|
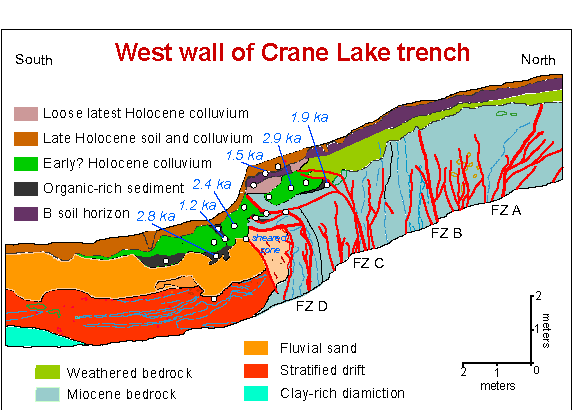
Paleoseismology
Paleoseismology looks at geologic sediments and rocks, for signs of ancient earthquakes. It is used to supplement seismic monitoring, for the calculation of seismic hazard. Paleoseismology is usually restricted to geologic regimes that have undergone continuous sediment creation for the last few thousand years, such as swamps, lakes, river beds and shorelines. In this typical example, a trench is dug in an active sedimentation regime. Evidence of thrust faulting can be seen in the walls of the trench. It becomes a matter of deducting the relative age of each fault, by cross-cutting patterns. The faults can be dated in absolute terms, if there is dateable carbon, or human artifacts. Many notable discoveries have been made using the techniques of paleoseismology. For example, there is a common misconception that having many smaller earthquakes can somehow 'relieve' a major fault such as the San Andreas Fault, and reduce the chance of a major earthquake. It is now known ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Hazard
A seismic hazard is the probability that an earthquake will occur in a given geographic area, within a given window of time, and with ground motion intensity exceeding a given threshold. With a hazard thus estimated, risk can be assessed and included in such areas as building codes for standard buildings, designing larger buildings and infrastructure projects, land use planning and determining insurance rates. The seismic hazard studies also may generate two standard measures of anticipated ground motion, both confusingly abbreviated MCE; the simpler probabilistic Maximum Considered Earthquake (or Event ), used in standard building codes, and the more detailed and deterministic Maximum Credible Earthquake incorporated in the design of larger buildings and civil infrastructure like dams or bridges. It is important to clarify which MCE is being discussed. Calculations for determining seismic hazard were first formulated by C. Allin Cornell in 1968 and, depending on their l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megathrust Earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (''Mw'') that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes. The thrust faults responsible for megathrust earthquakes often lie at the bottom of oceanic trenches; in such cases, the earthquakes can abruptly displace the sea floor over a large area. As a result, megathrust earthquakes often generate tsunamis that are considerably more destructive than the earthquakes themselves. Teletsunamis can cross ocean basins to devastate areas far from the original earthquake. Terminology and mechanism The term ''megathrust'' refers to an extremely large thrust fault, typically formed at the plate interface along a subduction zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismite
{{Earthquakes Seismites are sedimentary beds and structures deformed by seismic shaking. The German paleontologist Adolf Seilacher first used the term in 1969 to describe earthquake-deformed layers. Today, the term is applied to both sedimentary ''layers'' and soft sediment deformation ''structures'' formed by shaking. This subtle change in usage accommodates structures that may not remain within a layer (i.e., clastic dikes or sand volcanos). Caution is urged when applying the term to features observed in the field, as similar-looking features may be products of either seismic or non-seismic perturbation. Several informal classification systems exist to help geologists distinguish seismites from other soft-sediment deformation features, though a formal, standardized system has not been developed. Geologists use seismites, in combination with other evidence, to better understand the earthquake history of an area. If age and distribution of seismically-generated features can be d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleotempestology
Paleotempestology is the study of past tropical cyclone activity by means of geological proxies as well as historical documentary records. The term was coined by American meteorologist Kerry Emanuel. The usual approach in paleotempestology is the identification of deposits left by storms. Most commonly, these are overwash deposits in waterbodies close to the coast; other means are oxygen isotope ratio variations caused by tropical cyclone rainfall in trees or speleothems (cave deposits), and identifying beach ridges kicked up by storm waves. The occurrence rate of tropical cyclones can then be inferred from these deposits and sometimes also their intensity – typically the stronger events are the most easily recognizable ones –, by comparing them to deposits left by historical events. Paleotempestological research has shown that in the Coast of the Gulf of Mexico and in Australia, the occurrence rate of intense tropical cyclones is about once every few centuries, and ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeoseismology
Archaeoseismology is the study of past earthquakes deriving from the analysis of archaeological sites. Such analyses reveal information about seismic events that have not been historically recorded. Such data can also help to document seismic risk in areas subject to extremely destructive earthquakes. In 1991, an international conference held in Athens marked the beginning of modern research in the field of archaeoseismology, described as a "study of ancient earthquakes, and their social, cultural, historical and natural effects". The main idea Earthquakes that happened during the far past hide a particularly important information for a regional seismic risk assessment. We have quantitative data concerning past earthquakes only from the beginning of the 20 century (as the invention of the seismograph is from the very late 19 century), but humanity is forced to deal with earthquakes since the very beginning of its time. So, we have an extremely limited information to deal with a reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
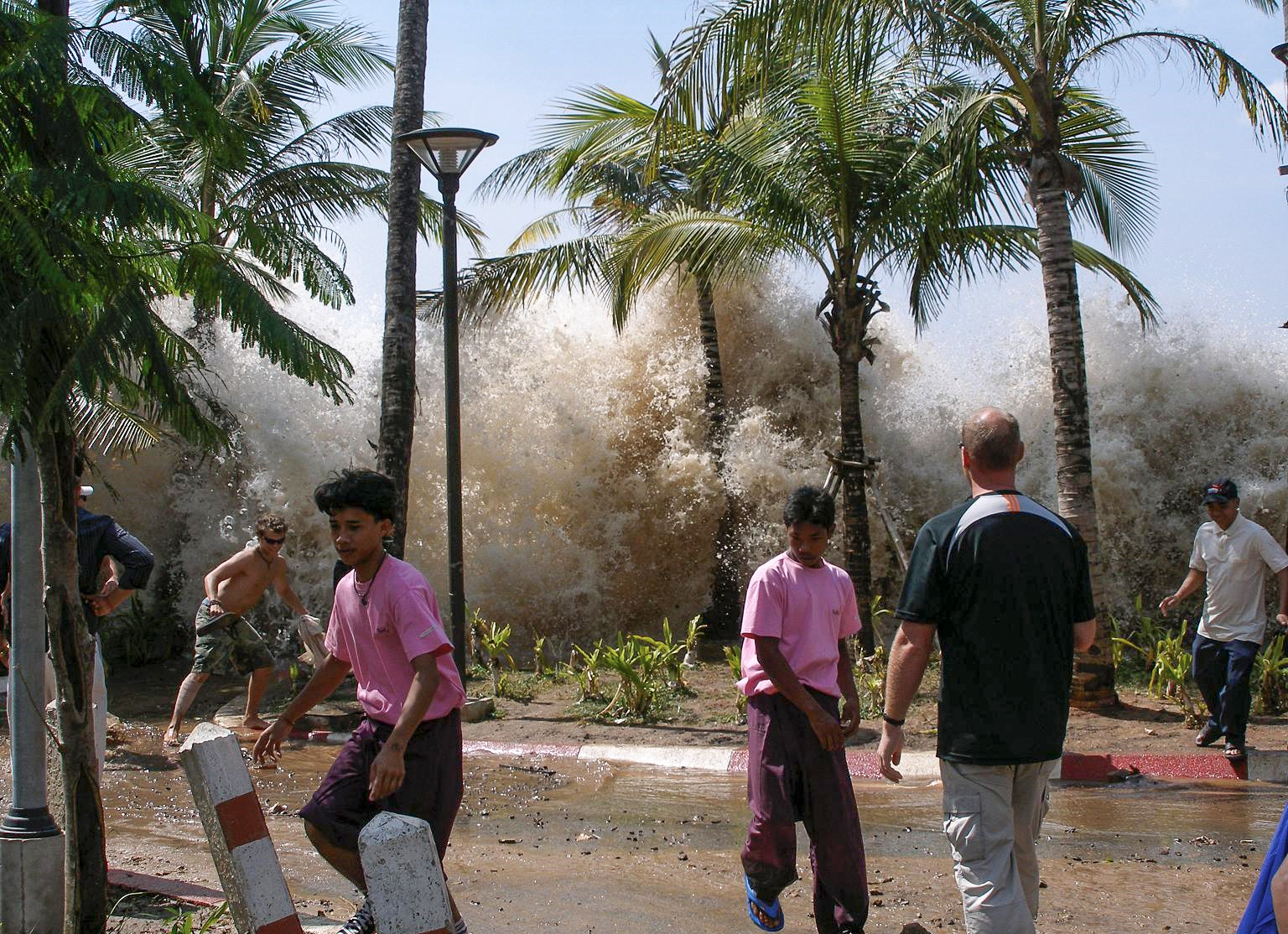
Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |