|
Quick-firing Gun
A quick-firing or rapid-firing gun is an artillery piece, typically a gun or howitzer, that has several characteristics which taken together mean the weapon can fire at a fast rate. Quick-firing was introduced worldwide in the 1880s and 1890s and had a marked impact on war both on land and at sea. Characteristics The characteristics of a quick-firing artillery piece are: *A breechloader, breech-loading weapon with a breech mechanism that allows rapid reloading *Single-part casing (ammunition), cased ammunition, i.e. a cartridge (firearms), cartridge containing both shell and propellant *Recoil buffers to limit recoil, so the barrel can quickly return to the same position after firing *The use of smokeless powder – nitrocellulose, nitroglycerine, or cordite – which create far less smoke than gunpowder, meaning that gun crews could still see their target These innovations, taken together, meant that the quick-firer could fire aimed shells much more rapidly than an older weapon. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons were developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armour. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannon, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to Shell (projectile), shell-firing Field gun, guns, howitzers, and Mortar (weapon), mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1-inch Nordenfelt Gun
The 1-inch Nordenfelt gun was an early quick-firing light gun intended to defend larger warships against the new small fast-moving torpedo boats in the late 1870s to the 1890s. Description The gun was an enlarged version of the successful rifle-calibre Nordenfelt hand-cranked "machine gun" designed by Helge Palmcrantz and was intended to combine its rapid rate of fire with a projectile capable of deterring attacking torpedo boats. The gun fired a solid steel bullet with hardened tip and brass jacket: under the terms of the St. Petersburg Declaration of 1868, exploding shells weighing less than 400 grams were not allowed to be used in warfare between the signatory nations. The gun was used in one, two and four-barrel versions. The ammunition was fed by gravity from a hopper above the breech subdivided into separate columns for each barrel. The gunner loaded and fired the multiple barrels by moving a lever on the right side of the gun forward and backwards. Pulling the lever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HMS Royal Sovereign (1891)
HMS ''Royal Sovereign'' was the lead ship of the seven ships in her class of pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Royal Navy in the 1890s. The ship was commissioned in 1892 and served as the flagship of the Channel Fleet for the next five years. She was transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet in 1897 and returned home in 1902, and was briefly assigned as a coast guard ship before she began a lengthy refit in 1903–1904. ''Royal Sovereign'' was reduced to reserve in 1905 and was taken out of service in 1909. The ship was sold for scrap four years later and subsequently broken up in Italy. Design and description The design of the ''Royal Sovereign''-class ships was derived from that of the battleships, greatly enlarged to improve seakeeping and to provide space for a secondary armament as in the preceding battleships. The ships displaced at normal load and at deep load. They had a length between perpendiculars of and an overall length of , a beam of , and a draugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
QF 6 Inch /40 Naval Gun
The QF 6-inch 40 calibre naval gun (Quick firing gun, Quick-Firing) was used by many United Kingdom-built warships around the end of the 19th century and the start of the 20th century. In British service it was known as the QF 6-inch Mk I, II, III guns.Mk I, II and III = Marks 1, 2 and 3. Britain used Roman numerals to denote Marks (models) of service ordnance until after the Second World War. This article describes the first three models of Royal Navy 6-inch QF guns. As the 15 cm/40 (6") 41st Year Type naval gun it was used for pre-dreadnought battleships, armoured cruisers and protected cruisers of the early Imperial Japanese Navy built in UK and European shipyards. It was also the heaviest gun ever carried by a pre-Cold War destroyer. Design QF technology These guns were developed to exploit the new "British ordnance terms#QF, QF" technology, which involved loading the propellant charge in a brass case with integrated primer in its base. This allowed a faster rate of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
QF 4
QF may stand for: Businesses and organisations * Qantas, an Australian airline (IATA:QF) * Qatar Foundation The Qatar Foundation for Education, Science and Community Development () is a state-led non-profit organization in Qatar, founded in 1995 by then-List of emirs of Qatar, emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani and his second wife Moza bint Nasser Al-Miss ..., a non-profit * Quiverfull, a Christian movement Military * Quds Force, an Iranian expeditionary unit * Quick-firing gun, an artillery piece * A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges; see British ordnance terms#QF * Q-Fire, a decoy fire site used in World War II Other uses * Quality factor, in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system {{disambig fr:QF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Armstrong Whitworth
Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd was a major British manufacturing company of the early years of the 20th century. With headquarters in Elswick, Tyne and Wear, Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Armstrong Whitworth built armaments, ships, locomotives, automobiles and aircraft. The company was founded by William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, William Armstrong in 1847, becoming Armstrong Mitchell and then Armstrong Whitworth through mergers. In 1927, it merged with Vickers Limited to form Vickers-Armstrongs, with its automobile and aircraft interests purchased by John Siddeley, 1st Baron Kenilworth, J D Siddeley. History In 1847, the engineer William George Armstrong founded the Elswick, Tyne and Wear, Elswick works at Newcastle, to produce hydraulic machinery, cranes and bridges, soon to be followed by artillery, notably the Armstrong breech-loading gun, with which the British Army was re-equipped after the Crimean War. In 1882, it merged with the shipbuilding firm of Charles Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
QF 3 Pounder Hotchkiss
The QF 3-pounder Hotchkiss or in French use Canon Hotchkiss à tir rapide de 47 mm were a family of long-lived light naval guns introduced in 1886 to defend against new, small and fast vessels such as torpedo boats and later submarines. There were many variants produced, often under license, which ranged in length from 32 to 50 calibers but 40 caliber was the most common version. They were widely used by the navies of a number of nations and often used by both sides in a conflict. They were also used ashore as coastal defense guns and later as an anti-aircraft gun, whether on improvised or specialized HA/LA mounts. Operational history French service The French Navy used two versions of the Hotchkiss 3-pounder: the short-barreled M1885 and the long-barreled M1902, which had a larger muzzle velocity than its predecessor. The French L/40 M1885 and the British QF 3-pounder were largely the same gun. Like the British who paired their 3-pounders with the larger QF 6-po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
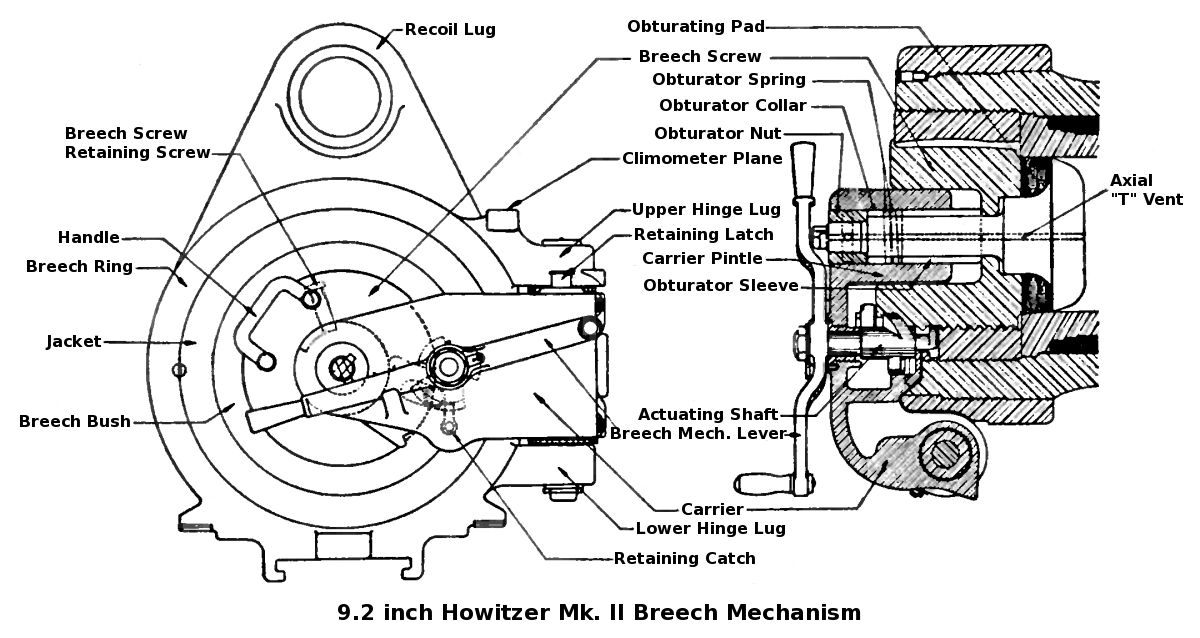
British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' Materiel, ordnance (weapons) and ammunition. The terms may have different meanings depending on their usage in another country's military. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile for a gun turret, turret, meaning that the turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation). BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of Rifled breech-loader, rifled breechloading gun for which the powder c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hotchkiss Et Cie
Société Anonyme des Anciens Etablissements Hotchkiss et Compagnie was a French arms and, in the 20th century, automobile manufacturer first established by American gunsmith Benjamin B. Hotchkiss. He moved to France and set up a factory, first at Viviez near Rodez in 1867, manufacturing arms used by the French in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870, then moving at Saint-Denis, Seine-Saint-Denis, Saint-Denis near Paris in 1875. It was merged into and succeeded by Thomson-CSF, now Thales Group. Arms An example of the company's output was the Hotchkiss revolving cannon (see picture from a privately circulated book dated 1874 by Alfred Koerner, later chairman of the company). The cannon had five barrels each able to fire 43 shells a minute a distance of one mile; it was made in four sizes from 37 mm to 57 mm, the largest intended for naval use. At the turn of the twentieth century, the company introduced the gas operation, gas-operated Hotchkiss machine gun, a sturdy and rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
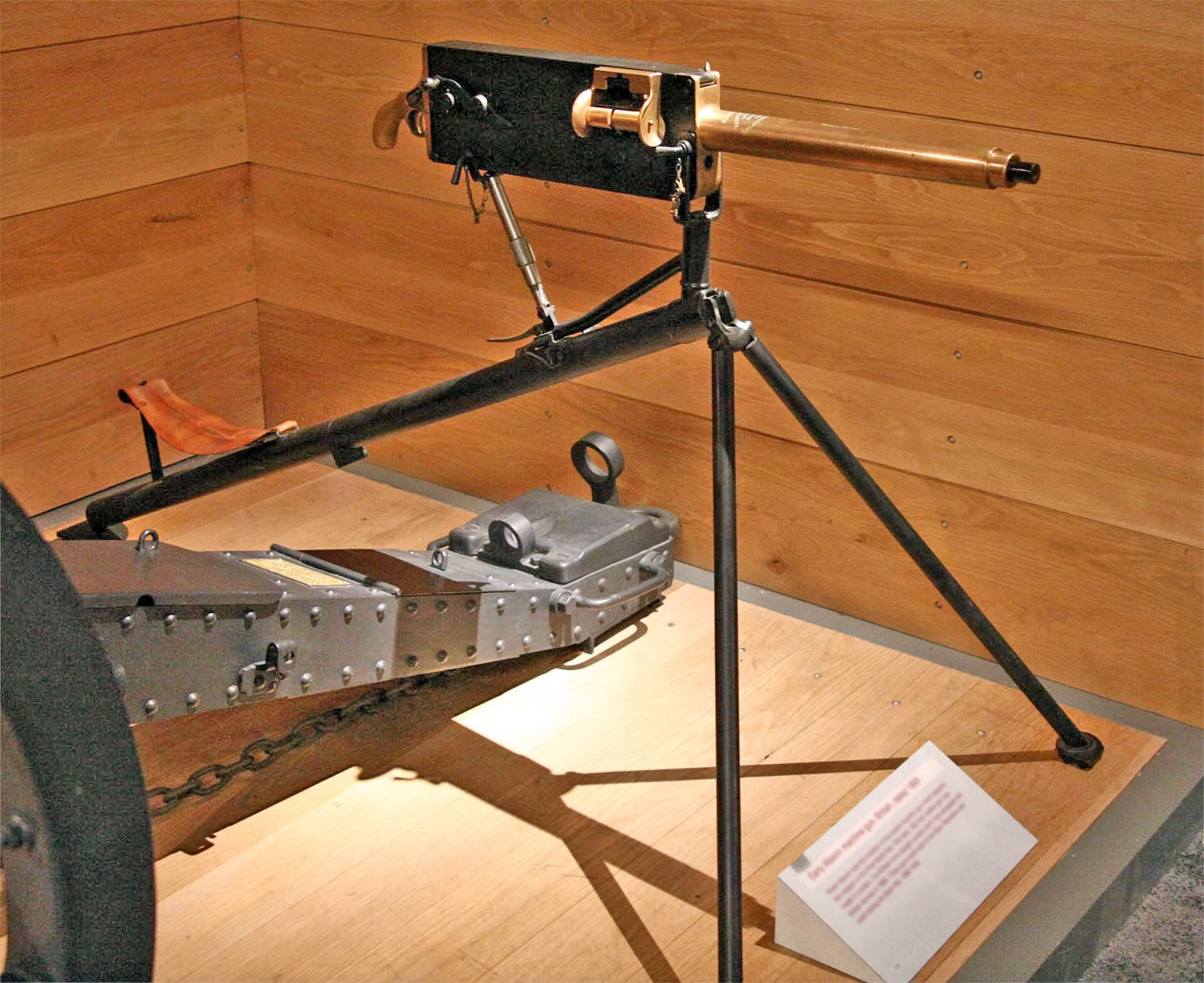
Maxim Gun
The Maxim gun is a Recoil operation, recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Maxim, Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first automatic firearm, fully automatic machine gun in the world. The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most associated with imperial conquest" by historian Martin Gilbert, and was heavily used by Colonialism, colonial powers during the "Scramble for Africa". Afterwards, Maxim guns also saw extensive usage by different armies during the Russo-Japanese War, the World War I, First and World War II, Second World Wars, as well as in contemporary conflicts. The Maxim gun was greatly influential in the development of machine guns, and it has multiple variants and derivatives. Design The Maxim gun featured one of the earliest recoil-operated firing systems in history. Energy from recoil acting on the breech block is used to eject each spent cartridge and insert the next one. Maxim's earliest designs used a 360-degree rotating cam to reverse the move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |