|
Shallow Frying
Shallow frying is a hot oil-based cooking technique. Pieces of food are cooked by partial submersion in hot oil. It is typically used to prepare portion-sized cuts of meat, fish, potatoes and patties such as fritters. Shallow frying can also be used to cook vegetables. Shallow frying is distinct from deep frying, which uses enough oil to fully submerge the food to be cooked, and pan frying, which only uses a negligible depth of oil. Technique It is a medium-high to high heat cooking process. Temperatures between are typical, but shallow frying may be performed at temperatures as low as for a longer period of time. The high heat promotes protein denaturation- browning and, in some cases, a Maillard reaction. Deep frying usually takes place at temperatures between so shallow-frying can oftentimes be considered a less intense cooking technique. Foods to be shallow fried are commonly pre-portioned into single servings before being placed in oil. Since the food is only partly s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shallow-frying Tofu Triangles
Shallow frying is a hot oil-based cooking technique. Pieces of food are cooked by partial submersion in hot oil. It is typically used to prepare portion-sized cuts of meat, fish, potatoes and patties such as fritters. Shallow frying can also be used to cook vegetables. Shallow frying is distinct from deep frying, which uses enough oil to fully submerge the food to be cooked, and pan frying, which only uses a negligible depth of oil. Technique It is a medium-high to high heat cooking process. Temperatures between are typical, but shallow frying may be performed at temperatures as low as for a longer period of time. The high heat promotes protein denaturation- browning and, in some cases, a Maillard reaction. Deep frying usually takes place at temperatures between so shallow-frying can oftentimes be considered a less intense cooking technique. Foods to be shallow fried are commonly pre-portioned into single servings before being placed in oil. Since the food is only partly su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crispiness
Crispiness or crispness is one of the most common food texture attributes. Crispiness refers to a hard food that emits a sound upon fracturing. Foods described as crisp tend not to show signs of deformation prior to fracture. Crispiness and crunchiness are often used interchangeably, however crispiness tends to be associated with a higher pitched sound, while crunchiness is associated with lower pitched sounds; however, this type of level of heating in cooking generally has a soft tender inside left after heating. Cooking techniques for crispiness There are a number of techniques to achieve crispiness when cooking. Frying food can make it crispy, such as seen in french fries. A breading coating using flour, egg wash, and bread crumbs will provide a layer of crispiness.{{cite book, author=Editors, America's Test Kitchen , title=The Science of Good Cooking, publisher=America's Test Kitchen, 2012 , page=152f , isbn=978-1-933615-98-1, year=2012 Baking and roasting impart cris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidulated Water
Acidulated water is water where some sort of acid is added—often lemon juice, lime juice, or vinegar—to prevent cut or skinned fruits or vegetables from browning so as to maintain their appearance. Some vegetables and fruits often placed in acidulated water are apples, avocados, celeriac, potatoes and pears. When the fruit or vegetable is removed from the mixture, it will usually resist browning for at least an hour or two, even though it is being exposed to oxygen Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non .... An added benefit of placing items in acidulated water is that the food item acquires a taste of the acid used, which can be very pleasant on the palate. Acidulated water, most often made with the use of vinegar, can be used on an aged, hanging beef carcass (butchere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distilled Water
Distilled water is water that has been purified by boiling it into vapor then condensing it back into liquid in a separate container. Impurities in the original water that do not boil below or near the boiling point of water remain in the original container. History Drinking water has been distilled from seawater since at least about AD 200, when the process was clearly described by Alexander of Aphrodisias. Its history predates this, as a passage in Aristotle's '' Meteorologica'' refers to the distillation of water. Captain Israel Williams of the ''Friendship'' (1797) improvised a way to distill water, which he described in his journal. Applications In chemical and biological laboratories, as well as in industry, in some appliances, deionized water or reverse osmosis water can be used instead of distilled water as a cheaper alternative. If exceptionally high-purity water is required, double distilled water is used. In general, non-purified water could cause or interfere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee On Food Additives
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) is an international scientific expert committee that is administered jointly by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO). It has been meeting since 1956 to provide independent scientific advice pertaining to the safety evaluation of food additives. Its current scope of work now also includes the evaluation of contaminants, naturally occurring toxicants and residues of veterinary drugs in food. The role of JECFA As the FAO/WTO publication describes, global food safety can be difficult to ensure without international reference standards. While all countries require access to reliable risk assessments of the various chemicals in our food, not all have the resources or the funds available to conduct such evaluations for a large number of substances. Through expert-driven risk assessments JECFA defines the safe exposure levels to chemicals found in food. JECFA p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylamide
Acrylamide (or acrylic amide) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH2=CHC(O)NH2. It is a white odorless solid, soluble in water and several organic solvents. From the chemistry perspective, acrylamide is a vinyl-substituted primary amide (CONH2). It is produced industrially mainly as a precursor to polyacrylamides, which find many uses as water-soluble thickeners and flocculation agents. Acrylamide forms in burnt areas of food, particularly starchy foods like potatoes, when cooked with high heat, above . Despite health scares following this discovery in 2002, and its classification as a probable carcinogen, acrylamide from diet is thought unlikely to cause cancer in humans; Cancer Research UK categorized the idea that eating burnt food causes cancer as a "myth". Production Acrylamide can be prepared by the hydration of acrylonitrile, which is catalyzed enzymatically: :CH2=CHCN + H2O → CH2=CHC(O)NH2 This reaction also is catalyzed by sulfuric acid as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weight Management
Weight management comprises behaviors, techniques, and Physiology, physiological processes that contribute to a person's ability to attain and maintain a healthy Human body weight, weight. Most weight management techniques encompass long-term lifestyle strategies that promote Healthy diet, healthy eating and daily physical activity. Weight management generally includes tracking weight over time and identifying an individual's ideal body weight. Weight management strategies most often focus on achieving healthy weights through slow but steady weight loss, followed by maintenance of an ideal body weight. However, weight neutral approaches to health have also been shown to result in positive health outcomes. Understanding the basic science of weight management and strategies for attaining and maintaining a healthy weight is important because obesity is a risk factor for development of many chronic diseases, like Type 2 diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Key factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Running Press
Running Press is an American publishing company and member of the Perseus Books Group, a division of the Hachette Book Group. The publisher's offices are located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, with many of the corporate functions taking place in Hachette's New York City headquarters. It was co-founded by Stuart "Buz" Teacher and his brother, Lawrence "Larry" Teacher, who died in March 2014. Black Dog & Leventhal Publishers became an imprint of Running Press in 2017. Select bibliography * Running Press Miniature Editions, 2" by 3" hardcover books (many of them abridgements of bestsellers and often sold as impulse or gift purchases at checkout counters) * ''Sneaky Chef'' cookbook series by Missy Chase Lapine * ''Images'' coloring book series, by Roger Burrows * '' Wisdom to Grow On'', Charles J. Acquisto (2006) * '' The Mammoth Book of Best New Manga'', ILYA (2006) * '' Cathy's Book'', Sean Stewart and Jordan Weisman (2006) * '' The Way of the Wiseguy'', Joseph D. Pistone (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooking Oils
Cooking oil (also known as edible oil) is a plant or animal liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. Oil allows higher cooking temperatures than water, making cooking faster and more flavorful, while likewise distributing heat, reducing burning and uneven cooking. It sometimes imparts its own flavor. Cooking oil is also used in food preparation and flavoring not involving heat, such as salad dressings and bread dips. Cooking oil is typically a liquid at room temperature, although some oils that contain saturated fat, such as coconut oil, palm oil and palm kernel oil are solid. There are a wide variety of cooking oils from plant sources such as olive oil, palm oil, soybean oil, canola oil (rapeseed oil), corn oil, peanut oil, sesame oil, sunflower oil and other vegetable oils, as well as animal-based oils like butter and lard. Oil can be flavored with aromatic foodstuffs such as herbs, chilies or garlic. Cooking spray is an aerosol of cooking oil. Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive Oil
Olive oil is a vegetable oil obtained by pressing whole olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea'', a traditional Tree fruit, tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin) and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking for frying foods, as a condiment, or as a salad dressing. It can also be found in some cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, soaps, and fuels for traditional oil lamps. It also has additional uses in some religions. The olive is one of three core food plants in Mediterranean cuisine, with wheat and grapes. Olive trees have been cultivated around the Mediterranean since the 8th millennium BC. In 2022, Spain was the world's largest producer, manufacturing 24% of the world's total. Other large producers were Italy, Greece, and Turkey, collectively accounting for 59% of the global market. The composition of olive oil varies with the cultivar, altitude, time of harvest, and extraction process. It consists mainly of oleic acid (up to 83%), with smaller amounts of other fatty acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
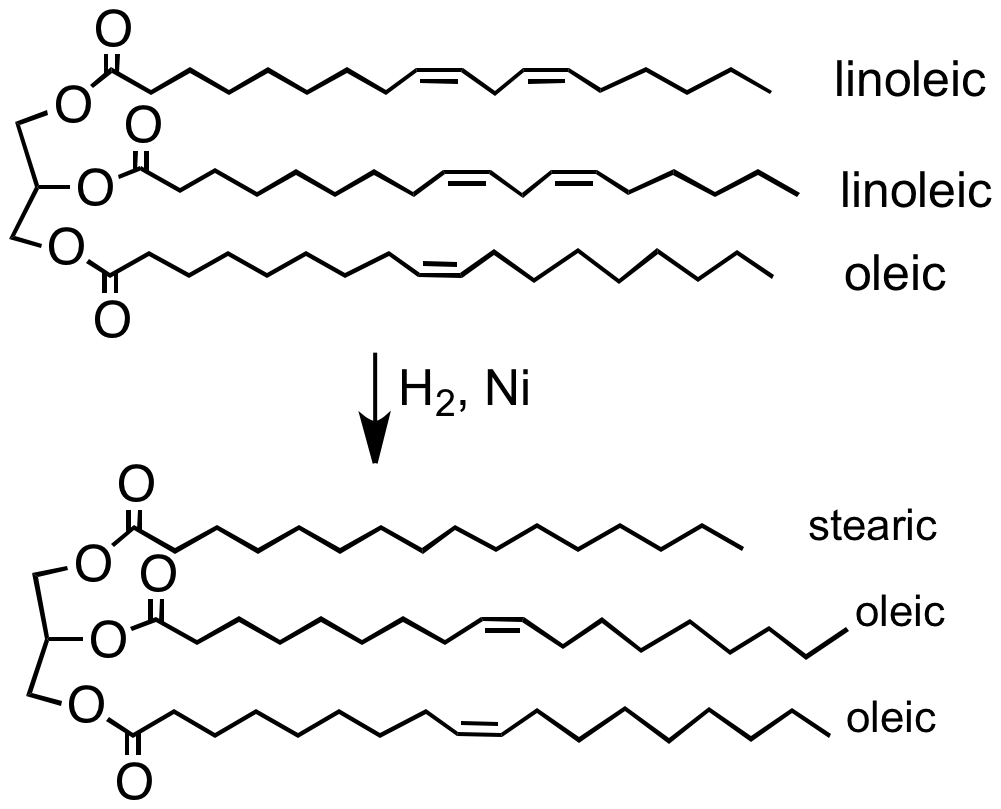
Margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a Spread (food), spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The spread was originally named ''oleomargarine'' from Latin for ''oleum'' (olive oil) and Greek language, Greek ''margarite'' ("pearl", indicating luster). The name was later shortened to ''margarine'', or sometimes ''oleo'' (particularly in the Deep South). Margarine consists of a water-in-fat emulsion, with tiny droplets of water dispersed uniformly throughout a fat phase (chemistry), phase in a stable solid form. While butter is made by concentrating the butterfat of milk through centrifugation, modern margarine is made through a more intensive processing of refined vegetable oil and water. Per US federal regulation, products must have a minimum fat content of 80% (with a maximum of 16% water) to be labeled as such in the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |