|
Protists
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic rank, taxonomic kingdom (biology), kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroup (biology), supergroups, such as Archaeplastida (photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR supergroup, SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and "Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic diversity, genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
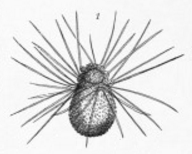
Dinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey ( phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, '' Oodinium'' and '' Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates produce resting stages, called dinoflagellate cys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telonemia
Telonemia is a phylum of microscopic eukaryotes commonly known as telonemids. They are unicellular free-living flagellates with a unique combination of Cell (biology), cell structures, including a highly complex cytoskeleton unseen in other eukaryotes. Telonemia shares several distinctive features with its related group, the SAR supergroup, SAR Supergroup (biology), supergroup. Among these features are cortical alveoli, small sacs beneath the cell's surface that act as cushions, providing support and helping to maintain the cell's shape. Additionally, they possess tripartite mastigonemes, complex three-part hair-like structures on their flagella, the whip-like tails used for movement. These structures enhance their swimming capabilities by increasing resistance against water. Furthermore, Telonemia is equipped with filopodia, very thin, thread-like projections extending from the cell body. These projections can serve various purposes, such as aiding in movement or capturing foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphoretickes
Diaphoretickes is a major group of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms spanning over 400,000 species. The majority of the earth's biomass that carries out photosynthesis belongs to Diaphoretickes. In older classification systems, members of the Diaphoretickes were variously placed in the Kingdom (biology), kingdoms Protozoa or Protist, Protista. Etymology The name Diaphoretickes derives (''diaforetikés'') meaning diverse, dissimilar, referring to the wide morphology (biology), morphological and cellular diversity among members of this clade. History Eukaryotes, organisms whose cells contain a cell nucleus, nucleus, have been traditionally grouped into four kingdom (biology), kingdoms: animals, plants, fungi and protists. In the late 20th century, molecular phylogenetic analyses revealed that protists are a paraphyletic assortment of many independent evolutionary lineages or clades, from which animals, fungi and plants evolved. However, the relationships between these clades re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoba
Excavata is an obsolete, extensive and diverse Paraphyly, paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryote, Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic protists, and includes some important parasites of humans such as ''Giardia'' and ''Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now- obsolete Protist, Protista kingdom. They were distinguished from other lineages based on electron-microscopic information about how the cells are arranged (they have a distinctive ultrastructural identity). They are considered to be a Basal_(phylogenetics), basal flagellate lineage. On the basis of phylogenomic analyses, the group was shown to contain three widely separated eukaryote groups, the discobids, metamonads, and malawimonads. A current view of the composition of the excavates is given below, indicating that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopodia, pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major Lineage (evolution), lineage of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the Class (biology), class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of Unicellular organism, single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stramenopiles
The stramenopiles, also called heterokonts, are Protist, protists distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost (in which case relatedness to stramenopile ancestors is evident from other shared cytological features or from genetic similarity). Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, SAR Supergroup (biology), supergroup, along with Alveolate, Alveolata and Rhizaria. Stramenopiles are Eukaryote, eukaryotes; most are single-celled, but some are multicellular including some large seaweeds, the brown algae. The group includes a variety of algal protists, heterotrophic flagellates, opalines and closely related proteromonad flagellates (all Endosymbiont, endobionts in other organisms); the actinophryid Heliozoa, and oomycetes. The tripartite hairs characteristic of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeplastida
The Archaeplastida (or kingdom Plantae '' sensu lato'' "in a broad sense"; pronounced ) are a major group of eukaryotes, comprising the photoautotrophic red algae (Rhodophyta), green algae, land plants, and the minor group glaucophytes. It also includes the non-photosynthetic lineage Rhodelphidia, a predatorial (eukaryotrophic) flagellate that is sister to the Rhodophyta, and probably the microscopic picozoans. The Archaeplastida have chloroplasts that are surrounded by two membranes, suggesting that they were acquired directly through a single endosymbiosis event by phagocytosis of a cyanobacterium. All other groups which have chloroplasts, besides the amoeboid genus '' Paulinella'', have chloroplasts surrounded by three or four membranes, suggesting they were acquired secondarily from red or green algae. Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes have never been involved in secondary endosymbiosis events. The cells of the Archaeplastida typically lack centrioles and have mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provora
Provora is a supergroup of eukaryotes made up of predatory microbes, whose name implies something such as "protists devouring voraciously". It was reported that ten strains were isolated and cultured in 2022. They are predators of other microorganisms. Their discovery was very delayed, compared to other microorganisms in their environments, due to their rarity. Their 18S ribosomal RNA is very different from that of other eukaryotes consistent with their being a lineage without known close relatives; this was confirmed by phylogenomic analyses of datasets of several hundred proteins, so they were taxonomically placed in a separate supergroup. Evolution External relationships The supergroup Provora is composed of microbes that form an ancient lineage of eukaryotes. The initial phylogenetic analyses recovered a position within the larger supergroup Diaphoretickes, particularly as sister to the protist groups TSAR and Haptista. However, a 2024 phylogenomic analysis recovered Provo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
SAR is a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and rhizarians. It is a node-based taxon (under the Sar name), including all descendants of the three groups' last common ancestor, and comprises most of the now-rejected Chromalveolata. Their sister group has been found to be telonemids, with which they make up the TSAR clade. Harosa is sometimes used synonymously with TSAR. Etymology The name SAR is an acronym derived from the first letters of its three constituent clades; it has been alternatively spelled RAS. The term Harosa (at the subkingdom level) has also been used, with Stramenopiles replaced by its synonym Heterokonta in this variant of the acronym. History of discovery Before the discovery of the SAR supergroup, stramenopiles and alveolates were classified in the supergroup Chromalveolata alongside haptophytes and cryptomonads, being believed to have acquired plastids th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haptista
Haptista is a proposed group of protists made up of centrohelids and haptophytes. Phylogenomic studies indicate that Haptista, together with ''Ancoracysta twista'', forms a sister clade to the SAR supergroup#Internal phylogeny, TSAR Supergroup (biology), supergroup, but it may also be sister to the Cryptista (+Archaeplastida). It is thus one of the earliest diverging Diaphoretickes. Taxonomy Based on studies done by Cavalier-Smith, Chao & Lewis 2015 and Ruggiero et al. 2015. * Subphylum Centroheliozoa Cushman & Jarvis 1929 sensu Durrschmidt & Patterson 1987 [Heliozoa Haeckel 1862 stat. n. Margulis 1974 em. Cavalier-Smith 2003] ** Class Centrohelea Kuhn 1926 stat. n. Cavalier-Smith 1993 [Centroplastiales; Centrohelina Hartmann 1913; Centroplasthelida Febvre-Chevalier 1984] * Subphylum Haptophyte, Haptophytina Cavalier-Smith 2015 (Haptophyta Hibberd 1976 sensu Ruggerio et al. 2015) ** Clade Rappemonada Kim et al. 2011 *** Class Rappephyceae Cavalier-Smith 2015 ** Clade Haptomonada ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancyromonadida
Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated eukaryotes found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013)Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and classification of the protozoan phyla Loukozoa, Sulcozoa, and Choanozoa European journal of protistology, 49(2), 115-178. They are freshwater or marine organisms, benthic, dorsoventrally compressed and with two unequal flagellae, each emerging from a separate pocket. The apical anterior flagellum can be very thin or end in the cell membrane, while the posterior flagellum is long and is inserted ventrally or laterally. The cell membrane is supported by a thin single-layered theca and the mitochondrial crests are discoidal/flat. The group's placement is doubtful, as it seems to fall outside the five supergroups of eukaryotes. Cavalier-Smith considers that they constitute a basal group to Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta and places it togeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |