software engineering, cycle time is a software metric which estimates development speed in ( agile) software projects. The cycle time measures how long it takes to process a given job - whether it's a client request, an order, or a defined production process stage. The crucial aspect of measuring the cycle time is considering only the active, operating processing time and discarding any idle, waiting, or service times occurring mid-process. According to the PMBOK (7th edition) by the Project Management Institute (PMI), cycle time is the "total elapsed time from the start of a particular activity or work item to its completion." In contrast to lead time, which measures the time that the customer waits for their request to be realized, cycle time only counts the time the team spends actively working on the request. The core use of cycle times is to identify the average development times for specific teams or given request types. This lets the software engineering manager predic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted Micro Function Points
Weighted Micro Function Points (WMFP) is a modern software sizing algorithm which is a successor to solid ancestor scientific methods as COCOMO, COSYSMO, maintainability index, cyclomatic complexity, function points, and Halstead complexity. It produces more accurate results than traditional software sizing methodologies, while requiring less configuration and knowledge from the end user, as most of the estimation is based on automatic measurements of an existing source code. As many ancestor measurement methods use source lines of code (SLOC) to measure software size, WMFP uses a parser to understand the source code breaking it down into micro functions and derive several code complexity and volume metrics, which are then dynamically interpolated into a final effort score. In addition to compatibility with the waterfall software development life cycle methodology, WMFP is also compatible with newer methodologies, such as Six Sigma, Boehm spiral, and Agile (AUP/Lean/XP/DSDM) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary File
A binary file is a computer file that is not a text file. The term "binary file" is often used as a term meaning "non-text file". Many binary file formats contain parts that can be interpreted as text; for example, some computer document files containing formatted text, such as older Microsoft Word document files, contain the text of the document but also contain formatting information in binary form. Background and terminology All modern computers store information in the form of bits (binary digits), using binary code. For this reason, all data stored on a computer is, in some sense, "binary". However, one particularly useful and ubiquitous type of data stored on a computer is one in which the bits represent text, by way of a character encoding. Those files are called " text files" and files which are not like that are referred to as "binary files", as a sort of retronym or hypernym. Some "text files" contain portions that are actually binary data, and many "binary fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loader (computing)
In computing, computer systems a loader is the part of an operating system that is responsible for loading computer program, programs and Library (computing), libraries. It is one of the essential stages in the process of starting a program, as it places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. Loading a program involves either memory-mapped file, memory-mapping or copying the contents of the executable, executable file containing the program instructions into memory, and then carrying out other required preparatory tasks to prepare the executable for running. Once loading is complete, the operating system starts the program by passing control to the loaded program code. All operating systems that support program loading have loaders, apart from highly specialized computer systems that only have a fixed set of specialized programs. Embedded systems typically do not have loaders, and instead, the code executes directly from ROM or similar. In order to load the operatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
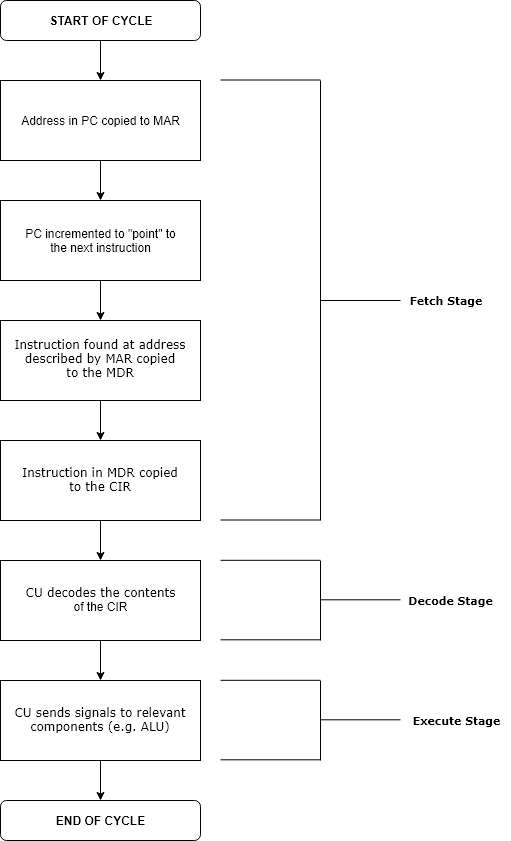
Run Time (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Lines Of Code
Source lines of code (SLOC), also known as lines of code (LOC), is a software metric used to measure the size of a computer program by counting the number of lines in the text of the program's source code. SLOC is typically used to predict the amount of effort that will be required to develop a program, as well as to estimate programming productivity or maintainability once the software is produced. Measurement methods Multiple useful comparisons involve only the order of magnitude of lines of code in a project. Using lines of code to compare a 10,000-line project to a 100,000-line project is far more useful than when comparing a 20,000-line project with a 21,000-line project. While it is debatable exactly how to measure lines of code, discrepancies of an order of magnitude can be clear indicators of software complexity or man-hours. There are two major types of SLOC measures: physical SLOC (LOC) and logical SLOC (LLOC). Specific definitions of these two measures vary, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maintainability
Maintainability is the ease of maintaining or providing maintenance for a functioning product or service. Depending on the field, it can have slightly different meanings. Usage in different fields Engineering In engineering, maintainability is the ease with which a product can be maintained to: * correct defects or their cause, * Repair or replace faulty or worn-out components without having to replace still working parts, * prevent unexpected working conditions, * maximize a product's useful life, * maximize efficiency, reliability, and safety, * meet new requirements, * make future maintenance easier, or * cope with a changing environment. In some cases, maintainability involves a system of continuous improvement - learning from the past to improve the ability to maintain systems, or improve the reliability of systems based on maintenance experience. Telecommunication In telecommunications and several other engineering fields, the term maintainability has the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |