|
Rozenite
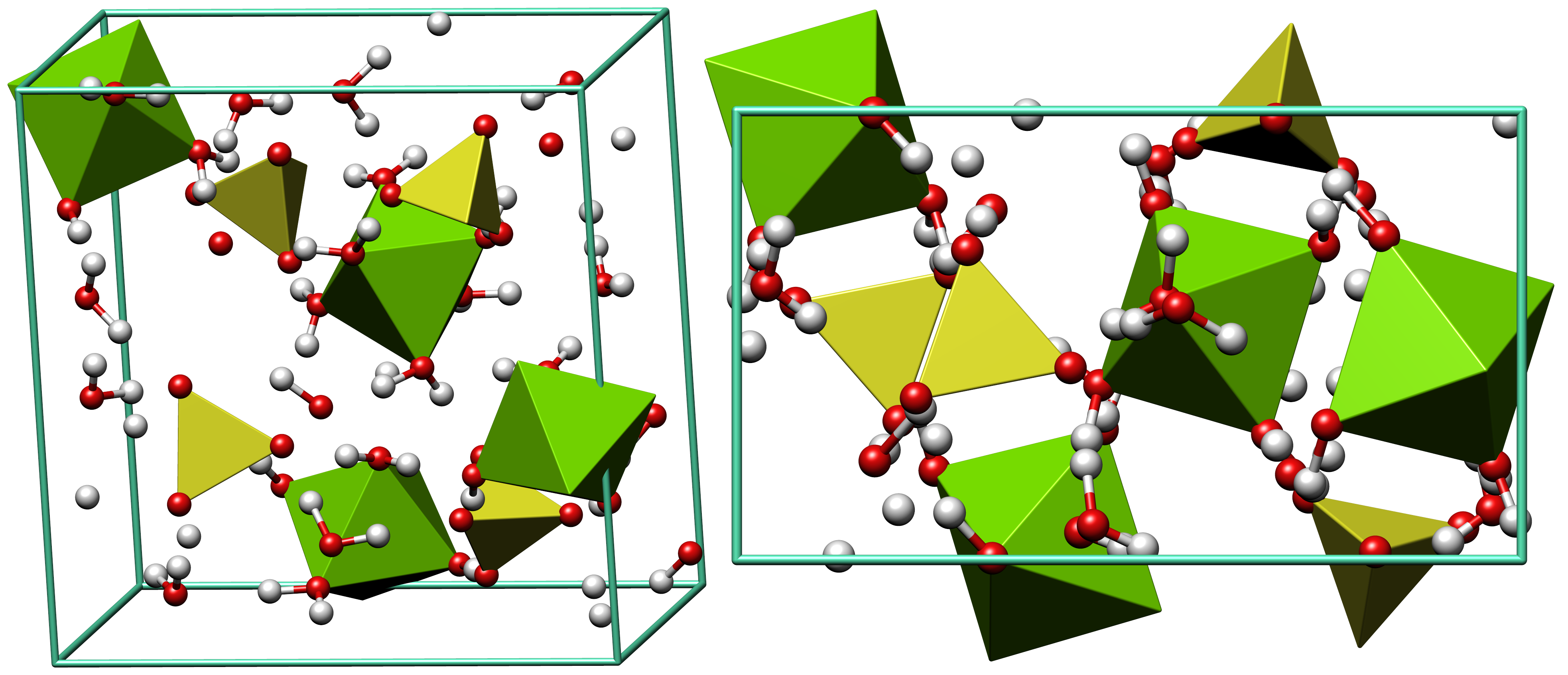
Rozenite is a hydrous iron sulfate mineral, Fe2+SO4·4(H2O). It occurs as a secondary mineral, formed under low humidity at less than as an alteration of copper-free melanterite, which is a post mine alteration product of pyrite or marcasite. It also occurs in lacustrine sediments and coal seams. Associated minerals include melanterite, epsomite, jarosite, gypsum, sulfur, pyrite, marcasite and limonite. It was first described in 1960 for an occurrence on Ornak Mountain, Western Tatra Mountains, Małopolskie, Poland. It was named for Polish mineralogist Zygmunt Rozen (1874–1936). The thermal expansion of rozenite was studied from to using neutron diffraction. Rozenite exhibits negative linear thermal expansion Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions). Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ..., meaning that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsomite
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula . Physical properties Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. The normal form is as massive encrustations, while acicular or fibrous crystals are rarely found. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. It is a soft mineral with variable Mohs hardness around 2.0~2.5, and it has a low specific gravity It is readily soluble in water, and absorbs water from the air. It converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure. The epsomite group includes solid solution series with morenosite (·) and goslarite (·). Etymology It was first systematically described in 1806 for an occurrence near Epsom, Surrey, England, after which it was named. It has been also referred to as "cave cotton" when in its fibrous form. Occurrence Epsomite forms as encrustations or efflorescences on limestone caver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Mineral
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal Vein (geology), veins and as secondary minerals in the Redox, oxidizing zone of sulfide mineral deposits. The Chromate ion, chromate and manganate minerals have a similar structure and are often included with the sulfates in mineral classification systems.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 347–354 . Sulfate minerals include: *Anhydrous sulfates **Barite BaSO4 **Celestite SrSO4 **Anglesite PbSO4 **Anhydrite CaSO4 **Hanksite Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl *Hydroxide and hydrous sulfates **Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O **Chalcanthite CuSO4·5H2O **Kieserite MgSO4·H2O **Starkeyite MgSO4·4H2O **Hexahydrite MgSO4·6H2O **Epsomite MgSO4·7H2O **Meridianiite MgSO4·11H2O **Melanterite FeSO4·7H2O **Antlerite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Minerals
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechanical pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Minerals
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal veins and as secondary minerals in the oxidizing zone of sulfide mineral deposits. The chromate and manganate minerals have a similar structure and are often included with the sulfates in mineral classification systems.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 347–354 . Sulfate minerals include: *Anhydrous sulfates ** Barite BaSO4 ** Celestite SrSO4 ** Anglesite PbSO4 ** Anhydrite CaSO4 ** Hanksite Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl *Hydroxide and hydrous sulfates ** Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O **Chalcanthite CuSO4·5H2O ** Kieserite MgSO4·H2O ** Starkeyite MgSO4·4H2O ** Hexahydrite MgSO4·6H2O ** Epsomite MgSO4·7H2O ** Meridianiite MgSO4·11H2O **Melanterite FeSO4·7H2O ** Antlerite Cu3SO4(OH)4 ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions). Substances usually contract with decreasing temperature (thermal contraction), with rare exceptions within limited temperature ranges ('' negative thermal expansion''). Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster, weakening the intermolecular forces between them and therefore expanding the substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. Prediction If an equation of state is available, it can be used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Diffraction
Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of Neutron temperature, thermal or cold neutron radiation, neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of the structure of the material. The technique is similar to X-ray diffraction but due to their different scattering properties, neutrons and X-rays provide complementary information: X-Rays are suited for superficial analysis, strong x-rays from synchrotron radiation are suited for shallow depths or thin specimens, while neutrons having high penetration depth are suited for bulk samples.Measurement of residual stress in materials using neutrons IAEA, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygmunt Rozen
Zygmunt, Zigmunt, Zigmund and spelling variations thereof are masculine given names and occasionally surnames. It has the same etymology as the Germanic name Zigmund. People so named include: Given name Medieval period * Sigismund I the Old (1467–1548), Zygmunt I Stary in Polish, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania * Sigismund II Augustus (1520–1572), Zygmunt II August in Polish, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, only son of Sigismund I * Sigismund III Vasa (1566–1632), Zygmunt III Waza in Polish, King of Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania, monarch of the united Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and King of Sweden * Zygmunt Grudziński (1560–1618), Polish nobleman, ''voivode'' (ruler) of Rawa * Zygmunt Grudziński (1568–1653), Polish nobleman, ''voivode'' of Innowrocław and Kalisz * Zygmunt Przyjemski of Rawicz (died 1652), Polish military commander * Zygmunt Kazanowski (1563–1634), Polish nobleman, soldier and magnate in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonweal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Małopolskie
Lesser Poland Voivodeship ( ) is a voivodeship in southern Poland. It has an area of , and a population of 3,404,863 (2019). Its capital and largest city is Kraków. The province's name recalls the traditional name of a historic Polish region, Lesser Poland, or in Polish: . The current Lesser Poland Voivodeship, however, covers only a small part of the broader ancient Małopolska region, which stretched far north, to Radom and Siedlce, also including such cities as Lublin, Kielce, Częstochowa, and Sosnowiec. The province is bounded on the north by the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (), on the west by '' Jura Krakowsko-Częstochowska'' (a broad range of hills stretching from Kraków to Częstochowa), and on the south by the Tatra, Pieniny and Beskidy Mountains. Politically, it is bordered by Silesian Voivodeship to the west, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship to the north, Subcarpathian Voivodeship to the east, and Slovakia (Prešov Region and Žilina Regions) to the south. Almost all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limonite
Limonite () is an iron ore consisting of a mixture of hydrated iron(III) oxide-hydroxides in varying composition. The generic formula is frequently written as , although this is not entirely accurate as the ratio of oxide to hydroxide can vary quite widely. Limonite is one of the three principal iron ores, the others being hematite and magnetite, and has been mining, mined for the production of iron since at least 400 BC. Names Limonite is named for the Ancient Greek word ( ), meaning "wet meadow", or ( ), meaning "marshy lake", as an allusion to its occurrence as in meadows and marshes. In its brown form, it is sometimes called brown hematite or brown iron ore. Characteristics Limonite is relatively density, dense with a specific gravity varying from 2.7 to 4.3.Northrop, Stuart A. (1959) "Limonite" ''Minerals of New Mexico'' (revised edition) University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque, New Mexico, pp. 329–333, It is usually medium to dark yellowish brown in color. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |