|
Ring Lasers
Ring lasers are composed of two beams of light of the same Polarization (waves), polarization traveling in opposite directions ("counter-rotating") in a closed loop. Ring lasers are used most frequently as gyroscopes (ring laser gyroscope) in moving vessels like cars, ships, planes, and missiles. The world's largest ring lasers can detect details of the Earth's rotation. Such large rings are also capable of extending scientific research in many new directions, including the detection of gravitational waves, Aether drag hypothesis, Fresnel drag, Lense-Thirring effect, and Quantum electrodynamics, quantum-electrodynamic effects. In a rotating ring laser gyroscope, the two counter-propagating waves are slightly shifted in frequency and an interference pattern is observed, which is used to determine the rotational speed. The response to a rotation is a frequency difference between the two beams, which is proportional to the rotation rate of the ring laser (Sagnac effect). The dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Lasers For Research
Ring lasers are composed of two beams of light of the same Polarization (waves), polarization traveling in opposite directions ("counter-rotating") in a closed loop. Ring lasers are used most frequently as gyroscopes (ring laser gyroscope) in moving vessels like cars, ships, planes, and missiles. The world's largest ring lasers can detect details of the Earth's rotation. Such large rings are also capable of extending scientific research in many new directions, including the detection of gravitational waves, Aether drag hypothesis, Fresnel drag, Lense-Thirring effect, and Quantum electrodynamics, quantum-electrodynamic effects. In a rotating ring laser gyroscope, the two counter-propagating waves are slightly shifted in frequency and an interference pattern is observed, which is used to determine the rotational speed. The response to a rotation is a frequency difference between the two beams, which is proportional to the rotation rate of the ring laser (Sagnac effect). The dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Optics
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data transfer rates) than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss; in addition, fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
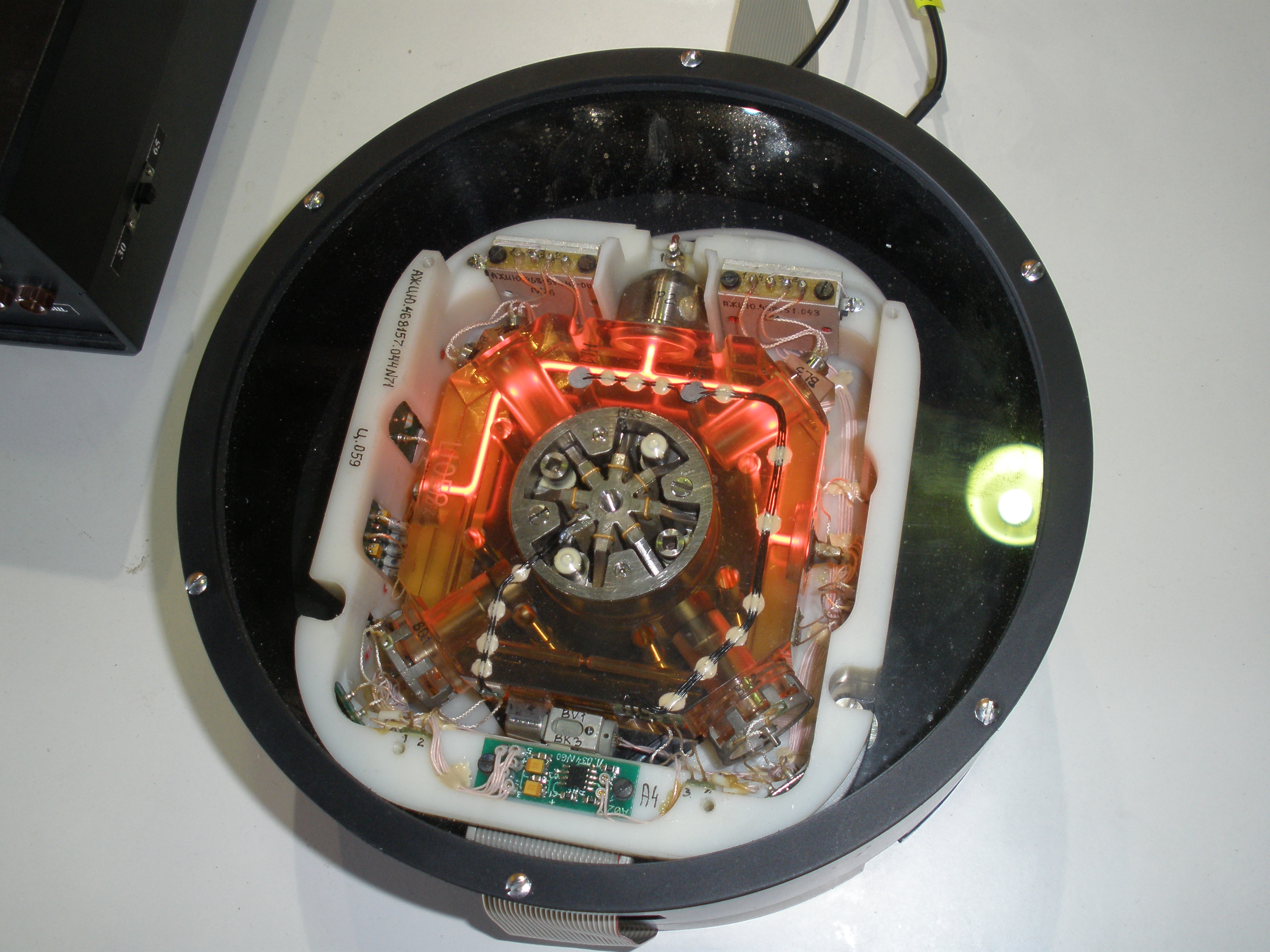
Ring Laser Gyroscope
A ring laser gyroscope (RLG) consists of a ring laser having two independent counter-propagating resonant modes over the same path; the difference in phase is used to detect rotation. It operates on the principle of the Sagnac effect which shifts the nulls of the internal standing wave pattern in response to angular rotation. Interference between the counter-propagating beams, observed externally, results in motion of the standing wave pattern, and thus indicates rotation. Description The first experimental ring laser gyroscope was demonstrated in the US by Macek and Davis in 1963. Various organizations worldwide subsequently developed ring-laser technology further. Many tens of thousands of RLGs are operating in inertial navigation systems and have established high accuracy, with better than 0.01°/hour bias uncertainty, and mean time between failures in excess of 60,000 hours. Ring laser gyroscopes can be used as the stable elements (for one degree of freedom each) in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Ring Resonators
An optical ring resonator is a set of waveguides in which at least one is a closed loop coupled to some sort of light input and output. (These can be, but are not limited to being, waveguides.) The concepts behind optical ring resonators are the same as those behind whispering galleries except that they use light and obey the properties behind constructive interference and total internal reflection. When light of the resonant wavelength is passed through the loop from the input waveguide, the light builds up in intensity over multiple round-trips owing to constructive interference and is output to the output bus waveguide which serves as a detector waveguide. Because only a select few wavelengths will be at resonance within the loop, the optical ring resonator functions as a filter. Additionally, as implied earlier, two or more ring waveguides can be coupled to each other to form an add/drop optical filter. Background Optical ring resonators work on the principles behind tota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Ring Laser
Semiconductor ring lasers (SRLs) are miniature ring laser devices with potential applications in optoelectronics, photonics and all-optical circuits. The first SRLs were developed in the 1980s. Recently, they have been of interest as potential random-access memory storage devices for all-optical computers. Semiconductor ring lasers are literally ring-shaped optical waveguides with a lasing medium. They have the ability to trap light in a ring, and recirculate it continuously as long as they remain powered. The material of choice for SRLs is indium phosphide. SRLs can be square with corner reflectors, or, as is more common with the smaller designs, have a curved, "racetrack" shape. Devices are currently on the order of a 100 micrometres, but further miniaturization should be possible using existing silicon microelectronics technology. In the summer of 2010 researchers Dr. Muhammad Maqbool and Kyle Main of Ball State University and Dr. Martin Kordesch of Ohio University were able ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Effect
The Faraday effect or Faraday rotation, sometimes referred to as the magneto-optic Faraday effect (MOFE), is a physical magneto-optical phenomenon. The Faraday effect causes a polarization rotation which is proportional to the projection of the magnetic field along the direction of the light propagation. Formally, it is a special case of gyroelectromagnetism obtained when the dielectric permittivity tensor is diagonal. This effect occurs in most optically transparent dielectric materials (including liquids) under the influence of magnetic fields. Discovered by Michael Faraday in 1845, the Faraday effect was the first experimental evidence that light and electromagnetism are related. The theoretical basis of electromagnetic radiation (which includes visible light) was completed by James Clerk Maxwell in the 1860s. Maxwell's equations were rewritten in their current form in the 1870s by Oliver Heaviside. The Faraday effect is caused by left and right circularly polarized waves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principles Of Optics
''Principles of Optics'', colloquially known as ''Born and Wolf'', is an optics textbook written by Max Born and Emil Wolf that was initially published in 1959 by Pergamon Press. After going through six editions with Pergamon Press, the book was transferred to Cambridge University Press who issued an expanded seventh edition in 1999. A 60th anniversary edition was published in 2019 with a foreword by Sir Peter Knight. It is considered a classic science book and one of the most influential optics books of the twentieth century. Background In 1933, Springer published Max Born's book “Optik”; this dealt with all optical phenomena for which the methods of classical physics, and Maxwell's equations in particular, were applicable. In 1950, with encouragement from Sir Edward Appleton, the principal of Edinburgh University, Born decided to produce an updated version of his “Optik” book in English. He was partly motivated by the need to make money, as he had not been wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
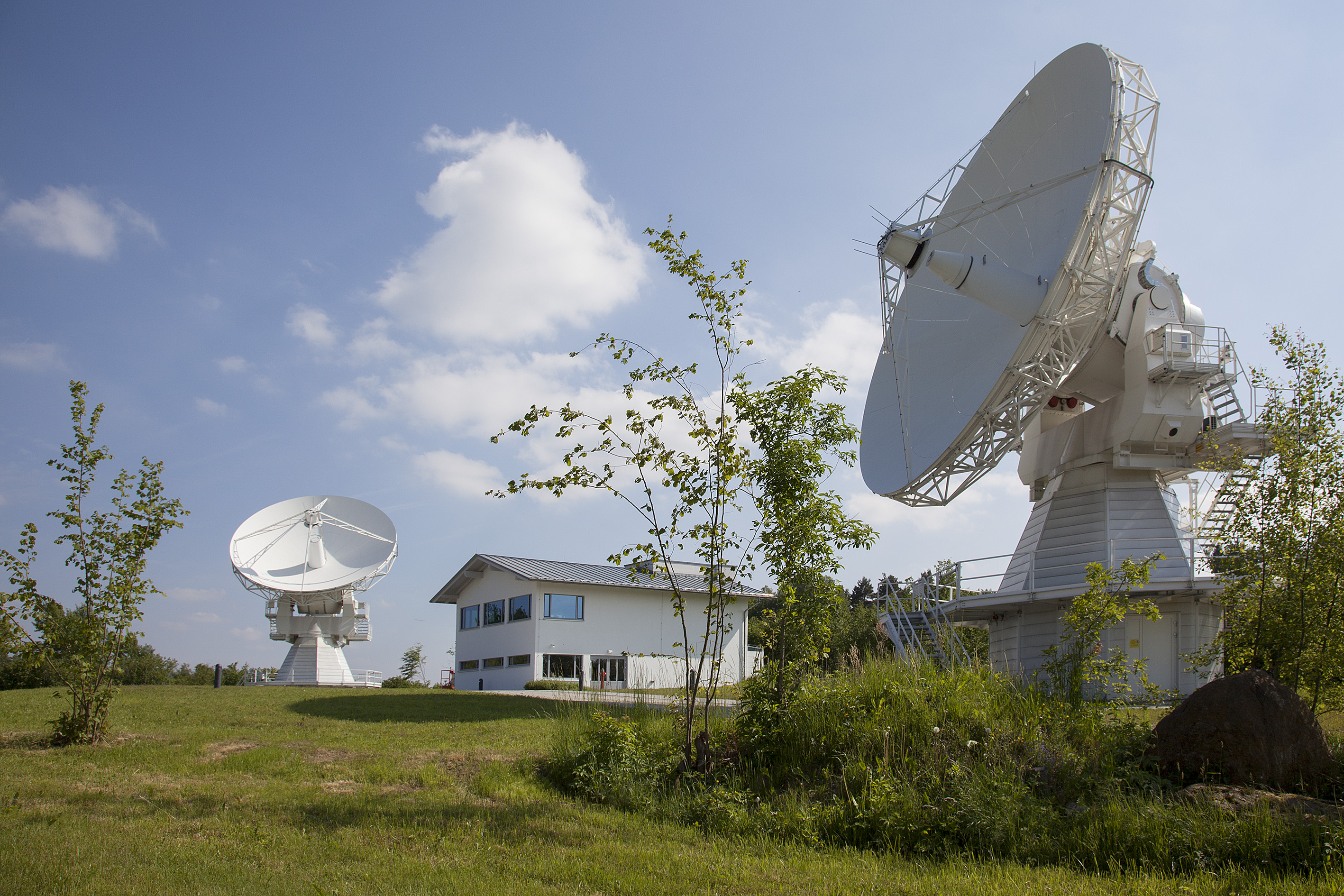
Geodetic Observatory Wettzell
The Geodetic Observatory Wettzell is located atop the 616 meter-high mountain Wagnerberg, west of the village Wettzell in the German district Cham in the Bavarian Forest. Tasks It is operated for the purpose of geodesy by the Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy together with the Technical University of Munich and is today one of the most important geodetic observatories in the world. As observing station, the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell has the task of gathering measuring data for the geodetic space techniques VLBI, SLR, GNSS and DORIS. These data are used for realizing global coordinate reference systems that form the basis for numerous issues in the field of geosciences (e.g. continental drift, sea level rise), in aerospace, but also in areas of everyday life (e.g. surveying, navigation). These global tasks can today only be solved through international cooperation. The activities like observations, data flow, data analysis and provision of results are coordina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christchurch
Christchurch ( ; mi, Ōtautahi) is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Canterbury Region. Christchurch lies on the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula on Pegasus Bay. The Avon River / Ōtākaro flows through the centre of the city, with an urban park along its banks. The city's territorial authority population is people, and includes a number of smaller urban areas as well as rural areas. The population of the urban area is people. Christchurch is the second-largest city by urban area population in New Zealand, after Auckland. It is the major urban area of an emerging sub-region known informally as Greater Christchurch. Notable smaller urban areas within this sub-region include Rangiora and Kaiapoi in Waimakariri District, north of the Waimakariri River, and Rolleston and Lincoln in Selwyn District to the south. The first inhabitants migrated to the area sometime between 1000 and 1250 AD. They hunted moa, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Patent Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark registration authority for the United States. The USPTO's headquarters are in Alexandria, Virginia, after a 2005 move from the Crystal City area of neighboring Arlington, Virginia. The USPTO is "unique among federal agencies because it operates solely on fees collected by its users, and not on taxpayer dollars". Its "operating structure is like a business in that it receives requests for services—applications for patents and trademark registrations—and charges fees projected to cover the cost of performing the services tprovide . The Office is headed by the Under Secretary of Commerce for Intellectual Property and Director of the United States Patent and Trademark Office, a position last held by Andrei Iancu until he left office on January 20, 2021. Commissioner of Patents Drew Hirshfeld is performing the funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |