|
Rotational Ellipsoid
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters. A spheroid has circular symmetry. If the ellipse is rotated about its major axis, the result is a ''prolate spheroid'', elongated like a rugby ball. The American football is similar but has a pointier end than a spheroid could. If the ellipse is rotated about its minor axis, the result is an ''oblate spheroid'', flattened like a lentil or a plain M&M. If the generating ellipse is a circle, the result is a sphere. Due to the combined effects of gravity and rotation, the figure of the Earth (and of all planets) is not quite a sphere, but instead is slightly flattened in the direction of its axis of rotation. For that reason, in cartography and geodesy the Earth is often approximated by an oblate spheroid, known as the reference ellipsoid, instead of a sphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spheroids
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface (mathematics), surface obtained by Surface of revolution, rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters. A spheroid has circular symmetry. If the ellipse is rotated about its major axis, the result is a ''prolate spheroid'', elongated like a rugby ball. The ball (gridiron football), American football is similar but has a pointier end than a spheroid could. If the ellipse is rotated about its minor axis, the result is an ''oblate spheroid'', flattened like a lentil or a plain M&M's, M&M. If the generating ellipse is a circle, the result is a sphere. Due to the combined effects of gravity and rotation of the Earth, rotation, the figure of the Earth (and of all planets) is not quite a sphere, but instead is slightly flattening, flattened in the direction of its axis of rotation. For that reason, in cartography and geode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
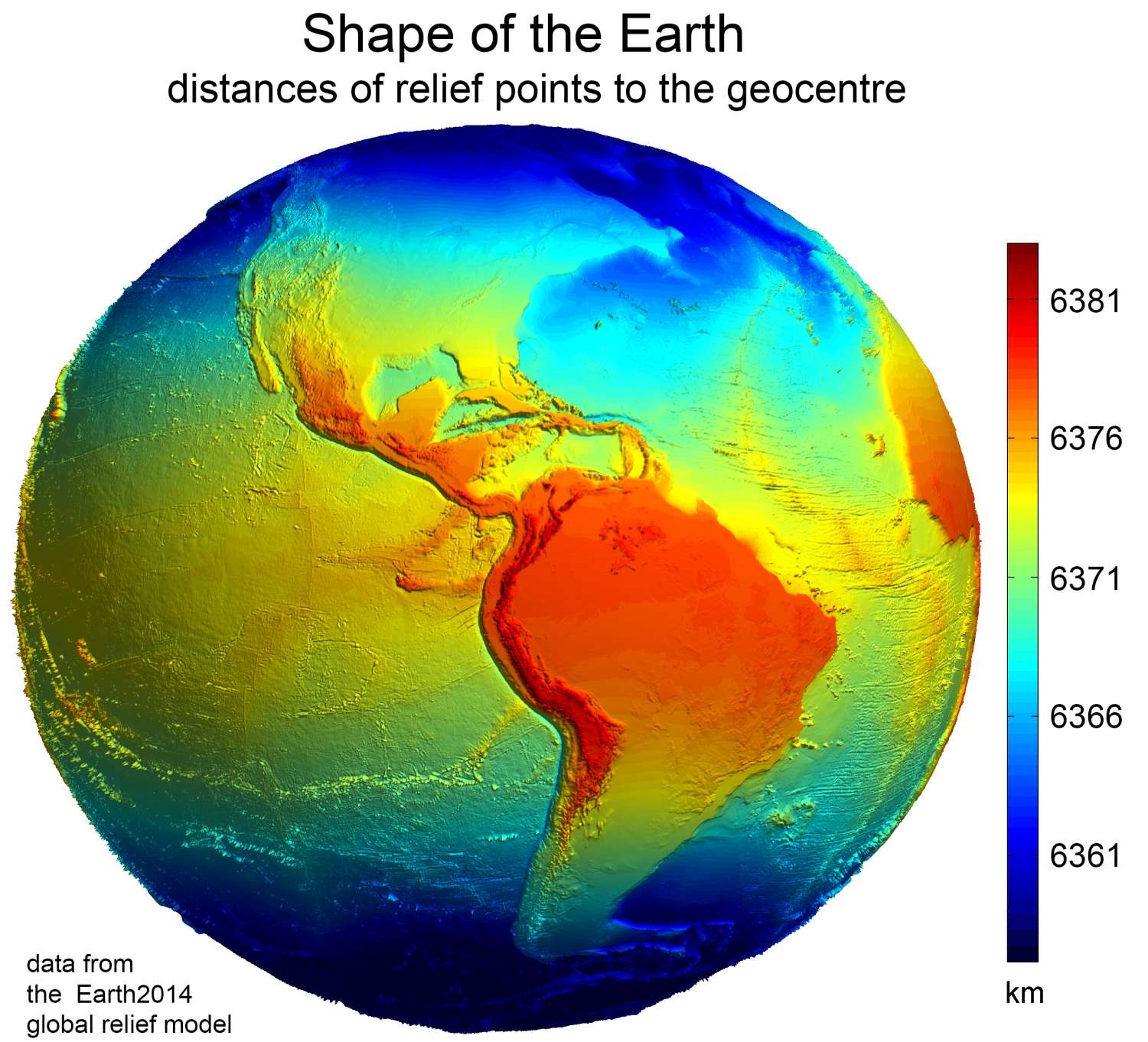
Figure Of The Earth
In geodesy, the figure of the Earth is the size and shape used to model planet Earth. The kind of figure depends on application, including the precision needed for the model. A spherical Earth is a well-known historical approximation that is satisfactory for geography, astronomy and many other purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including ellipsoid) have been developed so that coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, hydrographers, and geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely complicated. The Pythagorean concept of a spherical Earth offers a simple surface that is easy to deal with mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry Axis
Axial symmetry is symmetry around an axis or line (geometry). An object is said to be ''axially symmetric'' if its appearance is unchanged if transformed around an axis. The main types of axial symmetry are ''reflection symmetry'' and ''rotational symmetry'' (including circular symmetry for plane figures). glossary of meteorology. Retrieved 2010-04-08. For example, a baseball bat (without trademark or other design), or a plain white tea saucer, looks the same if it is rotat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter De Gruyter
Walter de Gruyter GmbH, known as De Gruyter (), is a German scholarly publishing house specializing in academic literature. History The roots of the company go back to 1749 when Frederick the Great granted the Königliche Realschule in Berlin the royal privilege to open a bookstore and "to publish good and useful books". In 1800, the store was taken over by Georg Reimer (1776–1842), operating as the ''Reimer'sche Buchhandlung'' from 1817, while the school's press eventually became the ''Georg Reimer Verlag''. From 1816, Reimer used a representative palace at Wilhelmstraße 73 in Berlin for his family and the publishing house, whereby the wings contained his print shop and press. The building later served as the Palace of the Reich President. Born in Ruhrort in 1862, Walter de Gruyter took a position with Reimer Verlag in 1894. By 1897, at the age of 35, he had become sole proprietor of the hundred-year-old company then known for publishing the works of German romantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geopotential Model
In geophysics and physical geodesy, a geopotential model is the theoretical analysis of measuring and calculating the effects of Earth's gravitational field (the geopotential). The Earth is not exactly spherical, mainly because of its rotation around the polar axis that makes its shape slightly oblate. However, a spherical harmonics series expansion captures the actual field with increasing fidelity. If Earth's shape were perfectly known together with the exact mass density ρ = ρ(''x'', ''y'', ''z''), it could be integrated numerically (when combined with a reciprocal distance kernel) to find an accurate model for Earth's gravitational field. However, the situation is in fact the opposite: by observing the orbits of spacecraft and the Moon, Earth's gravitational field can be determined quite accurately. The best estimate of Earth's mass is obtained by dividing the product ''GM'' as determined from the analysis of spacecraft orbit with a value for the gravitational constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Gravity
The gravity of Earth, denoted by , is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). It is a vector quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude is given by the norm g=\, \mathit\, . In SI units, this acceleration is expressed in metres per second squared (in symbols, m/ s2 or m·s−2) or equivalently in newtons per kilogram (N/kg or N·kg−1). Near Earth's surface, the acceleration due to gravity, accurate to 2 significant figures, is . This means that, ignoring the effects of air resistance, the speed of an object falling freely will increase by about every second. The precise strength of Earth's gravity varies with location. The agreed-upon value for is by definition. This quantity is denoted variously as , (though this sometimes means the normal gravity at the equator, ), , or simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Pole
A geographical pole or geographic pole is either of the two points on Earth where its axis of rotation intersects its surface. The North Pole lies in the Arctic Ocean while the South Pole is in Antarctica. North and South poles are also defined for other planets or satellites in the Solar System, with a North pole being on the same side of the invariable plane as Earth's North pole. Relative to Earth's surface, the geographic poles move by a few metres over periods of a few years. This is a combination of Chandler wobble, a free oscillation with a period of about 433 days; an annual motion responding to seasonal movements of air and water masses; and an irregular drift towards the 80th west meridian (geography), meridian. As cartography requires exact and unchanging coordinates, the averaged locations of geographical poles are taken as fixed ''cartographic poles'' and become the points where the body's great circles of longitude intersect. See also * Earth's rotation * Polar mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumference, halfway between the North Pole, North and South Pole, South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In three-dimensional space, spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its geographical pole, poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane (geometry), plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Geodetic System
The World Geodetic System (WGS) is a standard used in cartography, geodesy, and satellite navigation including GPS. The current version, WGS 84, defines an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system and a geodetic datum, and also describes the associated Earth Gravitational Model (EGM) and World Magnetic Model (WMM). The standard is published and maintained by the United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. History Efforts to supplement the various national surveying systems began in the 19th century with Friedrich Robert Helmert, F.R. Helmert's book (''Mathematical and Physical Theories of Physical Geodesy''). Austria and Germany founded the (Central Bureau of International Geodesy), and a series of global ellipsoids of the Earth were derived (e.g., Helmert 1906, John Fillmore Hayford, Hayford 1910 and 1924). A unified geodetic system for the whole world became essential in the 1950s for several reasons: * International space science and the beginning of as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Ellipsoid
An Earth ellipsoid or Earth spheroid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximations. It is a spheroid (an ellipsoid of revolution) whose minor axis (shorter diameter), which connects the geographical North Pole and South Pole, is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation. The ellipsoid is defined by the ''equatorial axis'' () and the ''polar axis'' (); their radial difference is slightly more than 21 km, or 0.335% of (which is not quite 6,400 km). Many methods exist for determination of the axes of an Earth ellipsoid, ranging from meridian arcs up to modern satellite geodesy or the analysis and interconnection of continental geodetic networks. Amongst the different set of data used in national surveys are several of special importance: the Bessel ellipsoid of 1841, the international Hayfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional space, 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical body, astronomical bodies, such as planets or Natural satellite, circumplanetary systems. Geodynamics, Geodynamical phenomena, including crust (geology), crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national Geodetic control network, control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on Geodetic datum, datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific Classical antiquity, antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |