|
Ribozymes
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both genetic material (like DNA) and a biological catalyst (like protein enzymes), and contributed to the RNA world hypothesis, which suggests that RNA may have been important in the evolution of prebiotic self-replicating systems. The most common activities of natural or in vitro-evolved ribozymes are the cleavage or ligation of RNA and DNA and peptide bond formation. For example, the smallest ribozyme known (GUGGC-3') can aminoacylate a GCCU-3' sequence in the presence of PheAMP. Within the ribosome, ribozymes function as part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA to link amino acids during protein synthesis. They also participate in a variety of RNA processing reactions, including RNA splicing, viral replication, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both genetic material (like DNA) and a biological catalyst (like protein enzymes), and contributed to the RNA world hypothesis, which suggests that RNA may have been important in the evolution of prebiotic self-replicating systems. The most common activities of natural or in vitro-evolved ribozymes are the cleavage or ligation of RNA and DNA and peptide bond formation. For example, the smallest ribozyme known (GUGGC-3') can aminoacylate a GCCU-3' sequence in the presence of PheAMP. Within the ribosome, ribozymes function as part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA to link amino acids during protein synthesis. They also participate in a variety of RNA processing reactions, including RNA splicing, viral replication, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairpin Ribozyme
The hairpin ribozyme is a small section of RNA that can act as a ribozyme. Like the hammerhead ribozyme it is found in RNA satellites of plant viruses. It was first identified in the minus strand of the tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV) satellite RNA where it catalyzes self-cleavage and joining (ligation) reactions to process the products of rolling circle virus replication into linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. The hairpin ribozyme is similar to the hammerhead ribozyme in that it does not require a metal ion for the reaction. Biological function The hairpin ribozyme is an RNA motif that catalyzes RNA processing reactions essential for replication of the satellite RNA molecules in which it is embedded. These reactions are self-processing, i.e. a molecule rearranging its own structure. Both cleavage and end joining reactions are mediated by the ribozyme motif, leading to a mixture of interconvertible linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. These reactions are imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadzyme
Leadzyme is a small ribozyme (catalytic RNA), which catalyzes the cleavage of a specific phosphodiester bond. It was discovered using an in-vitro evolution study where the researchers were selecting for RNAs that specifically cleaved themselves in the presence of lead. However, since then, it has been discovered in several natural systems. Leadzyme was found to be efficient and dynamic in the presence of micromolar concentrations of lead ions. Unlike in other small self-cleaving ribozymes, other divalent metal ions cannot replace Pb2+ in the leadzyme. Due to obligatory requirement for a lead, the ribozyme is called a metalloribozyme. Leadzyme has been subjected to extensive biochemical and structural characterization. The minimal secondary structure of leadzyme is surprisingly very simple . It comprises an asymmetric internal loop composed of six nucleotides and a helical region on each side of the internal loop. The cleavage site of leadzyme is located within a four-nucleotide l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
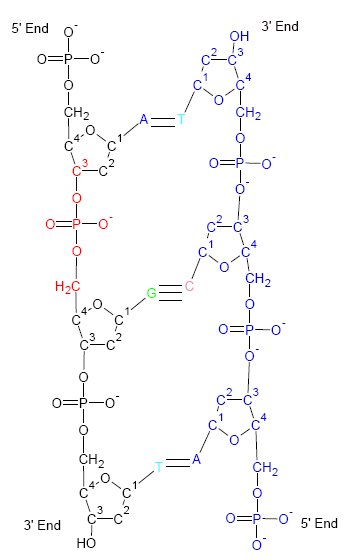
RNA World
The RNA world is a hypothetical stage in the evolutionary history of life on Earth, in which self-replicating RNA molecules proliferated before the evolution of DNA and proteins. The term also refers to the hypothesis that posits the existence of this stage. Alexander Rich first proposed the concept of the RNA world in 1962, and Walter Gilbert coined the term in 1986. Alternative chemical paths to life have been proposed, and RNA-based life may not have been the first life to exist. Even so, the evidence for an RNA world is strong enough that the hypothesis has gained wide acceptance. The concurrent formation of all four RNA building blocks further strengthened the hypothesis. Regardless of its plausibility in a prebiotic scenario, the RNA world can serve as a model system for studying the origin of life. Like DNA, RNA can store and replicate genetic information; like protein enzymes, RNA enzymes ( ribozymes) can catalyze (start or accelerate) chemical reactions that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammerhead Ribozyme
The hammerhead ribozyme is an RNA motif that catalyzes reversible cleavage and ligation reactions at a specific site within an RNA molecule. It is one of several catalytic RNAs (ribozymes) known to occur in nature. It serves as a model system for research on the structure and properties of RNA, and is used for targeted RNA cleavage experiments, some with proposed therapeutic applications. Named for the resemblance of early secondary structure diagrams to a hammerhead shark, hammerhead ribozymes were originally discovered in two classes of plant virus-like RNAs: satellite RNAs and viroids. They are also known in some classes of retrotransposons, including the retrozymes. The hammerhead ribozyme motif has been ubiquitously reported in lineages across the tree of life. The self-cleavage reactions, first reported in 1986, are part of a rolling circle replication mechanism. The hammerhead sequence is sufficient for self-cleavage and acts by forming a conserved three-dimensional ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA World Hypothesis
The RNA world is a hypothetical stage in the evolutionary history of life on Earth, in which self-replicating RNA molecules proliferated before the evolution of DNA and proteins. The term also refers to the hypothesis that posits the existence of this stage. Alexander Rich first proposed the concept of the RNA world in 1962, and Walter Gilbert coined the term in 1986. Alternative chemical paths to life have been proposed, and RNA-based life may not have been the first life to exist. Even so, the evidence for an RNA world is strong enough that the hypothesis has gained wide acceptance. The concurrent formation of all four RNA building blocks further strengthened the hypothesis. Regardless of its plausibility in a prebiotic scenario, the RNA world can serve as a model system for studying the origin of life. Like DNA, RNA can store and replicate genetic information; like protein enzymes, RNA enzymes ( ribozymes) can catalyze (start or accelerate) chemical reactions that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA chain. Ribosomes bind to messenger RNAs and use their sequences for determining the correct sequence of amino acids to generate a given protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anti-co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VS Ribozyme
The Varkud satellite (VS) ribozyme is an RNA enzyme that carries out the cleavage of a phosphodiester bond. Introduction Varkud satellite (VS) ribozyme is the largest known nucleolytic ribozyme and found to be embedded in VS RNA. VS RNA is a long non-coding RNA exists as a satellite RNA and is found in mitochondria of Varkud-1C and few other strains of ''Neurospora''. VS ribozyme contains features of both catalytic RNAs and group 1 introns. VS ribozyme has both cleavage and ligation activity and can perform both cleavage and ligation reactions efficiently in the absence of proteins. VS ribozyme undergo horizontal gene transfer with other ''Neurospora'' strains. VS ribozymes have nothing in common with other nucleolytic ribozymes. VS RNA has a unique primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. The secondary structure of the VS ribozyme consists of six helical domains (Figure 1). Stem loop I forms the substrate domain while stem-loop II-VI forms the catalytic domain. When these 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Woese
Carl Richard Woese (; July 15, 1928 – December 30, 2012) was an American microbiologist and biophysicist. Woese is famous for defining the Archaea (a new domain of life) in 1977 through a pioneering phylogenetic taxonomy of 16S ribosomal RNA, a technique that has revolutionized microbiology. He also originated the RNA world hypothesis in 1967, although not by that name. Woese held the Stanley O. Ikenberry Chair and was professor of microbiology at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. Life and education Carl Woese was born in Syracuse, New York on July 15, 1928. Woese attended Deerfield Academy in Massachusetts. He received a bachelor's degree in mathematics and physics from Amherst College in 1950. During his time at Amherst, Woese took only one biology course (Biochemistry, in his senior year) and had "no scientific interest in plants and animals" until advised by William M. Fairbank, then an assistant professor of physics at Amherst, to pursue biophysics at Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Orgel
Leslie Eleazer Orgel FRS (12 January 1927 – 27 October 2007) was a British chemist. He is known for his theories on the origin of life. Biography Leslie Orgel was born in London, England, on . He received his Bachelor of Arts degree in chemistry with first-class honours from the University of Oxford in 1948. In 1951 he was elected a Fellow of Magdalen College, Oxford and in 1953 was awarded his PhD in chemistry. Orgel started his career as a theoretical inorganic chemist and continued his studies in this field at Oxford, the California Institute of Technology and the University of Chicago. Together with Sydney Brenner, Jack Dunitz, Dorothy Hodgkin, and Beryl M. Oughton he was one of the first people in April 1953 to see the model of the structure of DNA, constructed by Francis Crick and James Watson, at the time he and the other scientists were working at Oxford University's Chemistry Department. According to the late Dr. Beryl Oughton, later Rimmer, they all travelled toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term " central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to proteins, it cannot flow back to nucleic acids. In other wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |