|
Qpel
Quarter-pixel motion ''(also known as Q-pel motion or Qpel motion)'' refers to using a quarter of the distance between pixels (or luma sample positions) as the motion vector precision for motion estimation and motion compensation in video compression schemes. It is used in many modern video coding formats such as MPEG-4 ASP and H.264/AVC. Though higher precision motion vectors take more bits to encode, they can sometimes result in more efficient compression overall, by increasing the quality of the prediction signal. Operation Video encoding software products such as Xvid, 3ivx, and DivX Pro Codec, which are based upon the MPEG-4 specification, use motion estimation algorithms to significantly improve video compression. The default level of resolution for motion estimation for most MPEG-4 ASP implementations is half a pixel, although quarter pixel is specified under the standard. H.264 decoders always support quarter-pixel motion. Quarter-pixel resolution can improve the qual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Compensation
Motion compensation in computing is an algorithmic technique used to predict a frame in a video given the previous and/or future frames by accounting for motion of the camera and/or objects in the video. It is employed in the encoding of video data for video compression, for example in the generation of files. Motion compensation describes a picture in terms of the transformation of a reference picture to the current picture. The reference picture may be previous in time or even from the future. When images can be accurately synthesized from previously transmitted/stored images, the compression efficiency can be improved. Motion compensation is one of the two key video compression techniques used in video coding standards, along with the discrete cosine transform (DCT). Most video coding standards, such as the H.26x and MPEG formats, typically use motion-compensated DCT hybrid coding, known as block motion compensation (BMC) or motion-compensated DCT (MC DCT). Functionality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
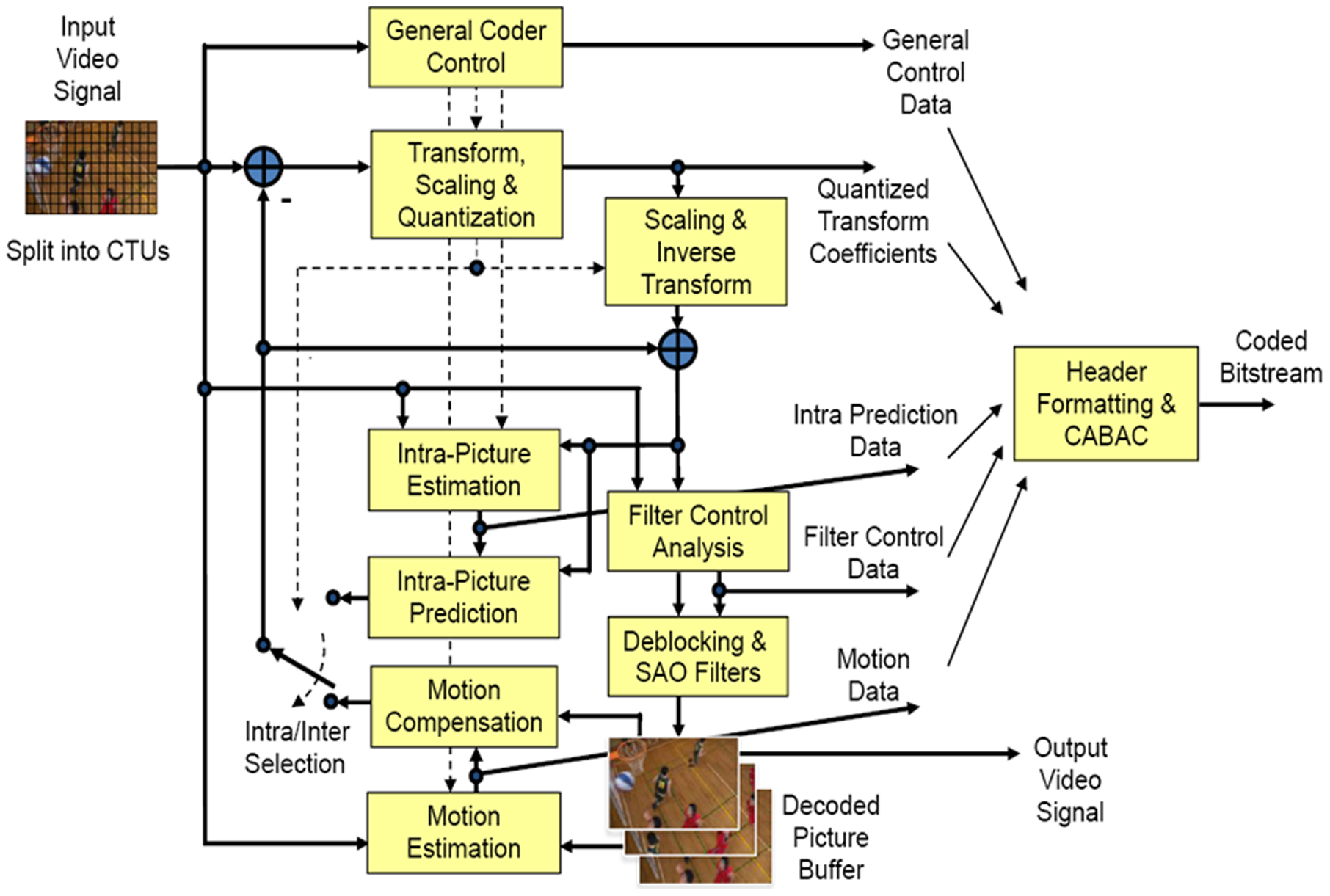
HEVC
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses both integer DCT and discrete sine transform (DST) with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an extension of the concepts in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Both work by comparing different parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 ASP
MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual (formally ISO/IEC 14496-2) is a video encoding specification designed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC family of encoders. It uses block-wise motion compensation and a discrete cosine transform (DCT), similar to previous encoders such as MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2. Examples of popular implementations of the encoder specifications include DivX, Xvid and Nero Digital. MPEG-4 Part 2 is H.263 compatible in the sense that a basic H.263 bitstream is correctly decoded by an MPEG-4 Video decoder. (MPEG-4 Video decoder is natively capable of decoding a basic form of H.263.) In MPEG-4 Visual, there are two types of video object layers: the video object layer that provides full MPEG-4 functionality, and a reduced functionality video object layer, the video object layer with short headers (which provides bitstream compatibility with base-line H.263). MPEG-4 Part 2 is partially based on ITU-T H.263. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a Sampling (signal processing), sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The Intensity (physics), intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as RGB color model, red, green, and blue, or CMYK color model, cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''wikt:sensel, sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
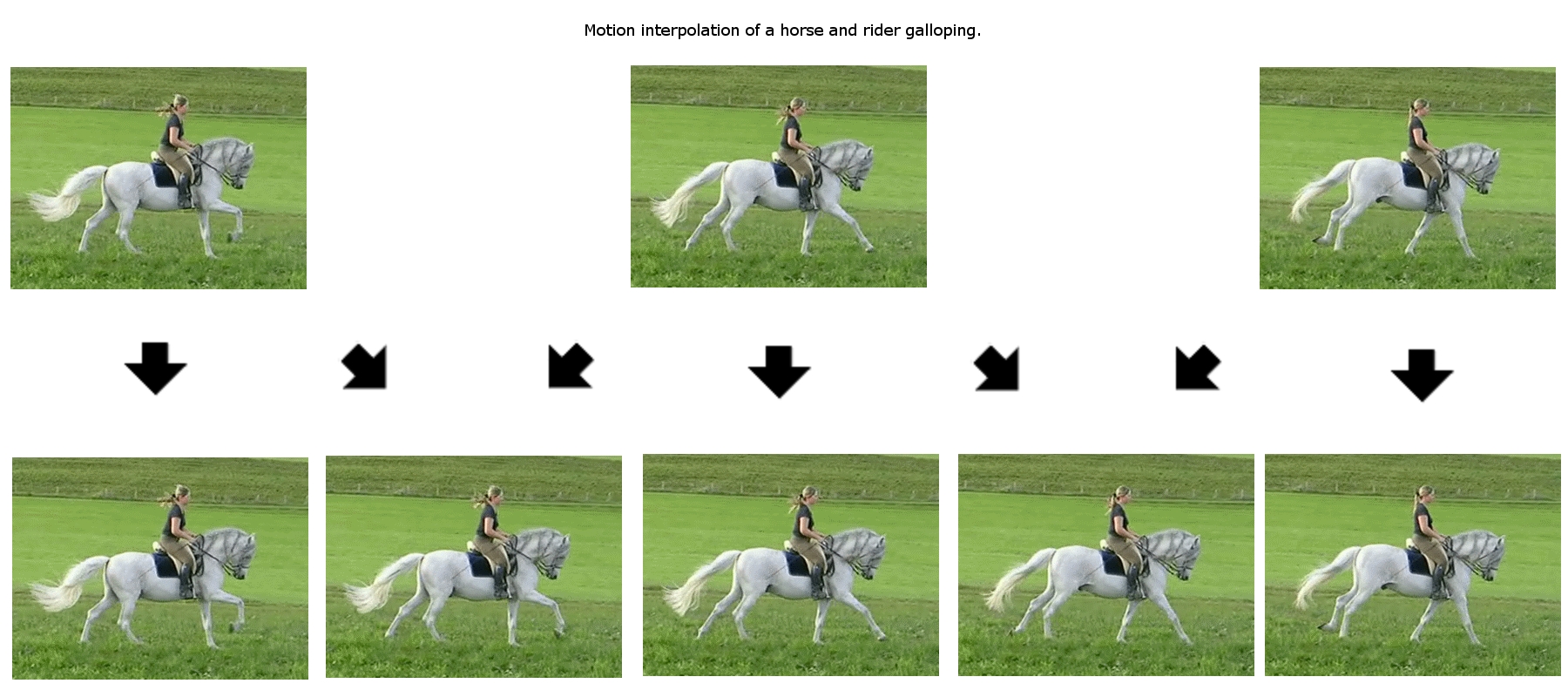
Interpolation (computer Graphics)
In the context of live-action and computer animation, interpolation is inbetweening,{{Cite web, url=https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/understanding-linear-interpolation-in-ui-animations-74701eb9957c/, title=Understanding Linear Interpolation in UI Animation, date=2017-05-14, website=Developer News, language=en, access-date=2019-08-26 or filling in frames between the key frames. It typically calculates the in-between frames through use of (usually) piecewise polynomial interpolation to draw images semi-automatically. For all applications of this type, a set of "key points" is defined by the graphic artist. These are values that are rather widely separated in space or time, and represent the desired result, but only in very coarse steps. The computed interpolation process is then used to insert many new values in between these key points to give a "smoother" result. In its simplest form, this is the drawing of two-dimensional curves. The key points, placed by the artist, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Codecs
The following is a list of compression formats and related codecs. Audio compression formats Non-compression * Linear pulse-code modulation (LPCM, generally only described as PCM) is the format for uncompressed audio in media files and it is also the standard for CD-DA; note that in computers, LPCM is usually stored in container formats such as WAV, AIFF, or AU, or as raw audio format, although not technically necessary. ** FFmpeg * Pulse-density modulation (PDM) ** Direct Stream Digital (DSD) is standard for Super Audio CD *** foobar2000 Super Audio CD Decoder (based on MPEG-4 DST reference decoder) *** FFmpeg (based on dsd2pcm) * Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) Lossless compression * Actively used ** Most popular *** Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC) **** libFLAC **** FFmpeg *** Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC) **** Apple QuickTime **** libalac **** FFmpeg **** Apple Music *** Monkey's Audio (APE) **** Monkey's Audio SDK **** FFmpeg (decoder only) *** OptimFROG (OFR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Interpolation
In mathematics, linear interpolation is a method of curve fitting using linear polynomials to construct new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points. Linear interpolation between two known points If the two known points are given by the coordinates (x_0,y_0) and the linear interpolant is the straight line between these points. For a value x in the interval the value y along the straight line is given from the equation of slopes \frac = \frac, which can be derived geometrically from the figure on the right. It is a special case of polynomial interpolation with Solving this equation for y, which is the unknown value at x, gives \begin y &= y_0 + (x-x_0)\frac \\ &= \frac + \frac\\ &= \frac \\ &= \frac, \end which is the formula for linear interpolation in the interval Outside this interval, the formula is identical to linear extrapolation. This formula can also be understood as a weighted average. The weights are inversely related to the dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicubic Interpolation
In mathematics, bicubic interpolation is an extension of cubic spline interpolation (a method of applying cubic interpolation to a data set) for interpolating data points on a two-dimensional regular grid. The interpolated surface (meaning the kernel shape, not the image) is smoother than corresponding surfaces obtained by bilinear interpolation or nearest-neighbor interpolation. Bicubic interpolation can be accomplished using either Lagrange polynomials, cubic splines, or cubic convolution algorithm. In image processing, bicubic interpolation is often chosen over bilinear or nearest-neighbor interpolation in image resampling, when speed is not an issue. In contrast to bilinear interpolation, which only takes 4 pixels (2×2) into account, bicubic interpolation considers 16 pixels (4×4). Images resampled with bicubic interpolation can have different interpolation artifacts, depending on the b and c values chosen. Computation Suppose the function values f and the deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VC-1
SMPTE 421, informally known as VC-1, is a video coding format. Most of it was initially developed as Microsoft's proprietary video format Windows Media Video 9 in 2003. With some enhancements including the development of a new Advanced Profile, it was officially approved as an SMPTE standard on April 3, 2006. It was primarily marketed as a lower-complexity competitor to the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard. After its development, several companies other than Microsoft asserted that they held patents that applied to the technology, including Panasonic, LG Electronics and Samsung Electronics. VC-1 is supported in the now-deprecated Microsoft Silverlight, the briefly-offered HD DVD disc format, and the Blu-ray Disc format. Format VC-1 is an evolution of the conventional block-based motion-compensated hybrid video coding design also found in H.261, MPEG-1 Part 2, H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2, H.263, and MPEG-4 Part 2. It was widely characterized as an alternative to the ITU-T and MPEG video ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a group of international standards for the compression of digital audio and visual data, multimedia systems, and file storage formats. It was originally introduced in late 1998 as a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) (ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC29/WG11) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496 – ''Coding of audio-visual objects''. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of audiovisual data for Internet video and CD distribution, voice (telephone, videophone) and broadcast television applications. The MPEG-4 standard was developed by a group led by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president) and Fernando Pereira. Background MPEG-4 absorbs many of the features of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 and other related standards, adding new features such as (extended) VRML support for 3D rendering, object-oriented composite files (including audio, video and VRML objects), support for externally specified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Vector
In computer vision and image processing, motion estimation is the process of determining ''motion vectors'' that describe the transformation from one 2D image to another; usually from adjacent frames in a video sequence. It is an ill-posed problem as the motion happens in three dimensions (3D) but the images are a projection of the 3D scene onto a 2D plane. The motion vectors may relate to the whole image (''global motion estimation'') or specific parts, such as rectangular blocks, arbitrary shaped patches or even per pixel. The motion vectors may be represented by a translational model or many other models that can approximate the motion of a real video camera, such as rotation and translation in all three dimensions and zoom. Related terms More often than not, the term motion estimation and the term ''optical flow'' are used interchangeably. It is also related in concept to ''image registration'' and ''stereo correspondence''. In fact all of these terms refer to the process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |