|
Screw
A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the screw head, head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety of materials. Screws might be inserted into holes in assembled parts or a screw may form its own thread. The #Differentiation between bolt and screw, difference between a screw and a bolt is that the latter is designed to be tightened or released by torquing a Nut (hardware), nut. The screw head on one end has a slot or other feature that commonly requires a tool to transfer the twisting force. Common tools for driving screws include screwdrivers, wrenches, coins and hex keys. The head is usually larger than the body, which provides a ''bearing surface'' and keeps the screw from being driven deeper than its length; an exception being the ''set screw'' (aka grub screw). The cylindrical portion of the screw from the underside of the head t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Screw Making Machine, 1871
A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety of materials. Screws might be inserted into holes in assembled parts or a screw may form its own thread. The difference between a screw and a bolt is that the latter is designed to be tightened or released by torquing a nut. The screw head on one end has a slot or other feature that commonly requires a tool to transfer the twisting force. Common tools for driving screws include screwdrivers, wrenches, coins and hex keys. The head is usually larger than the body, which provides a ''bearing surface'' and keeps the screw from being driven deeper than its length; an exception being the ''set screw'' (aka grub screw). The cylindrical portion of the screw from the underside of the head to the tip is called the ''shank''; it may be fully or partia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Screwdriver
A screwdriver is a tool, manual or powered, used for turning screws. Description A typical simple screwdriver has a handle and a shaft, ending in a tip the user puts into the screw head before turning the handle. This form of the screwdriver has been replaced in many workplaces and homes with a more modern and versatile tool, a power drill, as they are quicker, easier, and can also drill holes. The shaft is usually made of tough steel to resist bending or twisting. The tip may be hardened to resist wear, treated with a dark tip coating for improved visual contrast between tip and screw—or ridged or treated for additional "grip". Handles are typically wood, metal, or plastic and usually hexagonal, square, or oval in cross-section to improve grip and prevent the tool from rolling when set down. Some manual screwdrivers have interchangeable tips that fit into a socket on the end of the shaft and are held in mechanically or magnetically. These often have a hollow handle that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Screw Mechanism
The screw is a mechanism that converts rotational motion to linear motion, and a torque (rotational force) to a linear force. It is one of the six classical simple machines. The most common form consists of a cylindrical shaft with helical grooves or ridges called '' threads'' around the outside. The screw passes through a hole in another object or medium, with threads on the inside of the hole that mesh with the screw's threads. When the shaft of the screw is rotated relative to the stationary threads, the screw moves along its axis relative to the medium surrounding it; for example rotating a wood screw forces it into wood. In screw mechanisms, either the screw shaft can rotate through a threaded hole in a stationary object, or a threaded collar such as a nut can rotate around a stationary screw shaft. Geometrically, a screw can be viewed as a narrow inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. Like the other simple machines a screw can amplify force; a small rotational forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Helical Thread
A screw thread is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a ''straight'' thread and the latter called a ''tapered'' thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener. The mechanical advantage of a screw thread depends on its ''lead'', which is the linear distance the screw travels in one revolution. In most applications, the lead of a screw thread is chosen so that friction is sufficient to prevent linear motion being converted to rotary, that is so the screw does not slip even when linear force is applied, as long as no external rotational force is present. This characteristic is essential to the vast majority of its uses. The tightening of a fastener's screw thread is comparable to driving a wedge into a gap until it sticks fast through friction and slight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
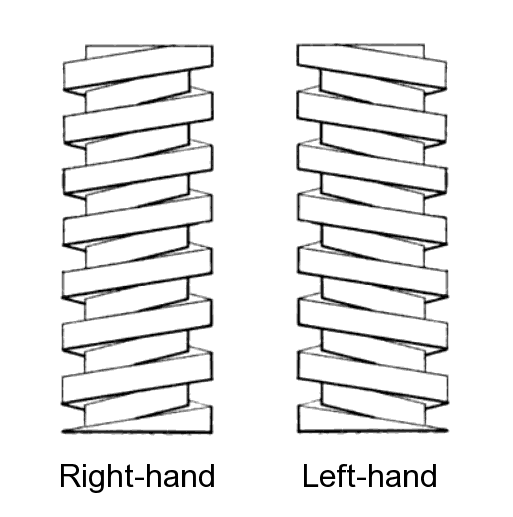
Left-hand Thread
A screw thread is a helix, helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder (geometry), cylinder or cone (geometry), cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a ''straight'' thread and the latter called a ''tapered'' thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw (simple machine), screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener. The mechanical advantage of a screw thread depends on its ''lead'', which is the linear distance the screw travels in one revolution. In most applications, the lead of a screw thread is chosen so that friction is sufficient to prevent linear motion being converted to rotary, that is so the screw does not slip even when linear force is applied, as long as no external rotational force is present. This characteristic is essential to the vast majority of its uses. The tightening of a fastener's screw thread is comparable to driving a we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fastener
A fastener (US English) or fastening (UK English) is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or dismantled without damaging the joining components. Steel fasteners are usually made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel. Other methods of joining materials, some of which may create permanent joints, include: crimping, welding, soldering, brazing, taping, gluing, cement, or the use of other adhesives. Force may also be used, such as with magnets, vacuum (like suction cups), or even friction (like sticky pads). Some types of woodworking joints make use of separate internal reinforcements, such as dowels or biscuits, which in a sense can be considered fasteners within the scope of the joint system, although on their own they are not general-purpose fasteners. Furniture supplied in flat-pack form often uses cam dowels lock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Grub Screw
In American English, a set screw is a screw that is used to secure an object, by pressure and/or friction, within or against another object, such as fixing a pulley or gear to a shaft. A set screw is normally used without a nut (which distinguishes it from a bolt), being screwed instead in a threaded hole drilled in only one of the two objects to be secured. A set screw is often headless and threaded along its entire length, so that it will sit entirely inside that hole; in which case it may be called a grub screw or blind screw. Once fully and firmly screwed into the first object, the projecting tip of the set screw presses hard against the second object, acting like a clamp. The second object may have a machined detent (recess) to ensure that it cannot slide under the tip of the screw. On a shaft, this may be simply a flattened area. A set screw may have any type of drive, such as hex or square head, slot, or recessed --- cross (Phillips), hex (Allen), star (Torx), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hex Keys
A hex key (also, hex wrench, Allen key and Allen wrench, Unbrako or Inbus) is a simple driver for bolts or screws that have heads with ''internal'' hexagonal recesses ( sockets). Hex keys are formed from a single piece of hard hexagonal steel rod, having blunt ends that fit snugly into similarly shaped screw sockets. The rods are bent to 90°, forming two arms of unequal length resembling an "L". The tool is usually held and twisted by its long arm, creating a relatively large torque at the tip of the short arm; it can also be held by its short arm to access screws in difficult-to-reach locations and to turn screws faster at the expense of torque. Hex keys are designated with a socket size and are manufactured with tight tolerances. As such, they are commonly sold in kits that include a variety of sizes. Key length typically increases with size but not necessarily proportionally so. Variants on this design have the short end inserted in a transverse handle, which may contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nut (hardware)
A nut is a type of fastener with a screw thread, threaded hole. Nuts are almost always used in conjunction with a mating bolt (fastener), bolt to fasten multiple parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction with slight deformation (engineering)#Elastic deformation, elastic deformation, a slight Tension (physics), stretching of the bolt, and compression (physics), compression of the parts to be held together. In applications where vibration or rotation may work a nut loose, various locking mechanisms may be employed: lock washers, jam nuts, eccentric double nuts, specialist adhesive thread-locking fluid such as Loctite, safety pins (split pins) or lockwire in conjunction with castellated nuts, nylon inserts (nyloc nut), or slightly oval-shaped threads. Square nuts, as well as bolt heads, were the first shape made and used to be the most common largely because they were much easier to manufacture, especially by hand. While rare toda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nail (fastener)
In woodworking and construction, a nail is a small object made of metal (or wood, called a tree nail or "trunnel") which is used as a fastener, as a peg to hang something, or sometimes as a decoration. Generally, nails have a sharp point on one end and a flattened head on the other, but headless nails are available. Nails are made in a great variety of forms for specialized purposes. The most common is a ''wire nail''. Other types of nails include ''pins'', ''Thumbtack, tacks'', ''wikt:brad, brads'', ''spikes'', and ''cleat (shoe), cleats.'' Nails are typically driven into the workpiece by a hammer or nail gun. A nail holds materials together by friction in the axial direction and Shear stress, shear strength laterally. The point of the nail is also sometimes bent over or ''clinched'' after driving to prevent pulling out. History The history of the nail is divided roughly into three distinct periods: * Hand-wrought (forged) nail (pre-history until 19th century) * Cut nail (ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |