|
Polyalphabetic Substitution
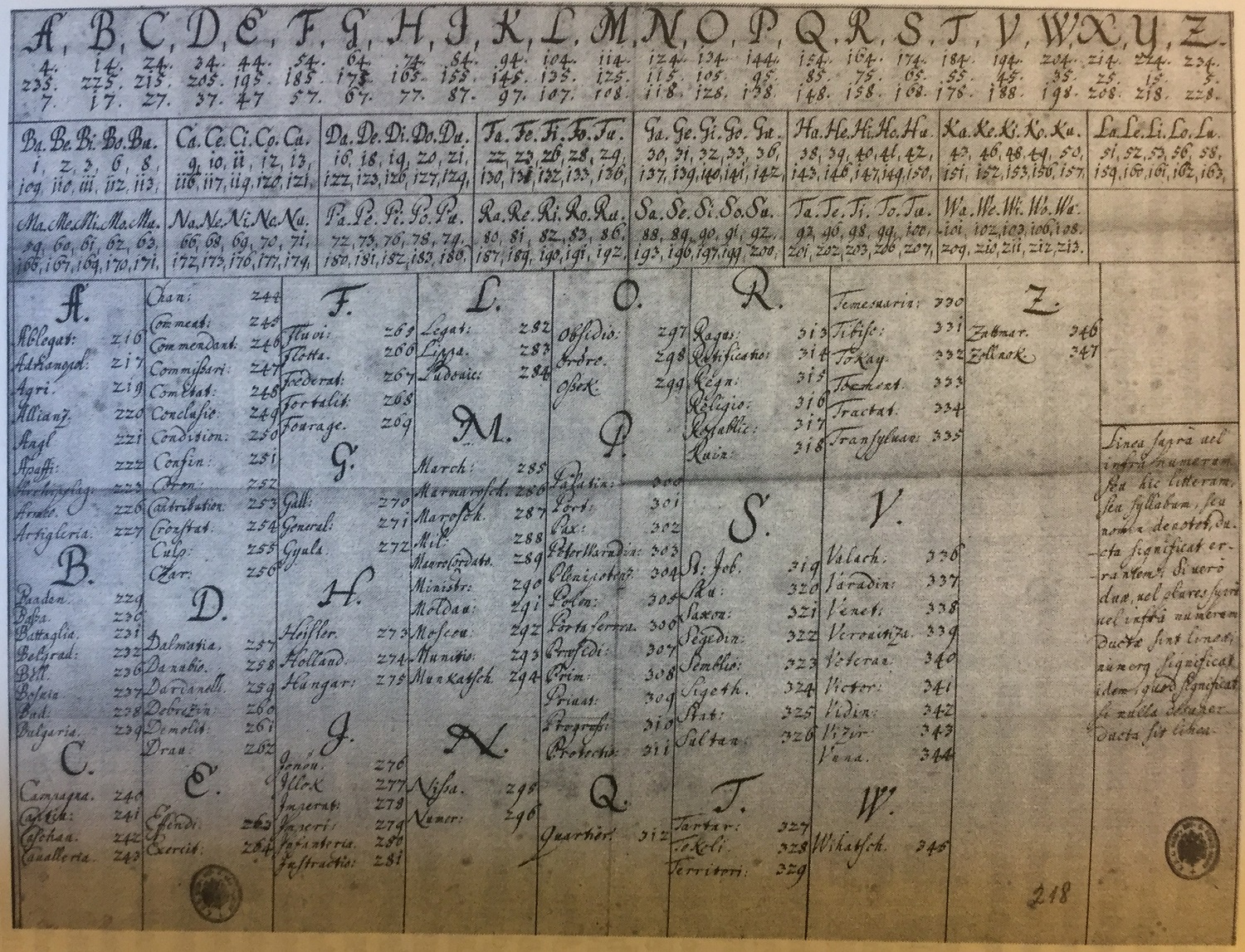
A polyalphabetic cipher substitution, using multiple substitution alphabets. The Vigenère cipher is probably the best-known example of a polyalphabetic cipher, though it is a simplified special case. The Enigma machine is more complex but is still fundamentally a polyalphabetic substitution cipher. History The work of Al-Qalqashandi (1355–1418), based on the earlier work of Ibn al-Durayhim (1312–1359), contained the first published discussion of the substitution and transposition of ciphers, as well as the first description of a polyalphabetic cipher, in which each plaintext letter is assigned more than one substitute. However, it has been claimed that polyalphabetic ciphers may have been developed by the Arab cryptologist Al Kindi (801–873) centuries earlier. The Alberti cipher by Leon Battista Alberti around 1467 was an early polyalphabetic cipher. Alberti used a mixed alphabet to encrypt a message, but whenever he wanted to, he would switch to a different alphabet, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitution Cipher
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encrypting in which units of plaintext are replaced with the ciphertext, in a defined manner, with the help of a key; the "units" may be single letters (the most common), pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth. The receiver deciphers the text by performing the inverse substitution process to extract the original message. Substitution ciphers can be compared with transposition ciphers. In a transposition cipher, the units of the plaintext are rearranged in a different and usually quite complex order, but the units themselves are left unchanged. By contrast, in a substitution cipher, the units of the plaintext are retained in the same sequence in the ciphertext, but the units themselves are altered. There are a number of different types of substitution cipher. If the cipher operates on single letters, it is termed a simple substitution cipher; a cipher that operates on larger groups of letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vigenère Square Shading , a cipher whose invention was later misattributed to Vigenère
{{Disambig ...
Vigenère may refer to: *Blaise de Vigenère, a 16th-century French cryptographer *The Vigenère cipher The Vigenère cipher () is a method of encrypting alphabetic text by using a series of interwoven Caesar ciphers, based on the letters of a keyword. It employs a form of polyalphabetic substitution. First described by Giovan Battista Bella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Ciphers
Classical may refer to: European antiquity *Classical antiquity, a period of history from roughly the 7th or 8th century B.C.E. to the 5th century C.E. centered on the Mediterranean Sea *Classical architecture, architecture derived from Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity *Classical mythology, the body of myths from the ancient Greeks and Romans *Classical tradition, the reception of classical Greco-Roman antiquity by later cultures *Classics, study of the language and culture of classical antiquity, particularly its literature *Classicism, a high regard for classical antiquity in the arts Music and arts *Classical ballet, the most formal of the ballet styles *Classical music, a variety of Western musical styles from the 9th century to the present *Classical guitar, a common type of acoustic guitar *Classical Hollywood cinema Classical Hollywood cinema is a term used in film criticism to describe both a narrative and visual style of filmmaking which became cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topics In Cryptography
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cryptography: Cryptography (or cryptology) – practice and study of hiding information. Modern cryptography intersects the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, and engineering. Applications of cryptography include ATM cards, computer passwords, and electronic commerce. Essence of cryptography * Cryptographer * Encryption/decryption * Cryptographic key * Cipher * Ciphertext * Plaintext * Code * Tabula recta * Alice and Bob Uses of cryptographic techniques * Commitment schemes * Secure multiparty computation * Electronic voting * Authentication * Digital signatures * Crypto systems * Dining cryptographers problem * Anonymous remailer * Pseudonymity * Onion routing * Digital currency * Secret sharing * Indistinguishability obfuscation Branches of cryptography * Multivariate cryptography * Post-quantum cryptography * Quantum cryptography * Steganography * Visual cryptography Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Kahn (writer)
David Kahn (b. February 7, 1930* ) is an American historian, journalist, and writer. He has written extensively on the history of cryptography and military intelligence. Kahn's first published book, '' The Codebreakers - The Story of Secret Writing'' (1967), has been widely considered to be a definitive account of the history of cryptography. Biography David Kahn was born in New York City to Florence Abraham Kahn, a glass manufacturer, and Jesse Kahn, a lawyer. Kahn has said he traces his interest in cryptography to reading Fletcher Pratt's ''Secret and Urgent'' as a boy. Kahn is a founding editor of the ''Cryptologia'' journal. In 1969, Kahn married Susanne Fiedler; they are now divorced. They have two sons, Oliver and Michael. He attended Bucknell University. After graduation, he worked as a reporter at ''Newsday''. He also served as an editor at the ''International Herald Tribune'' in Paris in the 1960s. It was during this period that he wrote an article for the '' N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasiski Examination
In cryptanalysis, Kasiski examination (also referred to as Kasiski's test or Kasiski's method) is a method of attacking polyalphabetic substitution ciphers, such as the Vigenère cipher. It was first published by Friedrich Kasiski in 1863, but seems to have been independently discovered by Charles Babbage as early as 1846. How it works In polyalphabetic substitution ciphers where the substitution alphabets are chosen by the use of a keyword, the Kasiski examination allows a cryptanalyst to deduce the length of the keyword. Once the length of the keyword is discovered, the cryptanalyst lines up the ciphertext in ''n'' columns, where ''n'' is the length of the keyword. Then each column can be treated as the ciphertext of a monoalphabetic substitution cipher. As such, each column can be attacked with frequency analysis. Similarly, where a rotor stream cipher machine has been used, this method may allow the deduction of the length of individual rotors. The Kasiski examination i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown. In addition to mathematical analysis of cryptographic algorithms, cryptanalysis includes the study of side-channel attacks that do not target weaknesses in the cryptographic algorithms themselves, but instead exploit weaknesses in their implementation. Even though the goal has been the same, the methods and techniques of cryptanalysis have changed drastically through the history of cryptography, adapting to increasing cryptographic complexity, ranging from the pen-and-paper methods of the past, through machines like the British Bombes and Colossus computers at Bletchley Park in World War II, to the mathematically advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Kasiski
Major Friedrich Wilhelm Kasiski (29 November 1805 – 22 May 1881) was a German infantry officer, cryptographer and archeologist. Kasiski was born in Schlochau, Kingdom of Prussia (now Człuchów, Poland). Military service Kasiski enlisted in East Prussia's 33rd Infantry Regiment on 20 March 1823 at the age of 17. In May 1824, he was promoted to the rank of Master Sergeant, and eight months later was commissioned as a Second Lieutenant in February 1825. It took fourteen years to earn his next promotion when, in May 1839, he advanced to the rank of First Lieutenant. His next advancement was quicker, promoted to Captain in November 1842. Kasiski finally retired from active service with the rank of Major on 17 February 1852. Between 1860 and 1868 he was the commander of a National Guard battalion. Cryptography In 1863, Kasiski published a 95-page book on cryptography, ''Die Geheimschriften und die Dechiffrir-Kunst'' (German, "Secret writing and the Art of Deciphering"). This wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia. Geopolitical causes of the war included the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the expansion of the Russian Empire in the preceding Russo-Turkish Wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a disagreement over the rights of Christian minorities in Palestine, then part of the Ottoman Empire, with the French promoting the rights of Roman Catholics, and Russia promoting those of the Eastern Orthodox Church. The churches worked out their differences with the Ottomans and came to an agreement, but both the French Emperor Napoleon III and the Russian Tsar Nicholas I refused to back down. Nicholas issued an ultimatum that demanded the Orthodox subjects of the Ottoman Empire be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. Babbage is considered by some to be " father of the computer". Babbage is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the Difference Engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in Babbage's Analytical Engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. Babbage had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. His varied work in other fields has led him to be described as "pre-eminent" among the many polymaths of his century. Babbage, who died before the complete successful engineering of many of his designs, including his Difference Engine and Analytical En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Analysis
In cryptanalysis, frequency analysis (also known as counting letters) is the study of the frequency of letters or groups of letters in a ciphertext. The method is used as an aid to breaking classical ciphers. Frequency analysis is based on the fact that, in any given stretch of written language, certain letters and combinations of letters occur with varying frequencies. Moreover, there is a characteristic distribution of letters that is roughly the same for almost all samples of that language. For instance, given a section of English language, , , and are the most common, while , , and are rare. Likewise, , , , and are the most common pairs of letters (termed '' bigrams'' or ''digraphs''), and , , , and are the most common repeats. The nonsense phrase " ETAOIN SHRDLU" represents the 12 most frequent letters in typical English language text. In some ciphers, such properties of the natural language plaintext are preserved in the ciphertext, and these patterns have the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_School_-_Charles_Babbage_(1792–1871)_-_814168_-_National_Trust.jpg)