|
Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the Hevea brasiliensis, Pará rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". Manufacturers refine this latex into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination with other materials. In most of its useful forms, it has a large stretch ratio and high resilience and also is buoyant and water-proof. Industrial demand for rubber-like materials began to out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taraxacum Kok-saghyz
''Taraxacum kok-saghyz'', often abbreviated as ''TKS'' and commonly referred to as the Kazakh dandelion, rubber root, or Russian dandelion, is a species of dandelion native to Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, notable for its production of high-quality rubber. ''T. kok-saghyz'' was discovered in Kazakhstan in 1932 by Soviet Union, Soviet scientists seeking a domestic source of rubber. Etymology ''Kok-saghyz'' is derived from the Kazakh ''kök-sağız'' (көк-сағыз), with ''kök'' meaning green and ''saghyz'' meaning rubber or gum. Its latex was traditionally used as a kind of chewing gum. Description ''Taraxacum kok-saghyz'' is a perennial plant with a yellow composite flower characteristic of the genus ''Taraxacum''. Each flower head may be approximately one inch in diameter and be made up for 50 to 90 florets. Plants may contain 25 to 50 leaves arranged in one or more rosettes at the upper end of the root. ''Taraxacum kok-saghyz'' can be differentiated from the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About of rubber is produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubber, just like natural rubber, has many uses in the automotive industry for tires, door and window profiles, seals such as O-rings and gaskets, hoses, belts, matting, and flooring. They offer a different range of physical and chemical properties which can improve the reliability of a given product or application. Synthetic rubbers are superior to natural rubbers in two major respects: thermal stability, and resistance to oils and related compounds. They are more resistant to oxidizing agents, such as oxygen and ozone which can reduce the life of products like tires. History The expanded use of bicycles, and particularly their pneumatic tires, starting in the 1890s, created increased demand for rubber. In 1909, a team headed by Fritz Hofmann, working at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
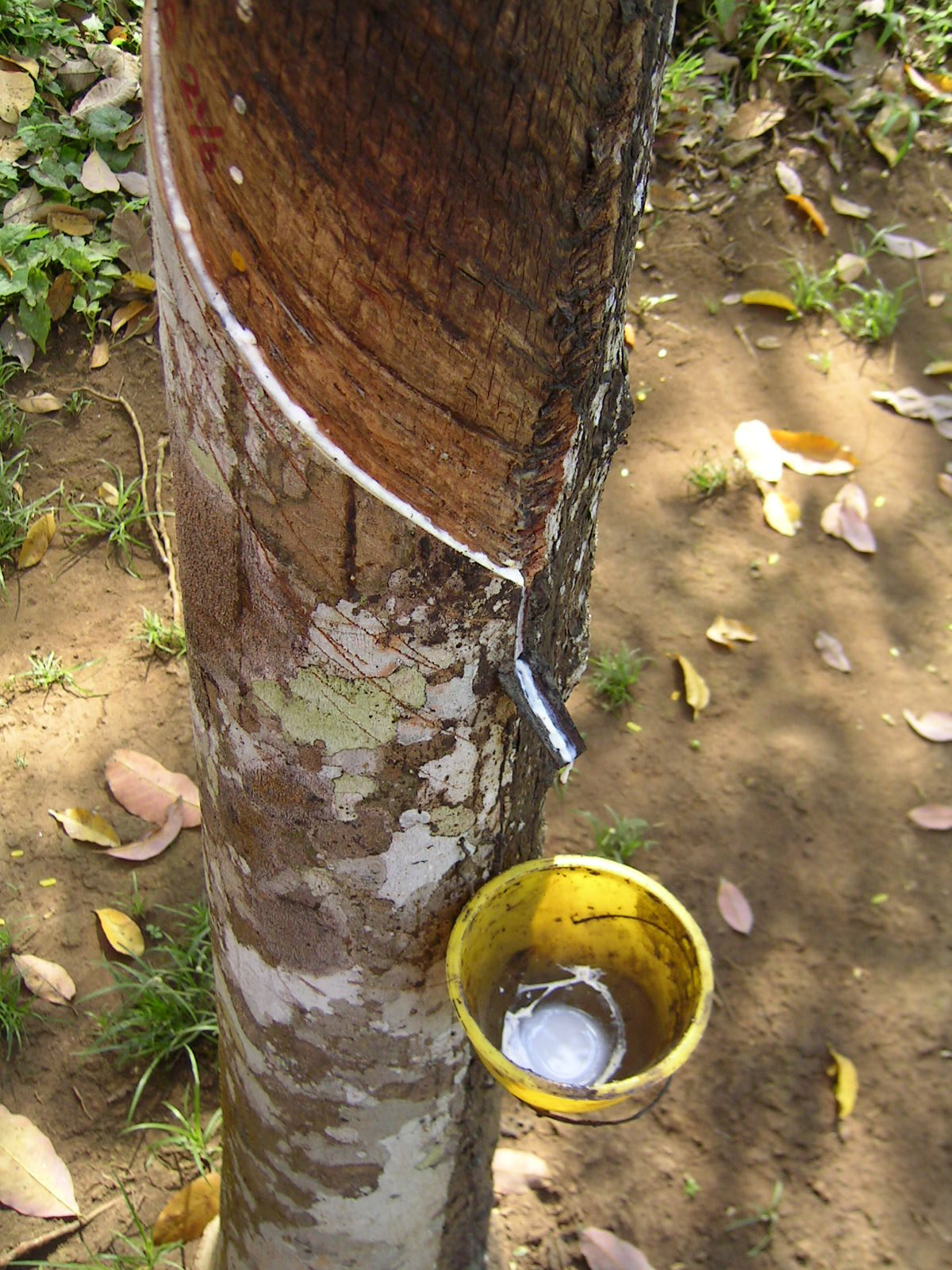
Hevea Brasiliensis
''Hevea brasiliensis'', the Pará rubber tree, ''sharinga'' tree, seringueira, or most commonly, rubber tree or rubber plant, is a flowering plant belonging to the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, originally native to the Amazon basin, but is now pantropical in distribution due to introductions. It is the most economically important member of the genus ''Hevea'' because the milky latex extracted from the tree is the primary source of natural rubber. Description ''Hevea brasiliensis'' is a tall deciduous tree growing to a height of up to in the wild. Cultivated trees are usually much smaller because drawing off the latex restricts their growth. The trunk is cylindrical and may have a swollen, bottle-shaped base. The bark is some shade of brown, and the inner bark oozes latex when damaged. The leaves have three leaflets and are spirally arranged. The inflorescences include separate male and female flowers. The flowers are pungent, creamy-yellow and have no petals. The fruit is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrocities In The Congo Free State
From 1885 to 1908, many atrocities were committed in the Congo Free State (today the Democratic Republic of the Congo) under the absolute rule of King Leopold II of Belgium. These atrocities were particularly associated with the labour policies, enforced by colonial administrators, used to collect natural rubber for export. Combined with epidemic disease, famine, mass population displacement and falling birth rates caused by these disruptions, the atrocities contributed to a sharp decline in the Congolese population. Estimates of up to 13 million have been suggested, though some of the highest estimates were later retracted. A demographic study from 2020 concludes that a population decline outside the range of one to five million is improbable. At the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, the European powers recognized the claims of a supposedly philanthropic organisation run by Leopold II, to most of the Congo Basin region. Leopold had long held ambitions for colonial expansion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congo Rubber
''Landolphia owariensis'' is a species of liana from the family Apocynaceae found in tropical Africa. Latex can be extracted from this plant for the manufacture of natural rubber. Other names for this vine are eta, the white rubber vine and the Congo rubber plant. Congo rubber was a commercial rubber exported from the Congo Free State starting in 1890, most notable for its forced harvesting under conditions of great human suffering, in the Congo Free State, detailed in the 1904 Casement Report. From 1885 to 1908, millions died as a result of murder, deprivation, and disease, with population falling by millions in this period; some writers estimate this loss to be as high as 10 million people. Description When growing in savannah, ''Landolphia owariensis'' is an erect bush or small tree, but when growing among trees, it can develop into a woody vine with a stem that grows to a metre wide and long. The bark is rough, dark brown or greyish-brown, and often covered with pale yellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus (E) and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic polymer'', is often used interchangeably with ''rubber'', although the latter is preferred when referring to vulcanisates. Each of the monomers which link to form the polymer is usually a compound of several elements among carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicon. Elastomers are amorphous polymers maintained above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable molecular reconformation is feasible without breaking of covalent bonds. Rubber-like solids with elastic properties are called elastomers. Polymer chains are held together in these materials by relatively weak intermolecular bonds, which permit the polymers to stretch in response to macroscopic stresses. Elastomers are usually thermosets (requiring vulcanization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compound (chemistry), compounds, produces unique physical property, physical properties including toughness, high rubber elasticity, elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form Amorphous solid, amorphous and crystallization of polymers, semicrystalline structures rath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well. In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms) and in some Mushroom, mushrooms (especially species of ''Lactarius''). It is a complex emulsion that coagulation, coagulates on exposure to air, consisting of proteins, alkaloids, starches, sugars, Vegetable oil, oils, tannins, resins, and Natural gum, gums. It is usually exuded after tissue injury. In most plants, latex is white, but some have yellow, orange, or scarlet latex. Since the 17th century, latex has been used as a term for the fluid substance in plants, deriving from the Latin word for "liquid". It serves mainly as Antipredator adaptation, defense against Herbivore, herbivores and Fungivore, fungivores.Taskirawati, I. and Tuno, N., 2016Fungal defense against mycophagy in milk caps ''Science Report Kanazaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latex - Hevea - Cameroun
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well. In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms) and in some mushrooms (especially species of ''Lactarius''). It is a complex emulsion that coagulates on exposure to air, consisting of proteins, alkaloids, starches, sugars, oils, tannins, resins, and gums. It is usually exuded after tissue injury. In most plants, latex is white, but some have yellow, orange, or scarlet latex. Since the 17th century, latex has been used as a term for the fluid substance in plants, deriving from the Latin word for "liquid". It serves mainly as defense against herbivores and fungivores.Taskirawati, I. and Tuno, N., 2016Fungal defense against mycophagy in milk caps ''Science Report Kanazawa University'', ''60'', pp.1-10. Latex is not to be confused with plant sap; it is a distinct substance, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |