|
Service Bureau
A service bureau is a company that provides business services for a fee. The term has been extensively used to describe technology-based services to financial services companies, particularly banks. Service bureaus are a significant sector within the growing 3D printing industry that allow customers to make a decision whether to buy their own equipment or outsource production. Customers of service bureaus typically do not have the scale or expertise to incorporate these services into their internal operations and prefer to outsource them to a service bureau. Outsourced payroll services constitute a commonly provisioned service from a service bureau. The business model question One writer described the ideal service bureau customer as only needing vanilla: very little customization per customer. The phrasing is catering "to the bell curve of customer requirements." If strawberry banana is needed, it is important to ask: :Did they develop their own platform or license or purchase it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Service (economics)
A service is an act or use for which a consumer, company, or government is willing to payment, pay. Examples include work done by barbers, doctors, lawyers, mechanics, banks, insurance companies, and so on. Public services are those that society (nation state, fiscal union or region) as a whole pays for. Using resources, skill, ingenuity, and experience, service providers benefit service consumers. Services may be defined as intangible acts or performances whereby the service provider provides value to the customer. Key characteristics Services have three key characteristics: Intangibility Services are by definition intangible. They are not manufactured, transported or stocked. One cannot store services for future use. They are produced and consumed simultaneously. Perishability Services are perishable in two regards: * Service-relevant resources, processes, and systems are assigned for service delivery during a specific period in time. If the service consumer does not request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xerox 9700
The Xerox 9700 Electronic Printing System was a high-end laser printer manufactured by Xerox Corporation beginning in 1977. Based on the Xerox 9200 copier, the 9700 printed at 300 dots-per-inch on cut-sheet paper at up to two pages per second (pps), one- or two-sided, that is simplex or duplex, landscape or portrait. Development Development of the laser printing technology behind the Xerox 9700 began in the late 1960s and was led by Gary Starkweather, with Butler Lampson and Ron Rider. It was the successor product to the Xerox 1200 Computer Printing System. Description The 9700 was intended for high-volume applications. It included a disk drive and a modified Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) PDP-11/34 as a print controller and rasterizer. It could connect to an IBM mainframe via a parallel channel. It offered an input tray that could hold up to 2500 sheets of paper (20lb bond/75gsm) and an auxiliary input tray for an additional 400 sheets. It had two output stack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
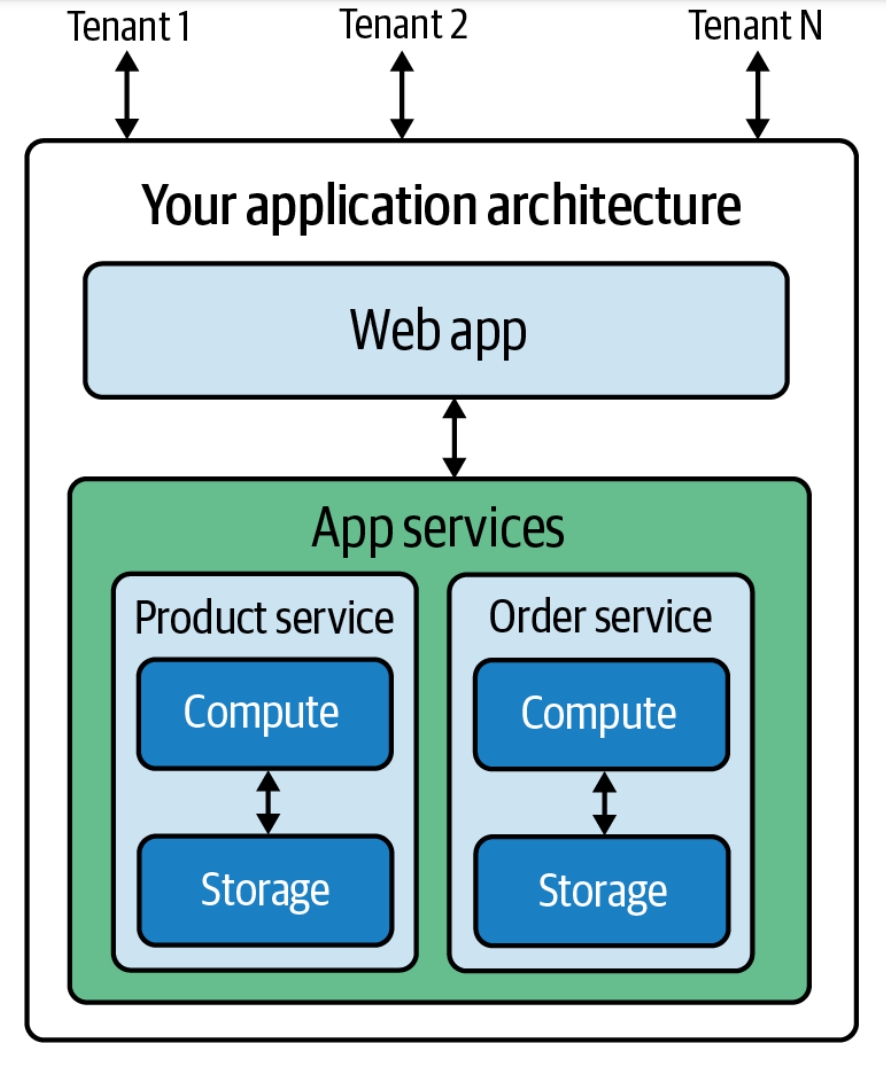
Utility Computing
Utility computing, or computer utility, is a service provisioning model in which a service provider makes computing resources and infrastructure management available to the customer as needed, and charges them for specific usage rather than a flat rate. Like other types of on-demand computing (such as grid computing), the utility model seeks to maximize the efficient use of resources and/or minimize associated costs. Utility is the packaging of system resources, such as computation, storage and services, as a metered service. This model has the advantage of a low or no initial cost to acquire computer resources; instead, resources are essentially rented. This repackaging of computing services became the foundation of the shift to "on demand" computing, software as a service and cloud computing models that further propagated the idea of computing, application and network as a service. There was some initial skepticism about such a significant shift. However, the new model of com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Time-sharing
In computing, time-sharing is the Concurrency (computer science), concurrent sharing of a computing resource among many tasks or users by giving each Process (computing), task or User (computing), user a small slice of CPU time, processing time. This quick switch between tasks or users gives the illusion of Parallel computing, simultaneous execution. It enables computer multitasking, multi-tasking by a single user or enables multiple-user sessions. Developed during the 1960s, its emergence as the prominent model of computing in the 1970s represented a major technological shift in the history of computing. By allowing many users to interact concurrent computing, concurrently with a single computer, time-sharing dramatically lowered the cost of providing computing capability, made it possible for individuals and organizations to use a computer without owning one, and promoted the Interactive computing, interactive use of computers and the development of new interactive application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software As A Service
Software as a service (SaaS ) is a cloud computing service model where the provider offers use of application software to a client and manages all needed physical and software resources. SaaS is usually accessed via a web application. Unlike other software delivery models, it separates "the possession and ownership of software from its use". SaaS use began around 2000, and by 2023 was the main form of software application deployment. Unlike most self-hosted software products, only one version of the software exists and only one operating system and configuration is supported. SaaS products typically run on rented infrastructure as a service (IaaS) or platform as a service (PaaS) systems including hardware and sometimes operating systems and middleware, to accommodate rapid increases in usage while providing instant and continuous availability to customers. SaaS customers have the abstraction of limitless computing resources, while economy of scale drives down the cost. Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Service Provider
A service provider (SP) is an organization that provides services, such as consulting, legal, real estate, communications, storage, and processing services, to other organizations. Although a service provider can be a sub-unit of the organization that it serves, it is usually a third-party or outsourced supplier. Examples include telecommunications service providers (TSPs), application service providers (ASPs), storage service providers (SSPs), and internet service providers (ISPs). A more traditional term is service bureau. IT professionals sometimes differentiate between service providers by categorizing them as type I, II, or III. The three service types are recognized by the IT industry although specifically defined by ITIL and the U.S. Telecommunications Act of 1996. *Type I: internal service provider *Type II: shared service provider *Type III: external service provider Type III SPs provide IT services to external customers and subsequently can be referred to as external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Bureau
A computer bureau is a service bureau providing computer services. Computer bureaus developed during the early 1960s, following the development of time-sharing operating systems. These allowed the services of a single large and expensive mainframe computer to be divided up and sold as a fungible commodity. Development of telecommunications and the first modems encouraged the growth of computer bureau as they allowed immediate access to the computer facilities from a customer's own premises. The computer bureau model shrank during the 1980s, as cheap commodity computers, particularly the PC clone but also the minicomputer allowed services to be hosted on-premises. See also * Batch processing * Cloud computing * Grid computing * Service Bureau Corporation * Utility computing Utility computing, or computer utility, is a service provisioning model in which a service provider makes computing resources and infrastructure management available to the customer as needed, and ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Payroll Service Bureau
A financial bureau is an accounting business whose main focus is the preparation of finance for other businesses. In the United States such firms are often run by Certified Public Accountants, though a typical financial processing company will refer to itself as a bureau rather than a CPA firm, to distinguish its finance from the general tax and accounting that are generally not offered by a financial bureau. The typical client of a bureau is a small business - one just large enough for finance to be complicated to the point of a hassle, but one still small enough to not merit its own full-time finance department. The tasks that can generally be expected of just about all finance bureaus in the USA are as follows: * Printing of employee pay checks on time for payday * Direct deposit of pay into employee bank accounts, when desired * Appropriate calculation and withholding of federal, state, and local taxes * Calculation of financial taxes to be paid by employer (such as Social S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DECsystem-20
The DECSYSTEM-20 was a family of 36-bit Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-10 mainframe computers running the TOPS-20 operating system and was introduced in 1977. PDP-10 computers running the TOPS-10 operating system were labeled ''DECsystem-10'' as a way of differentiating them from the PDP-11. Later on, those systems running TOPS-20 (on the KL10 PDP-10 processors) were labeled ''DECSYSTEM-20'' (the block capitals being the result of a lawsuit brought against DEC by Singer, which made its own System Ten model, occasionally referenced in reporting as the "System 10"). The DECSYSTEM-20 was sometimes called PDP-20, although this designation was never used by DEC. Models The following models were produced: *DECSYSTEM-2020: KS10 bit-slice processor with up to 512 kilowords of solid state RAM (The ADP OnSite version of the DECSYSTEM-2020 supported 1 MW of RAM) *DECSYSTEM-2040: KL10 ECL processor with up to 1024 kilowords of magnetic core RAM *DECSYSTEM-2050: KL10 ECL proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology; in this context, the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise infeasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Timesharing
In computing, time-sharing is the concurrent sharing of a computing resource among many tasks or users by giving each task or user a small slice of processing time. This quick switch between tasks or users gives the illusion of simultaneous execution. It enables multi-tasking by a single user or enables multiple-user sessions. Developed during the 1960s, its emergence as the prominent model of computing in the 1970s represented a major technological shift in the history of computing. By allowing many users to interact concurrently with a single computer, time-sharing dramatically lowered the cost of providing computing capability, made it possible for individuals and organizations to use a computer without owning one, and promoted the interactive use of computers and the development of new interactive applications. History Batch processing The earliest computers were extremely expensive devices, and very slow. Machines were typically dedicated to a particular set of ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |