|
Scheelite
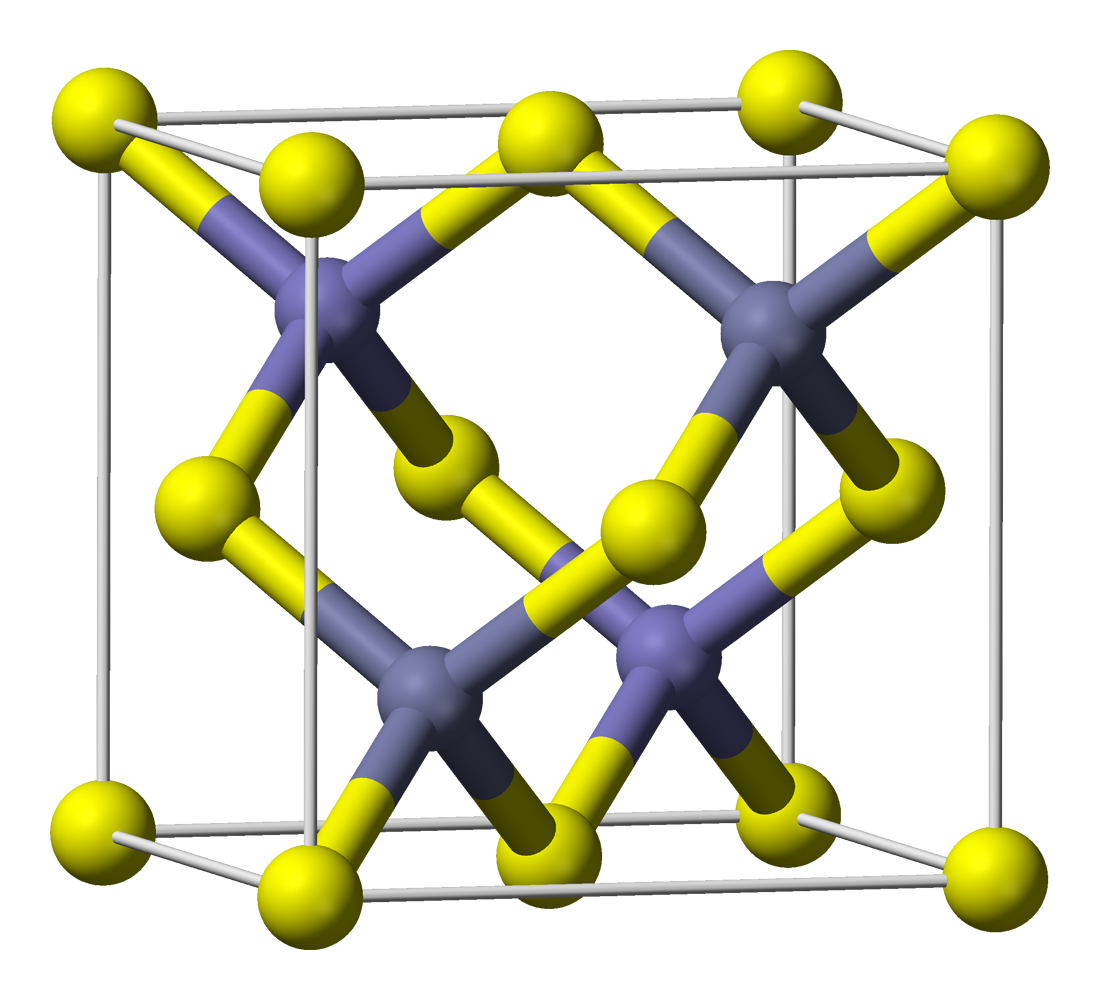
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Ca W O4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele (1742–1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors and are occasionally fashioned into gemstones when suitably free of flaws. Scheelite has been synthesized using the Czochralski process; the material produced may be used to imitate diamond, as a scintillator, or as a solid-state lasing medium. It was also used in radium paint in the same fashion as was zinc sulphide, and Thomas Edison invented a fluoroscope with a calcium tungstate-coated screen, making the images six times brighter than those with barium platinocyanide; the latter chemical allowed Röntgen to discover X-rays in early November 1895. The semi-precious stone marketed as 'blue scheelite' is actually a rock type consisting mostly of calcite and dolomite, with occasional traces of yellow-orange scheel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CaWO4
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Ca W O4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele (1742–1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors and are occasionally fashioned into gemstones when suitably free of flaws. Scheelite has been synthesized using the Czochralski process; the material produced may be used to imitate diamond, as a scintillator, or as a solid-state lasing medium. It was also used in radium paint in the same fashion as was zinc sulphide, and Thomas Edison invented a fluoroscope with a calcium tungstate-coated screen, making the images six times brighter than those with barium platinocyanide; the latter chemical allowed Röntgen to discover X-rays in early November 1895. The semi-precious stone marketed as 'blue scheelite' is actually a rock type consisting mostly of calcite and dolomite, with occasional traces of yellow-orange scheelite. Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish Pomerania, German-Swedish pharmaceutical chemist. Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified the elements molybdenum, tungsten, barium, nitrogen, and chlorine, among others. Scheele discovered organic acids Tartaric acid, tartaric, Oxalic acid, oxalic, Uric acid, uric, Lactic acid, lactic, and Citric acid, citric, as well as Hydrofluoric acid, hydrofluoric, Hydrocyanic acid, hydrocyanic, and Arsenic acid, arsenic acids. He preferred speaking German to Swedish his whole life, as German was commonly spoken among Swedish pharmacists.Fors, Hjalmar 2008. "Stepping through Science’s Door: C. W. Scheele, from Pharmacist's Apprentice to Man of Science". Ambix 55: 29–49 Biography Scheele was born in Stralsund, in western Pomerania, which at the time was a Dominions of Sweden, Swedish Dominion inside the Holy Roman Empire. Scheele's father, Joachim (or Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungstate
In chemistry, a tungstate is a Chemical compound, compound that contains an oxyanion of tungsten or is a mixed oxide containing tungsten. The simplest tungstate ion is , "orthotungstate". Many other tungstates belong to a large group of polyatomic ions that are termed polyoxometalates, ("POMs"), and specifically termed isopolyoxometalates as they contain, along with oxygen and maybe hydrogen, only one other element. Almost all useful tungsten ores are tungstates. Structures Orthotungstates feature tetrahedral W(VI) centres with short W–O distances of 1.79 Ångström, Å. Structurally, they resemble sulfates. Six-coordinate, octahedral tungsten dominates in the polyoxotungstates. In these compounds, the W–O distances are elongated. Some examples of tungstate ions: * (hydrogentungstate) * polymeric ions of various structures in , and Wells A.F. (1984) ''Structural Inorganic Chemistry'' 5th edition Oxford Science Publications * (paratungstate A) * (tungstate Y)Jon A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February11, 1847October18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, which include the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and early versions of the electric Incandescent light bulb, light bulb, have had a widespread impact on the modern industrial society, industrialized world. He was one of the first inventors to apply the principles of organized science and teamwork to the process of invention, working with many researchers and employees. He established the first industrial research laboratory. Edison was raised in the American Midwest. Early in his career he worked as a telegraph operator, which inspired some of his earliest inventions. In 1876, he established his first laboratory facility in Menlo Park, New Jersey, where many of his early inventions were developed. He later established a botanical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the Cube (geometry), cube becomes a rectangular Prism (geometry), prism with a square base (''a'' by ''a'') and height (''c'', which is different from ''a''). Bravais lattices There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal. The body-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell. Crystal classes The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Sulphide
Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the mineral sphalerite. Although this mineral is usually black because of various impurities, the pure material is white, and it is widely used as a pigment. In its dense synthetic form, zinc sulfide can be transparent, and it is used as a window for visible optics and infrared optics. Structure ZnS exists in two main crystalline forms. This dualism is an example of polymorphism. In each form, the coordination geometry at Zn and S is tetrahedral. The more stable cubic form is known also as zinc blende or sphalerite. The hexagonal form is known as the mineral wurtzite, although it also can be produced synthetically.. The transition from the sphalerite form to the wurtzite form occurs at around 1020 °C. Applications Luminescent material left, 200 px, samples of zinc sulfide with varying sulfur vacancies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conchoidal Fracture
A conchoidal fracture is a break or fracture of a brittle material that does not follow any natural planes of separation. Mindat.org defines ''conchoidal fracture'' as follows: "a fracture with smooth, curved surfaces, typically slightly concave, showing concentric undulations resembling the lines of growth of a shell".Conchoidal fracture at Mindat.org Materials that break in this way include , chert, , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleavage (crystal)
Cleavage, in mineralogy and materials science, is the tendency of crystalline materials to split along definite crystallographic structural planes. These planes of relative weakness are a result of the regular locations of atoms and ions in the crystal, which create smooth repeating surfaces that are visible both in the microscope and to the naked eye. If bonds in certain directions are weaker than others, the crystal will tend to split along the weakly bonded planes. These flat breaks are termed "cleavage".Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, '' Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., Wiley, The classic example of cleavage is mica, which cleaves in a single direction along the basal pinacoid, making the layers seem like pages in a book. In fact, mineralogists often refer to "books of mica". Diamond and graphite provide examples of cleavage. Each is composed solely of a single element, carbon. In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four others in a tetrahedral patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lustre (mineralogy)
Lustre (Commonwealth English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally implies radiance, gloss, or brilliance. A range of terms are used to describe lustre, such as ''earthy'', ''metallic'', ''greasy'', and ''silky''. Similarly, the term ''vitreous'' (derived from the Latin for glass, ''vitrum'') refers to a glassy lustre. A list of these terms is given below. Lustre varies over a wide continuum, and so there are no rigid boundaries between the different types of lustre. (For this reason, different sources can often describe the same mineral differently. This ambiguity is further complicated by lustre's ability to vary widely within a particular mineral species). The terms are frequently combined to describe intermediate types of lustre (for example, a "vitreous greasy" lustre). Some minerals exhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal System
In crystallography, a crystal system is a set of point groups (a group of geometric symmetries with at least one fixed point). A lattice system is a set of Bravais lattices (an infinite array of discrete points). Space groups (symmetry groups of a configuration in space) are classified into crystal systems according to their point groups, and into lattice systems according to their Bravais lattices. Crystal systems that have space groups assigned to a common lattice system are combined into a crystal family. The seven crystal systems are ''triclinic'', ''monoclinic'', ''orthorhombic'', ''tetragonal'', ''trigonal'', ''hexagonal'', and ''cubic''. Informally, two crystals are in the same crystal system if they have similar symmetries (though there are many exceptions). Classifications Crystals can be classified in three ways: lattice systems, crystal systems and crystal families. The various classifications are often confused: in particular the trigonal crystal system i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the Cube (geometry), cube becomes a rectangular Prism (geometry), prism with a square base (''a'' by ''a'') and height (''c'', which is different from ''a''). Bravais lattices There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal. The body-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell. Crystal classes The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |