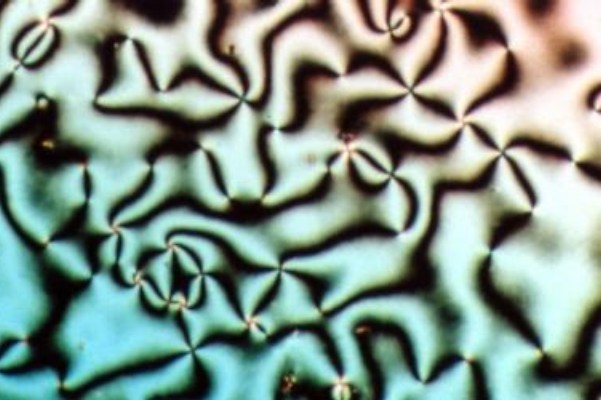
|
Smectic
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: *thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermotropic
A liquid crystal phase is thermotropic if its order parameter is determined by temperature. At high temperatures, liquid crystals become an isotropic liquid and at low temperatures, they tend to glassify. In a thermotropic crystal, those phase transitions occur only at temperature extremes; the phase is insensitive to concentration. Most thermotropic liquid crystals are composed of rod-like molecules, and admit nematic, smectic, or cholesterolic phases. References * See also * Thermochromism Thermochromism is the property of substances to change color due to a change in temperature. A mood ring is an excellent example of this phenomenon, but thermochromism also has more practical uses, such as baby bottles which change to a differen ... * Thermotropic liquid crystals External links What are Liquid Crystals? Liquid crystals {{chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyotropic
A liquid crystalline mesophase is called lyotropic (a portmanteau of lyo- "dissolve" and -tropic "change" ) if formed by dissolving an amphiphilic mesogen in a suitable solvent, under appropriate conditions of concentration, temperature and pressure. A mixture of soap and water is an everyday example of a lyotropic liquid crystal. Historically, the term was used to describe the common behavior of materials composed of amphiphilic molecules upon the addition of a solvent. Such molecules comprise a water-loving hydrophilic head-group (which may be ionic or non-ionic) attached to a water-hating, hydrophobic group. The micro-phase segregation of two incompatible components on a nanometer scale results in different type of solvent-induced extended anisotropic arrangement, depending on the volume balances between the hydrophilic part and hydrophobic part. In turn, they generate the long-range order of the phases, with the solvent molecules filling the space around the compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid-crystal Display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images (as in a general-purpose computer display) or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden. For instance: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clays
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privatdozent
''Privatdozent'' (for men) or ''Privatdozentin'' (for women), abbreviated PD, P.D. or Priv.-Doz., is an academic title conferred at some European universities, especially in German-speaking countries, to someone who holds certain formal qualifications that denote an ability (''facultas docendi'') and permission to teach ('' venia legendi'') a designated subject at the highest level. To be granted the title Priv.-Doz. by a university, a recipient has to fulfill the criteria set by the university which usually require excellence in research, teaching, and further education. In its current usage, the title indicates that the holder has completed their habilitation and is therefore granted permission to teach and examine students independently without having a professorship. Conferment and roles A university faculty can confer the title to an academic who has a higher doctoral degree - usually in the form of a habilitation. The title, ''Privatdozent'', as such does not imply a sala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Lehmann (physicist) Otto Lehmann (13 January 1855 in Konstanz, Germany – 17 June 1922 in Karlsruhe) was a German physicist and "father" of liquid crystal. Life Otto was the son of Franz Xavier Lehmann, a mathematics teacher in the Baden-Wurtemberg school system, with a strong interest in microscopes. Otto learned to experiment and keep records of this findings. Between 1872 and 1877, Lehmann studied natural sciences at the University of Strassburg and obtained the Ph.D. under crystallographer Paul Groth. Otto used polarizers in a microscope so that he might watch f |