|
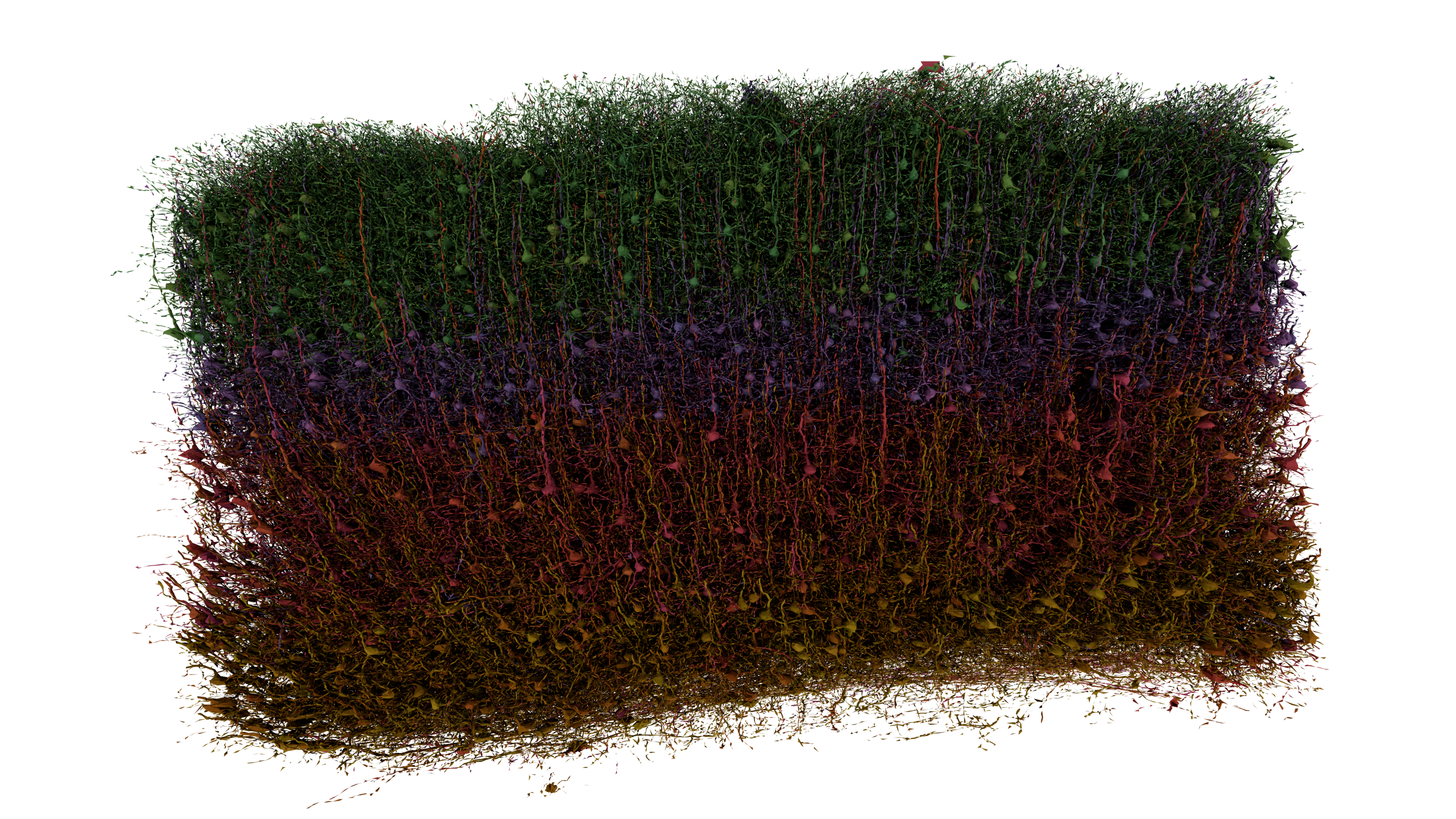
Pyramidal Neuron
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal cells are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cortex and the corticospinal tract. One of the main structural features of the pyramidal neuron is the conic shaped soma (biology), soma, or cell body, after which the neuron is named. Other key structural features of the pyramidal cell are a single axon, a large apical dendrite, multiple basal dendrites, and the presence of dendritic spines. Pyramidal neurons are also one of two cell types where the pathognomonic, characteristic Medical sign, sign, Negri bodies, are found in post-mortem rabies infection. Pyramidal neurons were first discovered and studied by Santiago Ramón y Cajal. Since then, studies on pyramidal neurons have focused on topics ranging from neuroplasticity to cognition. Structure One of the main structural features of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning, and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the cerebral cortex consists of the larger neocortex and the smaller allocortex, respectively taking up 90% and 10%. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisation and number of layers, of the cerebral tissues. The neocortex cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Spines
A dendritic spine (or spine) is a small membrane protrusion from a neuron's dendrite that typically receives input from a single axon at the synapse. Dendritic spines serve as a storage site for synaptic strength and help transmit electrical signals to the neuron's cell body. Most spines have a bulbous head (the spine head), and a thin neck that connects the head of the spine to the shaft of the dendrite. The dendrites of a single neuron can contain hundreds to thousands of spines. In addition to spines providing an anatomical substrate for memory storage and synaptic transmission, they may also serve to increase the number of possible contacts between neurons. It has also been suggested that changes in the activity of neurons have a positive effect on spine morphology. Structure Dendritic spines are small with spine head volumes ranging 0.01 μm3 to 0.8 μm3. Spines with strong synaptic contacts typically have a large spine head, which connects to the dendrite via a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progenitor Cells
A progenitor cell is a Cell (biology), biological cell that can Cellular differentiation, differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cell, Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only differentiate into their "target" cell type. The most important difference between stem cells and progenitor cells is that stem cells can replicate indefinitely, whereas progenitor cells can divide only a limited number of times. Controversy about the exact definition remains and the concept is still evolving. The terms "progenitor cell" and "stem cell" are sometimes equated. Properties Most progenitors are identified as Oligopotency, oligopotent. In this point of view, they can compare to adult stem cells, but progenitors are said to be in a further stage of cell differentiation. They are "midway" between stem cells and fully differentiated cells. The kind of potency they have depends on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential, caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell, is a result of opening ligand-gated ion channels. These are the opposite of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), which usually result from the flow of ''negative'' ions into the cell or positive ions ''out'' of the cell. EPSPs can also result from a decrease in outgoing positive charges, while IPSPs are sometimes caused by an increase in positive charge outflow. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC). EPSPs, like IPSPs, are graded (i.e. they have an additive effect). When multiple EPSPs occur on a single patch of postsynaptic membrane, their combined effect is the sum of the individual EPSPs. Larger EPSPs result in greater membra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Spines
A dendritic spine (or spine) is a small membrane protrusion from a neuron's dendrite that typically receives input from a single axon at the synapse. Dendritic spines serve as a storage site for synaptic strength and help transmit electrical signals to the neuron's cell body. Most spines have a bulbous head (the spine head), and a thin neck that connects the head of the spine to the shaft of the dendrite. The dendrites of a single neuron can contain hundreds to thousands of spines. In addition to spines providing an anatomical substrate for memory storage and synaptic transmission, they may also serve to increase the number of possible contacts between neurons. It has also been suggested that changes in the activity of neurons have a positive effect on spine morphology. Structure Dendritic spines are small with spine head volumes ranging 0.01 μm3 to 0.8 μm3. Spines with strong synaptic contacts typically have a large spine head, which connects to the dendrite via a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from very different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) are synthesized in the developing field of cognitive science, a progressively autonomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity or just plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through neurogenesis, growth and reorganization. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize and rewire its neural connections, enabling it to adapt and function in ways that differ from its prior state. This process can occur in response to learning new skills, experiencing environmental changes, recovering from injuries, or adapting to sensory or cognitive deficits. Such adaptability highlights the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the brain, even into adulthood. These changes range from individual neuron pathways making new connections, to systematic adjustments like cortical remapping or neural oscillation. Other forms of neuroplasticity include homologous area adaptation, cross modal reassignment, map expansion, and compensatory masquerade. Examples of neuroplasticity include neural circuit, circuit and network changes that result fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago Ramón Y Cajal
Santiago Ramón y Cajal (; 1 May 1852 – 17 October 1934) was a Spanish neuroscientist, pathologist, and histologist specializing in neuroanatomy, and the central nervous system. He and Camillo Golgi received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1906. Ramón y Cajal was the first Spaniard to win a scientific Nobel Prize. His original investigations of the microscopic structure of the brain made him a pioneer of modern neuroscience. Hundreds of his drawings illustrating the arborization (tree-like growth) of brain cells are still in use, since the mid-20th century, for educational and training purposes. Biography Santiago Ramón y Cajal was born on 1 May 1852, in the town of Petilla de Aragón, Navarre, Spain. As a child he was transferred many times from one school to another because of behavior that was declared poor, rebellious, and anti-authoritarian. An extreme example of his precociousness and rebelliousness at the age of eleven is his 1863 imprisonment for des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-mortem
An autopsy (also referred to as post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death; or the exam may be performed to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present for research or educational purposes. The term ''necropsy'' is generally used for non-human animals. Autopsies are usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathology, pathologist. Only a small portion of deaths require an autopsy to be performed, under certain circumstances. In most cases, a medical examiner or coroner can determine the cause of death. Purposes of performance Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. Autopsies can be performed when any of the following information is desired: * Manner of death must be determined ** Determine if death was natural or unnatural ** Injury source and extent on the corpse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |