|
Quantile Plot
In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities or dividing the observations in a sample in the same way. There is one fewer quantile than the number of groups created. Common quantiles have special names, such as ''quartiles'' (four groups), '' deciles'' (ten groups), and ''percentiles'' (100 groups). The groups created are termed halves, thirds, quarters, etc., though sometimes the terms for the quantile are used for the groups created, rather than for the cut points. -quantiles are values that partition a finite set of values into subsets of (nearly) equal sizes. There are partitions of the -quantiles, one for each integer satisfying . In some cases the value of a quantile may not be uniquely determined, as can be the case for the median (2-quantile) of a uniform probability distribution on a set of even size. Quantiles can also be applied to continuous distribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentile Rank
In statistics, the percentile rank (PR) of a given score is the percentage of scores in its frequency distribution that are less than that score. Formulation Its mathematical formula is : PR = \frac \times 100, where ''CF''—the cumulative frequency—is the count of all scores less than or equal to the score of interest, ''F'' is the frequency for the score of interest, and ''N'' is the number of scores in the distribution. Alternatively, if ''CF'' is the count of all scores less than the score of interest, then : PR = \frac \times 100. Example The figure illustrates the percentile rank computation and shows how the 0.5 × ''F'' term in the formula ensures that the percentile rank reflects a percentage of scores less than the specified score. For example, for the 10 scores shown in the figure, 60% of them are below a score of 4 (five less than 4 and half of the two equal to 4) and 95% are below 7 (nine less than 7 and half of the one equal to 7). Occasionally the percentile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Score
In statistics, the standard score or ''z''-score is the number of standard deviations by which the value of a raw score (i.e., an observed value or data point) is above or below the mean value of what is being observed or measured. Raw scores above the mean have positive standard scores, while those below the mean have negative standard scores. It is calculated by subtracting the population mean from an individual raw score and then dividing the difference by the Statistical population, population standard deviation. This process of converting a raw score into a standard score is called standardizing or normalizing (however, "normalizing" can refer to many types of ratios; see ''Normalization (statistics), Normalization'' for more). Standard scores are most commonly called ''z''-scores; the two terms may be used interchangeably, as they are in this article. Other equivalent terms in use include z-value, z-statistic, normal score, standardized variable and pull in high energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic Mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean ( ), arithmetic average, or just the ''mean'' or ''average'' is the sum of a collection of numbers divided by the count of numbers in the collection. The collection is often a set of results from an experiment, an observational study, or a Survey (statistics), survey. The term "arithmetic mean" is preferred in some contexts in mathematics and statistics because it helps to distinguish it from other types of means, such as geometric mean, geometric and harmonic mean, harmonic. Arithmetic means are also frequently used in economics, anthropology, history, and almost every other academic field to some extent. For example, per capita income is the arithmetic average of the income of a nation's Human population, population. While the arithmetic mean is often used to report central tendency, central tendencies, it is not a robust statistic: it is greatly influenced by outliers (Value (mathematics), values much larger or smaller than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet editor developed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows, Windows, macOS, Android (operating system), Android, iOS and iPadOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro (computer science), macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Office suites of software and has been developed since 1985. Features Basic operation Microsoft Excel has the basic features of all spreadsheets, using a grid of ''cells'' arranged in numbered ''rows'' and letter-named ''columns'' to organize data manipulations like arithmetic operations. It has a battery of supplied functions to answer statistical, engineering, and financial needs. In addition, it can display data as line graphs, histograms and charts, and with a very limited three-dimensional graphical display. It allows sectioning of data to view its dependencies on various factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
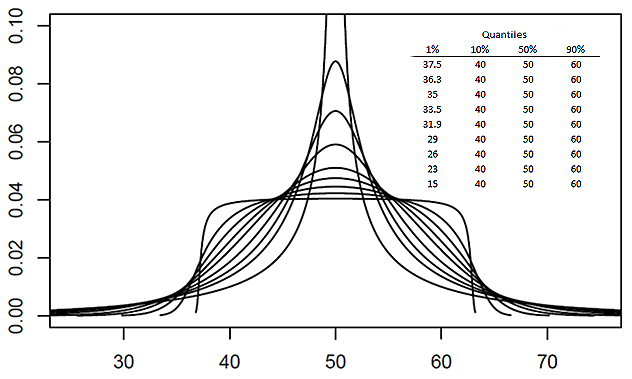
Quantile-parameterized Distribution
A quantile-parameterized distribution (QPD) is a probability distributions that is directly parameterized by data. They were created to meet the need for easy-to-use continuous probability distributions flexible enough to represent a wide range of uncertainties, such as those commonly encountered in business, economics, engineering, and science. Because QPDs are directly parameterized by data, they have the practical advantage of avoiding the intermediate step of Estimation theory, parameter estimation, a time-consuming process that typically requires non-linear iterative methods to estimate probability-distribution parameters from data. Some QPDs have virtually unlimited shape flexibility and closed-form moments as well. History The development of quantile-parameterized distributions was inspired by the practical need for flexible continuous probability distributions that are easy to fit to data. Historically, the Pearson distribution, Pearson and Norman Lloyd Johnson, Johnson fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real numbers are called irrational numbers. Some irrational numbers (as well as all the rationals) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estimating Quantiles From A Sample
Estimation (or estimating) is the process of finding an estimate or approximation, which is a value that is usable for some purpose even if input data may be incomplete, uncertain, or unstable. The value is nonetheless usable because it is derived from the best information available.C. Lon Enloe, Elizabeth Garnett, Jonathan Miles, ''Physical Science: What the Technology Professional Needs to Know'' (2000), p. 47. Typically, estimation involves "using the value of a statistic derived from a sample to estimate the value of a corresponding population parameter".Raymond A. Kent, "Estimation", ''Data Construction and Data Analysis for Survey Research'' (2001), p. 157. The sample provides information that can be projected, through various formal or informal processes, to determine a range most likely to describe the missing information. An estimate that turns out to be incorrect will be an overestimate if the estimate exceeds the actual result and an underestimate if the estimate fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a Function (mathematics), function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an Experiment (probability theory), experiment. It is a mathematical description of a Randomness, random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the Probability, probabilities of Event (probability theory), events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that fair coin, the coin is fair). More commonly, probability distributions are used to compare the relative occurrence of many different random values. Probability distributions can be defined in different ways and for discrete or for continuous variables. Distributions with special properties or for especially important applications are given specific names. Introduction A prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Population
In statistics, a population is a set of similar items or events which is of interest for some question or experiment. A statistical population can be a group of existing objects (e.g. the set of all stars within the Milky Way galaxy) or a hypothetical and potentially infinite group of objects conceived as a generalization from experience (e.g. the set of all possible hands in a game of poker). A population with finitely many values N in the support of the population distribution is a finite population with population size N. A population with infinitely many values in the support is called infinite population. A common aim of statistical analysis is to produce information about some chosen population. In statistical inference, a subset of the population (a statistical '' sample'') is chosen to represent the population in a statistical analysis. Moreover, the statistical sample must be unbiased and accurately model the population. The ratio of the size of this statistical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. The standard deviation is commonly used in the determination of what constitutes an outlier and what does not. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD or std dev, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lowercase Greek alphabet, Greek letter Sigma, σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin script, Latin letter ''s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, Sample (statistics), sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. (For a finite population, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Function
In mathematics, the inverse function of a function (also called the inverse of ) is a function that undoes the operation of . The inverse of exists if and only if is bijective, and if it exists, is denoted by f^ . For a function f\colon X\to Y, its inverse f^\colon Y\to X admits an explicit description: it sends each element y\in Y to the unique element x\in X such that . As an example, consider the real-valued function of a real variable given by . One can think of as the function which multiplies its input by 5 then subtracts 7 from the result. To undo this, one adds 7 to the input, then divides the result by 5. Therefore, the inverse of is the function f^\colon \R\to\R defined by f^(y) = \frac . Definitions Let be a function whose domain is the set , and whose codomain is the set . Then is ''invertible'' if there exists a function from to such that g(f(x))=x for all x\in X and f(g(y))=y for all y\in Y. If is invertible, then there is exactly one functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |