|
Shields
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry like spears or long ranged projectiles such as arrows. They function as means of active blocks, as well as to provide passive protection by closing one or more lines of engagement during combat. Shields vary greatly in size and shape, ranging from large panels that protect the user's whole body to small models (such as the buckler) that were intended for hand-to-hand-combat use. Shields also vary a great deal in thickness; whereas some shields were made of relatively deep, absorbent, wooden planking to protect soldiers from the impact of spears and crossbow bolts, others were thinner and lighter and designed mainly for deflecting blade strikes (like the roromaraugi or qauata). Finally, shields vary greatly in shape, ranging in roundness to angularity, proportional length and wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
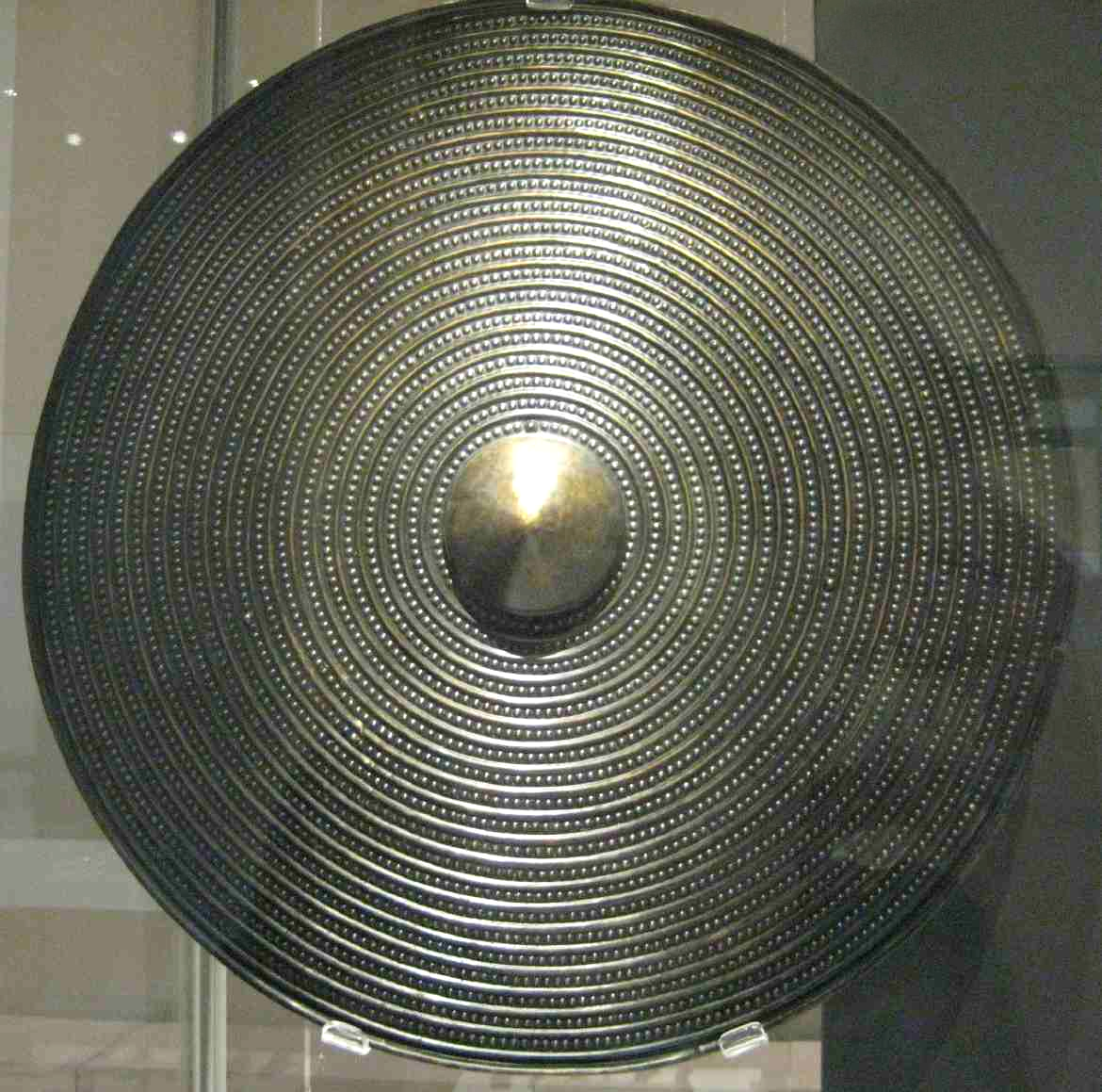
Yetholm-type Shields
The Yetholm-type shield is a distinctive type of shield dating from 1300-800 BC (Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age). The known shields come from Britain and Ireland, excepting one from Denmark. Their modern name comes from Yetholm in southern Scotland where a peat bog yielded three examples. Twenty-two examples are known, although some of these are fragmentary, and a further seven or eight are known from written sources but are lost today. The shields vary significantly in size, but are otherwise similar. Rock carvings from this period made in Southern Scandinavia include depictions of shields decorated with concentric rings or rings of dots. The artist could not hope to show the fine detail of a Yetholm-type shield, but the similarity is striking. The impressive shields would have indicated high social status. Construction The shields are made of a copper alloy sheet about 0.6 mm thick. The alloy is a high-tin bronze: copper with 11-14% tin. They are round with a central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraldic
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known branch of heraldry, concerns the design and transmission of the heraldic achievement. The achievement, or armorial bearings usually includes a coat of arms on a shield, helmet and crest, together with any accompanying devices, such as supporters, badges, heraldic banners and mottoes. Although the use of various devices to signify individuals and groups goes back to antiquity, both the form and use of such devices varied widely, as the concept of regular, hereditary designs, constituting the distinguishing feature of heraldry, did not develop until the High Middle Ages. It is often claimed that the use of helmets with face guards during this period made it difficult to recognize one's commanders in the field when large armies gathered toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
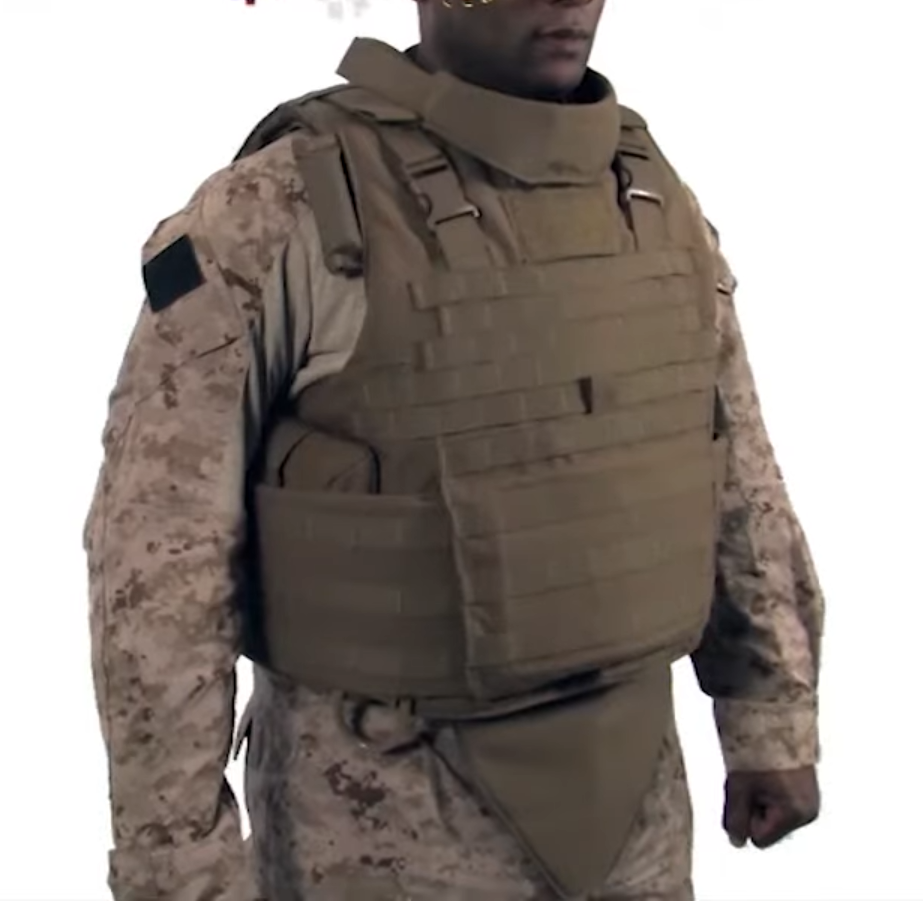
Personal Armour
Body armour, personal armour (also spelled ''armor''), armoured suit (''armored'') or coat of armour, among others, is armour for a person's body: protective clothing or close-fitting hands-free shields designed to absorb or deflect physical attacks. Historically used to protect military personnel, today it is also used by various types of police (riot police in particular), private security guards, or bodyguards, and occasionally ordinary citizens. Today there are two main types: regular non-plated body armor for moderate to substantial protection, and hard-plate reinforced body armor for maximum protection, such as used by combatants. History Many factors have affected the development of personal armor throughout human history. Significant factors in the development of armor include the economic and technological necessities of armor production. For instance full plate armor first appeared in medieval Europe when water-powered trip hammers made the formation of plates fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qauata
A qauata or qauaata is a parrying shield or war club of the San Cristobal Island in the Solomon Islands. Uses It was used to deflect the enemy’s arrows and spears. It has a leaf-shaped head without an ergot, which distinguishes it from the roromaraugi A roromaraugi is a parrying shield from Makira, San Cristobal Island in the Solomon Islands. Uses It was used to deflect the enemy’s arrows and spears. It has a broad sickle-shaped head that is separated by a well-marked central ridge with a .... The head is separated in two by a central ridge and the handle is often finished by an anthropomorphic sculpture. It is more common than the roromaraugi and was used for war.''Acta Ethnographica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae'', 1977, p.146 References Bibliography * Purissima Benitez, Jean-Paul Barbier, Alain-Michel Boyer, ''Boucliers d’Afrique, d’Asie du Sud-Est et d’Océanie'', Paris, Éditions Adam Biro, 1998. Clubs (weapon) Ritual weapons Shields Culture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roromaraugi
A roromaraugi is a parrying shield from Makira, San Cristobal Island in the Solomon Islands. Uses It was used to deflect the enemy’s arrows and spears. It has a broad sickle-shaped head that is separated by a well-marked central ridge with a spur on the back. The handle is often finished by an anthropomorphic sculpture and the whole is done in very hard wood. It was also used in war dances and measures more or less . It should not be confused with the ''qauata'' which does not have a spur and looks more like a leaf.Deborah Waite, ''Art of the Solomon Islands : The Conru Collection'', 2008, p.113 References Bibliography * Purissima Benitez, Jean-Paul Barbier, Alain-Michel Boyer, ''Boucliers d’Afrique, d’Asie du Sud-Est et d’Océanie'', Paris, Éditions Adam Biro, 1998. Clubs (weapon) Ritual weapons Shields Culture of the Solomon Islands {{Shield-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention. Key historical trends of the High Middle Ages include the medieval demography, rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, and the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1350, the robust population increase had greatly benefited the European economy, which had reached levels that would not be seen again in some areas until the 19th century. That trend faltered in the early 14th century, as the result of numerous events which together comprised the crisis of the late Middle Ages—most notable among them being the Black Death, in addition to various regional wars and economic stagnation. From , Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highland
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain ranges dominating the region, and includes the highest mountain in the British Isles, Ben Nevis. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the population of the Highlands rose to around 300,000, but from c. 1841 and for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
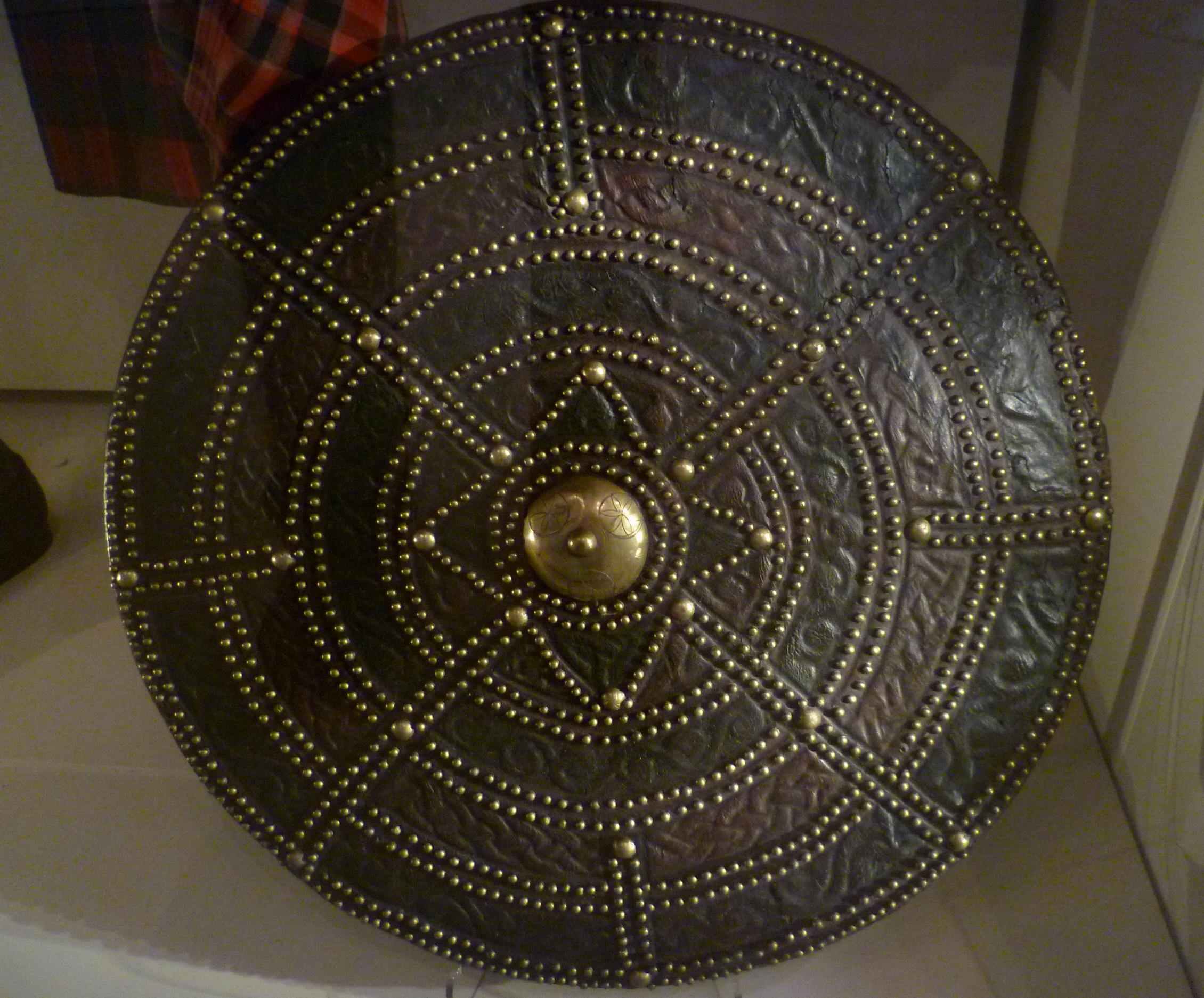
Targe
The targe is a type of strapped round shield that was used by Scottish Highlanders in the early modern period. From the late 16th century, until the Battle of Culloden in 1746, the Scottish Highlander's main means of defence in battle was his targe. In February 1596, the clan leader John Grant of Freuchie was able to muster 500 men, including 40 armed "according to the Highland custom" with bows, helmets, swords, and targes. After the disastrous defeat of the Jacobites at Culloden, the carrying of the targe had been banned by the Disarming Act, and many were destroyed or put to other uses. Those that remain have intricate patterns and are decorated, indicating that they would have originally belonged to important people. The targe is a concave shield fitted with enarmes on the inside, one adjustable by a buckle, to be attached to the forearm, and the other fixed as a grip for the left hand. Etymology ''Targe'' (, ) was a general word for a shield in late Old English. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom ( ; ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following which ruled a wide expanse of Southern Africa that extended along the coast of the Indian Ocean from the Tugela River in the south to the Pongola River in the north. A bitter civil war in the mid-19th century erupted which culminated in the 1856 Battle of Ndondakusuka between the brothers Cetshwayo and Mbuyazi. In 1879, a British force invaded Zululand, beginning the Anglo-Zulu War. After an initial Zulu victory at the Battle of Isandlwana in January, the British regrouped and defeated the Zulus in July during the Battle of Ulundi, ending the war. The area was absorbed into the Colony of Natal and later became part of the Union of South Africa. The current Zulu king is Misuzulu Sinqobile, who serves as the monarch of South Africa's KwaZulu-Natal province. States a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindanao Bangsamoro & Lumad Shields & Knives
Mindanao ( ) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao had a population of 26,252,442, while the entire island group had an estimated population of 27,021,036. Mindanao is divided into six administrative regions: the Zamboanga Peninsula, Northern Mindanao, the Caraga region, the Davao region, Soccsksargen, and the autonomous region of Bangsamoro. According to the 2020 census, Davao City is the most populous city on the island, with 1,776,949 people, followed by Zamboanga City (pop. 977,234), Cagayan de Oro (pop. 728,402), General Santos (pop. 697,315), Butuan (pop. 372,910), Iligan (pop. 363,115) and Cotabato City (pop. 325,079). About 70% of residents identify as Christian and 24% as Muslim. Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Uncivilized Races Of Men In All Countries Of The World; Being A Comprehensive Account Of Their Manners And Customs, And Of Their Physical, Social, Mental, Moral And Religious Characteristics
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun '' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |