|
Reproductive Immunology
Reproductive immunology refers to a field of medicine that studies interactions (or the absence of them) between the immune system and components related to the reproductive system, such as maternal immune tolerance towards the fetus, or immunological interactions across the blood-testis barrier. The concept has been used by fertility clinics to explain fertility problems, recurrent miscarriages and pregnancy complications observed when this state of immunological tolerance is not successfully achieved. Immunological therapy is a method for treating many cases of previously unexplained infertility or recurrent miscarriage. Immune system in pregnancy The immunological system of the mother plays an important role in pregnancy considering the embryo's tissue is half foreign and unlike mismatched organ transplant, is not normally rejected. During pregnancy, immunological events that take place within the body of the mother are crucial in determining the health of both mother and fetu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic worms, and also objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy biological tissue, tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transforming Growth Factor Beta
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages. Activated TGF-β complexes with other factors to form a serine/threonine kinase complex that binds to TGF-β receptors. TGF-β receptors are composed of both type 1 and type 2 receptor subunits. After the binding of TGF-β, the type 2 receptor kinase phosphorylates and activates the type 1 receptor kinase that activates a signaling cascade. This leads to the activation of different downstream substrates and regulatory proteins, inducing transcription of different target genes that function in differentiation, chemotaxis, proliferation, and activation of many immune cells. TGF-β is secreted by many cell types, including macrophages, in a latent form in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Natural Killer Cells
Uterine natural killer cells make up approximately 70% of maternal lymphocytes during pregnancy, occupying both the decidua basalis of the endometrium at the implantation site and the mesometrial lymphoid aggregate of pregnancy (MLAp) that surrounds the blood vessels supplying the placenta. This number is at its peak in early pregnancy but declines at parturition. Morphology General Most studies of uterine natural killer cells use murine cells to model the human equivalent: unless stated otherwise, this section focuses on murine uterine natural killer cells. Uterine natural killer cells are large, granular, rounded or oval lymphocytes. On microscopic examination, they may have one or more cytoplasmic projections and/or be binucleate. Characteristically they contain eosinophilic granules that stain darkly with PAS, indicating the presence of glycoproteins. These granules usually appear regular (but some can be irregularly shaped), and they grow in size and number until approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells, are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system. They are a kind of large granular lymphocytes (LGL), and belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cells, stressed cells, tumor cells, and other intracellular pathogens based on signals from several activating and inhibitory receptors. Most immune cells detect the antigen presented on MHC class I, major histocompatibility complex I (MHC-I) on infected cell surfaces, but NK cells can recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because of the notion that they do not require activation to kill cells that are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome, or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies. APS can lead to blood clots (thrombosis) in both arteries and veins, pregnancy-related complications, and other symptoms like low platelets, kidney disease, heart disease, and rash. Although the exact etiology of APS is still not clear, genetics is believed to play a key role in the development of the disease. Diagnosis is made based on symptoms and testing, but sometimes research criteria are used to aid in diagnosis. The research criteria for definite APS requires one clinical event (i.e. thrombosis or pregnancy complication) and two positive blood test results spaced at least three months apart that detect lupus anticoagulant, anti-apolipoprotein antibodies, and/or anti-cardiolipin antibodies. Antiphospholipid syndrome can be primary or secondary. • Primary antiphospholipid syndrome occurs in the absence of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recurrent Miscarriage
Recurrent miscarriage or recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) is the spontaneous loss of 2-3 pregnancies that is estimated to affect up to 5% of women. The exact number of pregnancy losses and gestational weeks used to define RPL differs among medical societies. In the majority of cases, the exact cause of pregnancy loss is unexplained despite genetic testing and a thorough evaluation. When a cause for RPL is identified, almost half are attributed to a chromosomal abnormality (ie. aneuploidy). RPL has been associated with several risk factors including parental and genetic factors (ie. advanced maternal age, chromosomal abnormalities, sperm DNA fragmentation), congenital and acquired anatomical conditions, lifestyle factors (ie. cigarette smoking, caffeine, alcohol, stress), endocrine disorders, thrombophila (clotting disorders), immunological factors, and infections. The American Society of Reproductive Medicine recommends a thorough evaluation after 2 consecutive pregnancy losses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
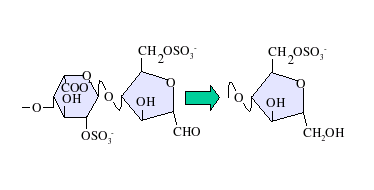
Low-molecular-weight Heparin
Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is a class of anticoagulant medications. They are used in the prevention of blood clots and, in the treatment of venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism), and the treatment of myocardial infarction. Heparin is a naturally occurring polysaccharide that inhibits coagulation, preventing thrombosis. Natural heparin consists of molecular chains of varying lengths or molecular weights. Chains of varying molecular weights, from 5000 to over 40,000 daltons, make up polydisperse pharmaceutical-grade heparin. LMWHs, in contrast, consist of only short chains of polysaccharides. LMWHs are defined as heparin salts having an average molecular weight of less than 8000 Da and for which at least 60% of all chains have a molecular weight less than 8000 Da. Various methods of fractionation or depolymerization of polymeric heparin obtain these. Heparin derived from natural sources, mainly porcine intestine or bovine lung, can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unfractionated Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It can be given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Its anticoagulant properties make it useful to prevent blood clotting in blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as argatroban or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis fetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus at or around birth, when the IgG molecules (one of the five main types of antibodies) produced by the mother pass through the placenta. Among these antibodies are some which attack antigens on the red blood cells in the fetal circulation, breaking down and destroying the cells. The fetus can develop reticulocytosis and anemia. The intensity of this fetal disease ranges from mild to very severe, and fetal death from heart failure ( hydrops fetalis) can occur. When the disease is moderate or severe, many erythroblasts (immature red blood cells) are present in the fetal blood, earning these forms of the disease the name ''erythroblastosis fetalis'' ( HDFN represents a breach of immune privilege for the fetus or some other form of impairment of the immune tolerance in pregnancy. Various types of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |