|
Response Modulation Hypothesis
The response modulation hypothesis is an etiological theory which argues that psychopathy is an attention disorder, and is not caused by an inherent lack of empathy or fear. It posits that when psychopaths focus on a particular goal, they are unable to shift their attention to peripheral signals or cues if they are unrelated to the main goal. Usually outside signals prevent people from antisocial behaviors (such as anxiety deterring someone from environmental dangers or empathy deterring someone from harming others) but psychopaths do not focus on these signals if they do not relate to their main goal. Response modulation argues that the attention to goals is what modulates whether psychopaths have normal or abnormal levels of fear and empathy. In studies when psychopaths were asked to focus on these cues, they had normal levels of fear and empathy. History and evolution The theory was first proposed by Gorenstein and Newman (1980) and has since gone through changes. Initially i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etiology (medicine)
Cause, also known as etiology () and aetiology, is the reason or origination of something. The word '' etiology'' is derived from the Greek , ''aitiologia'', "giving a reason for" (, ''aitia'', "cause"; and , ''-logia''). Description In medicine, etiology refers to the cause or causes of diseases or pathologies. Where no etiology can be ascertained, the disorder is said to be idiopathic. Traditional accounts of the causes of disease may point to the "evil eye". The Ancient Roman scholar Marcus Terentius Varro put forward early ideas about microorganisms in a 1st-century BC book titled ''On Agriculture''. Medieval thinking on the etiology of disease showed the influence of Galen and of Hippocrates. Medieval European doctors generally held the view that disease was related to the air and adopted a miasmatic approach to disease etiology. Etiological discovery in medicine has a history in Robert Koch's demonstration that species of the pathogenic bacteria '' Mycobacterium tuberc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychopathy
Psychopathy, sometimes considered synonymous with sociopathy, is characterized by persistent antisocial behavior, impaired empathy and remorse, and bold, disinhibited, and egotistical traits. Different conceptions of psychopathy have been used throughout history that are only partly overlapping and may sometimes be contradictory. Hervey M. Cleckley, an American psychiatrist, influenced the initial diagnostic criteria for antisocial personality reaction/disturbance in the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (''DSM''), as did American psychologist George E. Partridge. The ''DSM'' and '' International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD) subsequently introduced the diagnoses of antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) and dissocial personality disorder (DPD) respectively, stating that these diagnoses have been referred to (or include what is referred to) as psychopathy or sociopathy. The creation of ASPD and DPD was driven by the fact that many of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-social Behaviour
Antisocial behavior is a behavior that is defined as the violation of the rights of others by committing crime, such as stealing and physical attack in addition to other behaviors such as lying and manipulation. It is considered to be disruptive to others in society. This can be carried out in various ways, which includes, but is not limited to, intentional aggression, as well as covert and overt hostility. Anti-social behaviour also develops through social interaction within the family and community. It continuously affects a child's temperament, cognitive ability and their involvement with negative peers, dramatically affecting children's cooperative problem-solving skills. Many people also label behaviour which is deemed contrary to prevailing norms for social conduct as anti-social behaviour. However, researchers have stated that it is a difficult term to define, particularly in the United Kingdom where many acts fall into its category. The term is especially used in Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David T
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, David c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadbent's Filter Model Of Attention
Broadbent's filter model is an early selection theory of attention. Description Donald Broadbent based the development of the filter model from findings by Kennith Craik, who took an engineering approach to cognitive processes. Cherry and Broadbent were concerned with the issue of selective attention. Broadbent was the first to describe the human attentional processing system using an information processing metaphor. In this view, Broadbent proposed a so-called "early selection" view of attention, such that humans process information with limited capacity and select information to be processed early. Due to this limited capacity, a selective filter is needed for information processing. Broadbent stated that all stimuli are processed initially for basic physical properties. These basic characteristics can include pitch, color, loudness, and direction.Friedenberg, J., & Silverman, G. (2012). ''Cognitive Science: An Introduction to the Study of Mind'' Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effect Size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the value of a parameter for a hypothetical population, or to the equation that operationalizes how statistics or parameters lead to the effect size value. Examples of effect sizes include the correlation between two variables, the regression coefficient in a regression, the mean difference, or the risk of a particular event (such as a heart attack) happening. Effect sizes complement statistical hypothesis testing, and play an important role in power analyses, sample size planning, and in meta-analyses. The cluster of data-analysis methods concerning effect sizes is referred to as estimation statistics. Effect size is an essential component when evaluating the strength of a statistical claim, and it is the first item (magnitude) in the MA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
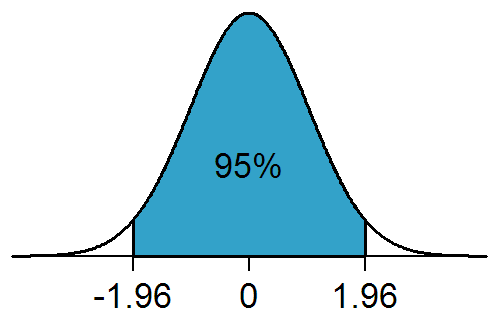
Statistical Significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or observation that involves drawing a sample from a population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the ''p''-value of an observed effect is less than (or equal to) the significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.Herrera Ortiz AF., Cadavid Camacho E, Cubillos Rojas J, Cadavid Camacho T, Zoe Guevara S, Tatiana Rincón Cuenca N, Vásquez Perdomo A, Del Castillo Herazo V, & Giraldo Malo R. A Practical Guide to Perform a Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Principles and Practice of Clinical Research. 2022;7(4):47–57. https://doi.org/10.21801/ppcrj.2021.74.6 Not only can meta-analyses provide an estimate of the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Lilienfeld
Scott O. Lilienfeld (December 23, 1960 – September 30, 2020) was a professor of psychology at Emory University and advocate for evidence-based treatments and methods within the field. He is known for his books '' 50 Great Myths of Popular Psychology'', ''Brainwashed'', and others that explore and sometimes debunk psychological claims that appear in the popular press. Along with having his work featured in major U.S. newspapers and journals such as ''The New York Times'', ''The New Yorker'', and ''Scientific American'', Lilienfeld made television appearances on ''20/20'', CNN and the ''CBS Evening News''. Background Lilienfeld was born on December 23, 1960, to Ralph and Thelma Lilienfeld of New York, N.Y.(in the Borough of Queens). Growing up, he was interested in paleontology and astronomy, but decided to study psychology after a high school course, then later a few college courses, piqued his interest. He has stated: "Although my love for natural science never waned, I ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publication Bias
In published academic research, publication bias occurs when the outcome of an experiment or research study biases the decision to publish or otherwise distribute it. Publishing only results that show a significant finding disturbs the balance of findings in favor of positive results. The study of publication bias is an important topic in metascience. Despite similar quality of execution and design, papers with statistically significant results are three times more likely to be published than those with null results. This unduly motivates researchers to manipulate their practices to ensure statistically significant results, such as by data dredging. Many factors contribute to publication bias. For instance, once a scientific finding is well established, it may become newsworthy to publish reliable papers that fail to reject the null hypothesis. Most commonly, investigators simply decline to submit results, leading to non-response bias. Investigators may also assume they made a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attenuation Theory
Attenuation theory is a model of selective attention proposed by Anne Treisman, and can be seen as a revision of Donald Broadbent's filter model. Treisman proposed attenuation theory as a means to explain how unattended stimuli sometimes came to be processed in a more rigorous manner than what Broadbent's filter model could account for. As a result, attenuation theory added layers of sophistication to Broadbent's original idea of how selective attention might operate: claiming that instead of a filter which barred unattended inputs from ever entering awareness, it was a process of attenuation. Thus, the attenuation of unattended stimuli would make it difficult, but not impossible to extract meaningful content from irrelevant inputs, so long as stimuli still possessed sufficient "strength" after attenuation to make it through a hierarchical analysis process. Brief overview and previous research Selective attention theories are aimed at explaining why and how individuals tend to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction, and emotional dysregulation is often considered a core symptom. In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance. ADHD is associated with other neurodevelopmental and mental disorders as well as some non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment, especially in modern society. Although people with ADHD struggle to focus on tasks they are not particularly interested in completing, they are often able to maintain an unusually prolonged and intense level of attention for tasks they do find interesting or rewarding; this is known as hyperfocus. The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in the majority of cases. Genetic factors play an impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |