|
Robotfindskitten
''robotfindskitten'' (''rfk'') is a " Zen simulation", originally written by Leonard Richardson for MS-DOS. Game It is a free video game with an ASCII interface in which the user (playing the eponymous robot and represented by a number sign "") must find kitten (represented by a random character) on a field of other random characters. Walking up to items allows robot to identify them as either kitten, or any of a variety of "Non-kitten Items" (NKIs) with whimsical, strange or simply random text descriptions. It is not possible to lose (though there is patchthat adds a 1 in 10 probability of the NKI killing robot). Simon Carless has characterized ''robotfindskitten'' as "less a game and more a way of life ... It's fun to wander around until you find a kitten, at which point you feel happy and can start again". The original ''robotfindskitten'' program was the sole entrant to a contest in 1997 at the now-defunct webzine '' Nerth Pork'' — the object: create a depiction of "ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Language
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language, or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an '' assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book '' The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax, and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DOS, Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-machine
The Z-machine is a virtual machine that was developed by Joel Berez and Marc Blank in 1979 and used by Infocom for its text adventure games. Infocom compiled game code to files containing Z-machine instructions (called story files or Z-code files) and could therefore port its text adventures to a new platform simply by writing a Z-machine implementation for that platform. With the large number of incompatible home computer systems in use at the time, this was an important advantage over using native code or developing a compiler for each system. History The "Z" of Z-machine stands for Zork, Infocom's first adventure game. Z-code files usually have names ending in .z1, .z2, .z3, .z4, .z5, .z6, .z7, or .z8, where the number is the version number of the Z-machine on which the file is intended to be run, as given by the first byte of the story file. This is a modern convention, however. Infocom itself used extensions of .dat (Data) and .zip (ZIP = Z-machine Interpreter Program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TI-99/4A
The TI-99/4 and TI-99/4A are home computers released by Texas Instruments in 1979 and 1981, respectively. Based on the Texas Instruments TMS9900 microprocessor originally used in minicomputers, the TI-99/4 was the first 16-bit home computer. The associated video display controller provides color graphics and sprite support which were only comparable with those of the Atari 400 and 800 released a month after the TI-99/4. The calculator-style keyboard of the TI-99/4 was cited as a weak point, and TI's reliance on ROM cartridges and their practice of limiting developer information to select third parties resulted in a lack of software for the system. The TI-99/4A was released in June 1981 to address some of these issues with a simplified internal design, full-travel keyboard, improved graphics, and a unique expansion system. At half the price of the original model, sales picked up significantly and TI supported the 4A with peripherals, including a speech synthesizer and a "Peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TI-83 Plus
The TI-83 series is a series of graphing calculators manufactured by Texas Instruments. The original TI-83 is itself an upgraded version of the TI-82. Released in 1996, it was one of the most popular graphing calculators for students. In addition to the functions present on normal scientific calculators, the TI-83 includes many features, including function graphing, polar/parametric/sequence graphing modes, statistics, trigonometric, and algebraic functions, along with many useful applications. Although it does not include as many calculus functions, applications and programs can be written on the calculator or loaded from external sources. The TI-83 was redesigned twice, first in 1999 and again in 2001. TI replaced the TI-83 with the ''TI-83 Plus'' in 1999. The 2001 redesign introduced a design very similar to the TI-73 and TI-83 Plus, eliminating the sloped screen that had been common on TI graphing calculators since the TI-81, and included Flash memory, enabling the device's o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockbox
Rockbox is a free and open-source software replacement for the OEM firmware in various forms of digital audio players (DAPs) with an original kernel. It offers an alternative to the player's operating system, in many cases without removing the original firmware, which provides a plug-in architecture for adding various enhancements and functions. Enhancements include personal digital assistant (PDA) functions, applications, utilities, and games. Rockbox can also retrofit video playback functions on players first released in mid-2000. Rockbox includes a voice-driven user-interface suitable for operation by visually impaired users. Rockbox runs on a wide variety of devices with very different hardware abilities: from early Archos players with 1-bit character cell-based displays, to modern players with high resolution color displays, digital optical audio hardware and advanced recording abilities. History The Rockbox project began in late 2001 and was first implemented on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines both the system- and user-level application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with variants of Unix and other operating systems. POSIX is also a trademark of the IEEE. POSIX is intended to be used by both application and system developers. Name Originally, the name "POSIX" referred to IEEE Std 1003.1-1988, released in 1988. The family of POSIX standards is formally designated as IEEE 1003 and the ISO/IEC standard number is ISO/ IEC 9945. The standards emerged from a project that began in 1984 building on work from related activity in the ''/usr/group'' association. Richard Stallman suggested the name ''POSIX'' (pronounced as ''pahz-icks,'' as in ''positive'', not as ''poh-six'') to the IEEE instead of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PlayStation Portable
The PlayStation Portable (PSP) is a handheld game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on December 12, 2004, in North America on March 24, 2005, and in PAL regions on September 1, 2005, and is the first handheld installment in the PlayStation line of consoles. As a seventh generation console, the PSP competed with the Nintendo DS. Development of the PSP was announced during E3 2003, and the console was unveiled at a Sony press conference on May 11, 2004. The system was the most powerful portable console when it was introduced, and was the first real competitor of Nintendo's handheld consoles after many challengers such as Nokia's N-Gage had failed. The PSP's advanced graphics capabilities made it a popular mobile entertainment device, which could connect to the PlayStation 2 and PlayStation 3, any computer with a USB interface, other PSP systems, and the Internet. The PSP also had a vast array of multimedia featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palm OS
Palm OS (also known as Garnet OS) was a mobile operating system initially developed by Palm, Inc., for personal digital assistants (PDAs) in 1996. Palm OS was designed for ease of use with a touchscreen-based graphical user interface. It is provided with a suite of basic applications for personal information management. Later versions of the OS have been extended to support smartphones. Several other licensees have manufactured devices powered by Palm OS. Following Palm's purchase of the Palm trademark, the currently licensed version from ACCESS was renamed ''Garnet OS''. In 2007, ACCESS introduced the successor to Garnet OS, called Access Linux Platform; additionally, in 2009, the main licensee of Palm OS, Palm, Inc., switched from Palm OS to webOS for their forthcoming devices. Creator and ownership Palm OS was originally developed under the direction of Jeff Hawkins at Palm Computing, Inc. Palm was later acquired by U.S. Robotics Corp., which in turn was later bought by 3Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
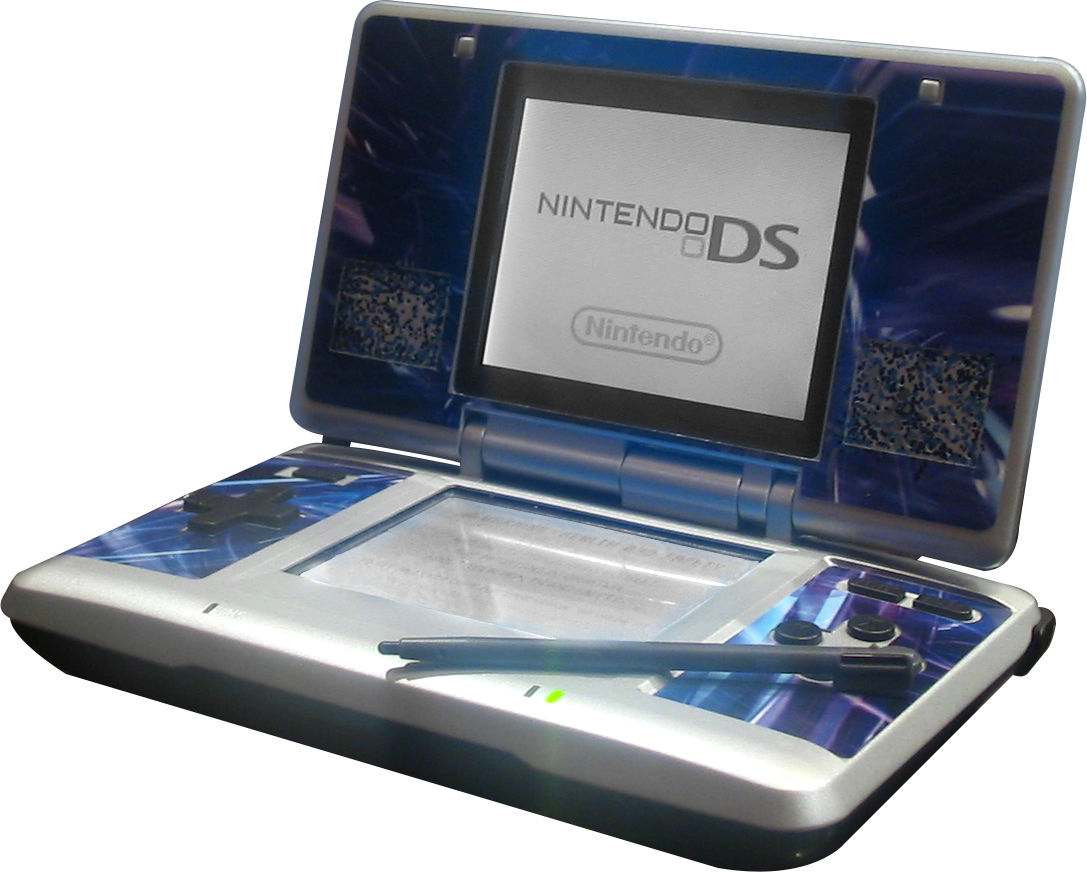
Nintendo DS
The is a handheld game console produced by Nintendo, released globally across 2004 and 2005. The DS, an initialism for "Developers' System" or "Dual Screen", introduced distinctive new features to handheld games: two LCD screens working in tandem (the bottom one being a touchscreen), a built-in microphone and support for wireless connectivity. Both screens are encompassed within a clamshell design similar to the Game Boy Advance SP. The Nintendo DS also features the ability for multiple DS consoles to directly interact with each other over Wi-Fi within a short range without the need to connect to an existing wireless network. Alternatively, they could interact online using the now-defunct Nintendo Wi-Fi Connection service. Its main competitor was Sony's PlayStation Portable during the seventh generation of video game consoles. Prior to its release, the Nintendo DS was marketed as an experimental "third pillar" in Nintendo's console lineup, meant to complement the Game Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maemo
Maemo is a software platform originally developed by Nokia, now developed by the community, for smartphones and Internet tablets. The platform comprises both the Maemo operating system and SDK. Maemo played a key role in Nokia's strategy to compete with Apple and Android, and that strategy failed for complex, institutional and strategic reasons. Maemo is mostly based on open-source code and has been developed by Maemo Devices within Nokia in collaboration with many open-source projects such as the Linux kernel, Debian, and GNOME. Maemo is based on Debian and draws much of its GUI, frameworks, and libraries from the GNOME project. It uses the Matchbox window manager and the GTK-based Hildon framework as its GUI and application framework. The user interface in Maemo 4 is similar to many hand-held interfaces and features a "home" screen, from which all applications and settings are accessed. The home screen is divided into areas for launching applications, a menu bar, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic (Mac OS X)
This is a list of macOS built-in apps and system components. Applications App Store The Mac App Store is macOS's digital distribution platform for macOS apps, created and maintained by Apple Inc. based on the iOS version, the platform was announced on October 20, 2010, at Apple's "Back to the Mac" event. First launched on January 6, 2011, as part of the free Mac OS X 10.6.6 update for all current Snow Leopard users, Apple began accepting app submissions from registered developers on November 3, 2010, in preparation for its launch. After 24 hours of release, Apple announced that there were over one million downloads. Automator Automator is an app used to create workflows for automating repetitive tasks into batches for quicker alteration via point-and-click (or drag and drop). This saves time and effort over human intervention to manually change each file separately. Automator enables the repetition of tasks across a wide variety of programs, including Finder, Safari, Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |