|
Reciprocal Causation
In biology, reciprocal causation arises when developing organisms are both ''products'' of evolution as well as ''causes'' of evolution. Formally, reciprocal causation exists when process A is a cause of process B and, subsequently, process B is a cause of process A, with this feedback potentially repeated. Some researchers, particularly advocates of the extended evolutionary synthesis, promote the view that causation in biological systems is inherently reciprocal. History Harvard evolutionary biologist Ernst Mayr (1961) suggested that there are two fundamentally different types of causation in biology, ‘ultimate’ and ‘proximate’. Ultimate causes (e.g. natural selection) were seen as (i) providing historical accounts for the existence of an organism's features, and (ii) explaining the function or ‘goal-directedness’ of living beings. In contrast, proximate causes (e.g. physiology) were seen as explaining how biological systems work. According to Mayr, the evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell (biology), cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple biological organisation, levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including scientific method, observation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coevolution
In biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well as gene-culture coevolution. Charles Darwin mentioned evolutionary interactions between flowering plants and insects in ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859). Although he did not use the word coevolution, he suggested how plants and insects could evolve through reciprocal evolutionary changes. Naturalists in the late 1800s studied other examples of how interactions among species could result in reciprocal evolutionary change. Beginning in the 1940s, plant pathologists developed breeding programs that were examples of human-induced coevolution. Development of new crop plant varieties that were resistant to some diseases favored rapid evolution in pathogen populations to overcome those plant defenses. That, in turn, required the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation and other forms of social transmission". Cultural evolution is the change of this information over time. Cultural evolution, historically also known as sociocultural evolution, was originally developed in the 19th century by anthropologists stemming from Charles Darwin's research on evolution. Today, cultural evolution has become the basis for a growing field of scientific research in the social sciences, including anthropology, economics, psychology, and organizational studies. Previously, it was believed that social change resulted from biological adaptations; anthropologists now commonly accept that social changes arise in consequence of a combination of social, environmental, and biological influences (viewed from a nature vs nurture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
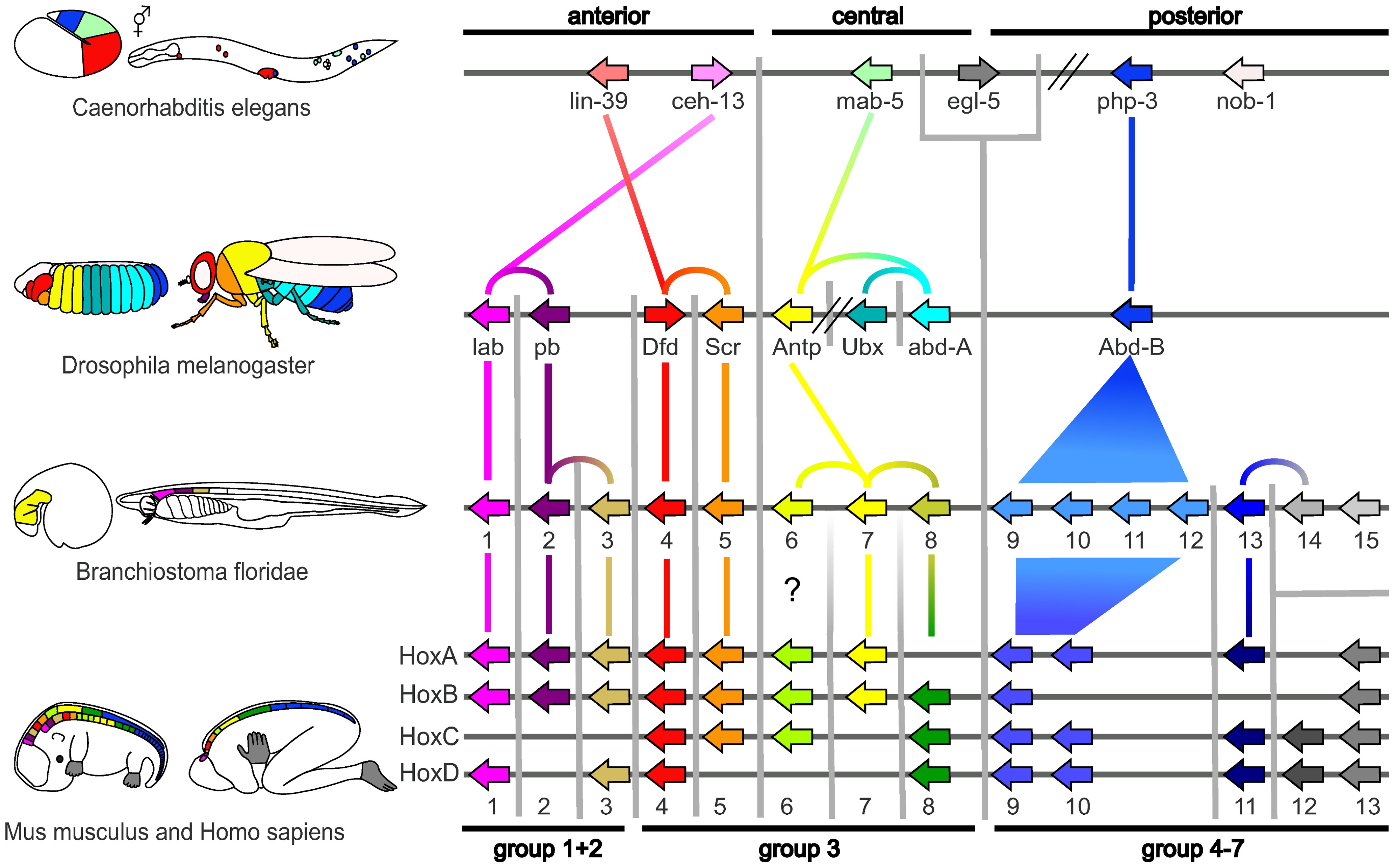
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Evolutionary developmental biology, informally known as evo-devo, is a field of biological research that compares the developmental biology, developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolution, evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoology, zoologists did not know how embryogenesis, embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was that of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the ovum, egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Evolution
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th-century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by changes in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations that inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niche Construction
Niche construction is the ecological process by which an organism alters its own (or another species') local environment. These alterations can be a physical change to the organism’s environment, or it can encompass the active movement of an organism from one habitat to another where it then experiences different environmental pressures. Examples of Ecological niche, niche construction include the building of nests and burrows by animals, the creation of shade, the influencing of wind speed, and alternations to nutrient cycling by plants. Although these modifications are often directly beneficial to the ''constructor'', they are not necessarily always. For example, when organisms dump detritus, they can degrade their own local environments. Within some biological evolutionary frameworks, niche construction can actively beget processes pertaining to ecological inheritance whereby the organism in question “constructs” new or unique ecologic, and perhaps even sociologic environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetic Inheritance
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the proposed transmission of epigenetic markers and modifications from one generation to multiple subsequent generations without altering the primary structure of DNA. Thus, the regulation of genes via epigenetic mechanisms can be heritable; the amount of transcripts and proteins produced can be altered by inherited epigenetic changes. In order for epigenetic marks to be heritable, however, they must occur in the gametes in animals, but since plants lack a definitive germline and can propagate, epigenetic marks in any tissue can be heritable. The inheritance of epigenetic marks in the immediate generation is referred to as intergenerational inheritance. In male mice, the epigenetic signal is maintained through the F1 generation. In female mice, the epigenetic signal is maintained through the F2 generation as a result of the exposure of the germline in the womb. Many epigenetic signals are lost beyond the F2/F3 generation and are no longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
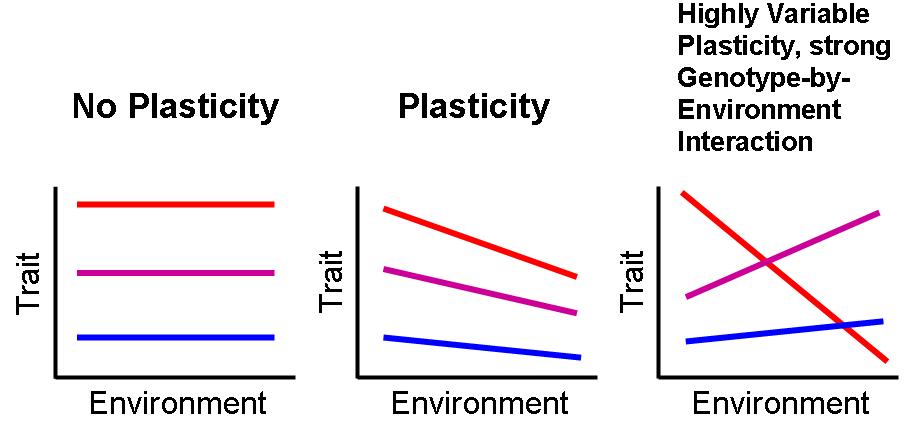
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes (e.g. morphological, physiological, behavioural, phenological) that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan. The term was originally used to describe developmental effects on morphological characters, but is now more broadly used to describe all phenotypic responses to environmental change, such as acclimation (acclimatization), as well as learning. The special case when differences in environment induce discrete phenotypes is termed polyphenism. Generally, phenotypic plasticity is more important for immobile organisms (e.g. plants) than mobile organisms (e.g. most animals), as mobile organisms can often move away from unfavourable environments. Nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mate Choice
Mate choice is one of the primary mechanisms under which evolution can occur. It is characterized by a "selective response by animals to particular stimuli" which can be observed as behavior.Bateson, Paul Patrick Gordon. "Mate Choice." Mate Choice, Cambridge University Press, 1985 In other words, before an animal engages with a potential mate, they first evaluate various aspects of that mate which are indicative of quality—such as the resources or phenotypes they have—and evaluate whether or not those particular Phenotypic trait, trait(s) are somehow beneficial to them. The evaluation will then incur a response of some sort. These mechanisms are a part of evolutionary change because they operate in a way that causes the qualities that are desired in a mate to be more frequently passed on to each generation over time. For example, if female peacocks desire mates who have a colourful plumage, then this trait will increase in frequency over time as male peacocks with a colourful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peafowl
Peafowl is a common name for two bird species of the genus '' Pavo'' and one species of the closely related genus '' Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae (the pheasants and their allies). Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are referred to as peahens. The two Asiatic species are the blue or Indian peafowl originally from the Indian subcontinent, and the green peafowl from Southeast Asia. The third peafowl species, the Congo peafowl, is native only to the Congo Basin. Male peafowl are known for their piercing calls and their extravagant plumage. The latter is especially prominent in the Asiatic species, which have an eye-spotted "tail" or "train" of covert feathers, which they display as part of a courtship ritual. The functions of the elaborate iridescent coloration and large "train" of peacocks have been the subject of extensive scientific debate. Charles Darwin suggested that they served to attract females, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency-dependent Selection
Frequency-dependent selection is an evolutionary process by which the fitness (biology), fitness of a phenotype or genotype depends on the phenotype or genotype composition of a given population. * In positive frequency-dependent selection, the fitness of a phenotype or genotype increases as it becomes more common. * In negative frequency-dependent selection, the fitness of a phenotype or genotype decreases as it becomes more common. This is an example of balancing selection. * More generally, frequency-dependent selection includes when biological interactions make an individual's fitness depend on the frequencies of other phenotypes or genotypes in the population. Frequency-dependent selection is usually the result of interactions between species (predation, parasitism, or competition), or between genotypes within species (usually competitive or symbiotic), and has been especially frequently discussed with relation to anti-predator adaptations. Frequency-dependent selection can lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |