|
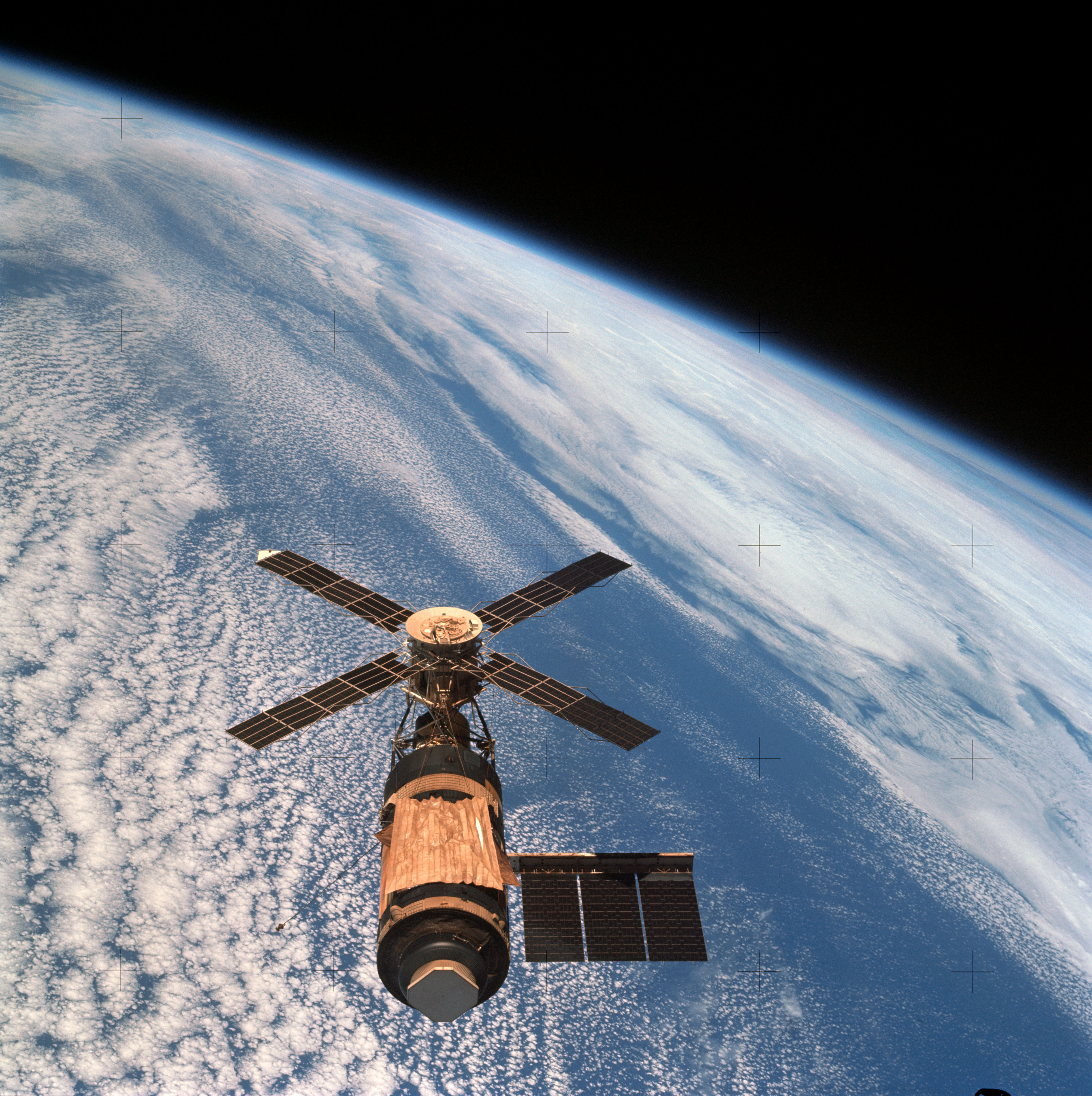
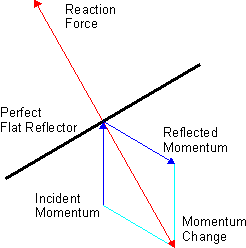
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure (also known as light pressure) is mechanical pressure exerted upon a surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, Reflection (physics), reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Engineering
Optical engineering is the field of engineering encompassing the physical phenomena and technologies associated with the generation, transmission, manipulation, detection, and utilization of light. Optical engineers use the science of optics to solve problems and to design and build devices that make light do something useful. They design and operate optical equipment that uses the properties of light using physics and chemistry, such as Lens (optics), lenses, microscopes, telescopes, lasers, sensors, fiber-optic communication systems and optical disc systems (e.g. CD, DVD). Optical engineering metrology uses optical methods to measure either micro-vibrations with instruments like the laser Speckle imaging, speckle interferometer, or properties of masses with instruments that measure refraction. Nano-measuring and nano-positioning machines are devices designed by optical engineers. These machines, for example microphotolithographic steppers, have Nanometre, nanometer precision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his Kepler's laws of planetary motion, laws of planetary motion, and his books ''Astronomia nova'', ''Harmonice Mundi'', and ''Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae'', influencing among others Isaac Newton, providing one of the foundations for his theory of Newton's law of universal gravitation, universal gravitation. The variety and impact of his work made Kepler one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, Natural science, natural and modern science. He has been described as the "father of science fiction" for his novel ''Somnium (novel), Somnium''. Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg, Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Third Law Of Motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows: # A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by a force. # At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is changing with time. # If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions. The three laws of motion were first stated by Isaac Newton in his '' Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), originally published in 1687. Newton used them to investigate and explain the motion of many physical objects and systems. In the time since Newton, new insights, especially aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass and is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum (from Latin '' pellere'' "push, drive") is: \mathbf = m \mathbf. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is dimensionally equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame of reference, it is a ''conserved'' quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photons
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Tweezers
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers. If the object is held in air or vacuum without additional support, it can be called optical levitation. The laser light provides an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the relative refractive index between particle and surrounding medium. Levitation is possible if the force of the light counters the force of gravity. The trapped particles are usually micron-sized, or even smaller. Dielectric and absorbing particles can be trapped, too. Optical tweezers are used in biology and medicine (for example to grab and hold a single bacterium, a cell like a sperm cell or a blood cell, or a molecule like DNA), nanoengineering and nanochemistry (to study and build materials from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, Optical fiber, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, Nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, interactome, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherent Control
Coherent control is a quantum mechanics-based method for controlling dynamic processes by light. The basic principle is to control quantum interference phenomena, typically by shaping the phase of laser pulses. The basic ideas have proliferated, finding vast application in spectroscopy, mass spectra, quantum information processing, laser cooling, ultracold physics and more. Brief History The initial idea was to control the outcome of chemical reactions. Two approaches were pursued: * in the time domain, a "pump-dump" scheme where the control is the time delay between pulses * in the frequency domain, interfering pathways controlled by one and three photons. The two basic methods eventually merged with the introduction of optimal control theory. Experimental realizations soon followed in the time domain and in the frequency domain. Two interlinked developments accelerated the field of coherent control: experimentally, it was the development of pulse shaping by a spatial light m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901, the others being the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Physics is traditionally the first award presented in the Nobel Prize ceremony. The prize consists of a medal along with a diploma and a certificate for the monetary award. The front side of the medal displays the same profile of Alfred Nobel depicted on the medals for Physics, Chemistry, and Literature. The first Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to German physicist Wilhelm Röntgen in recognition of the extraordinary services he rendered by the discovery of X-rays. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and is widely regarded as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Cooling
Laser cooling includes several techniques where atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled with laser light. The directed energy of lasers is often associated with heating materials, e.g. laser cutting, so it can be counterintuitive that laser cooling often results in sample temperatures approaching absolute zero. It is a routinely used in atomic physics experiments where the laser-cooled atoms are manipulated and measured, or in technologies, such as atom-based quantum computing architectures. Laser cooling reduces the random motion of particles or the random vibrations of mechanical systems. For atoms and molecules this reduces Doppler shifts in spectroscopy, allowing for high precision measurements and instruments such as optical clocks. The reduction in thermal energy also allows for efficient loading of atoms and molecules into traps where they can be used in experiments or atom-based devices for longer periods of time. Laser cooling relies on the momen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |