|
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases. Proteolysis can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks Covalent bond, bonds. Proteases are involved in numerous biological pathways, including Digestion#Protein digestion, digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism (breakdown of old proteins), and cell signaling. In the absence of functional accelerants, proteolysis would be very slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteases can be found in all forms of life and viruses. They have independently convergent evolution, evolved multiple times, and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms. Classification Based on catalytic residue Proteases can be classified into seven broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside Cell (biology), cells, homeostasis, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via Proteolysis, degradation or Protein targeting, export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences. Protein synthesis can be divided broadly into two phases: Transcription (biology), transcription and Translation (biology), translation. During transcription, a section of DNA encoding a protein, known as a gene, is converted into a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out by enzymes, known as RNA polymerases, in the cell nucleus, nucleus of the cell. In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form (Primary transcript, pre-mRNA) which undergoes post-transcriptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
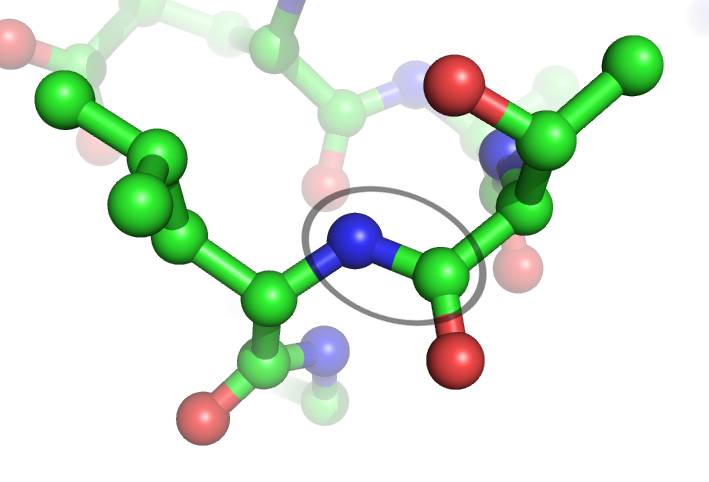
Peptide Bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a '' dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-end Rule
The ''N''-end rule is a rule that governs the rate of proteolysis, protein degradation through recognition of the N-terminal residue of proteins. The rule states that the N-terminus, ''N''-terminal amino acid of a protein determines its half-life (time after which half of the total amount of a given polypeptide is degraded). The rule applies to both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms, but with different strength, rules, and outcome. In eukaryotic cells, these N-terminal residues are recognized and targeted by ubiquitin ligases, mediating ubiquitination thereby marking the protein for degradation. The rule was initially discovered by Alexander Varshavsky and co-workers in 1986. However, only rough estimations of protein half-life can be deduced from this 'rule', as N-terminal amino acid modification can lead to variability and anomalies, whilst amino acid impact can also change from organism to organism. Other degradation signals, known as degrons, can also be found in sequence. Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro-opiomelanocortin
Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a precursor polypeptide with 241 amino acid residues. POMC is Protein biosynthesis, synthesized in Corticotropic cell, corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary from the 267-amino-acid-long Precursor polypeptide, polypeptide precursor pre-pro-opiomelanocortin (pre-POMC), by the removal of a 26-amino-acid-long signal peptide sequence during translation (biology), translation. POMC is part of the central melanocortin system. Function POMC is cut (cleaved) to give rise to multiple peptide hormones. Each of these peptides is packaged in large dense-core vesicle (biology), vesicles that are released from the cells by exocytosis in response to appropriate stimulation: * Melanocyte-stimulating hormone, α-MSH produced by neurons in the ventromedial nucleus has important roles in the regulation of appetite (POMC neuron stimulation results in Hunger (motivational state), satiety.) and Human sexual activity, sexual behavior, while α-MSH secreted from the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycistronic
A cistron is a region of DNA that is conceptually equivalent to some definitions of a gene, such that the terms are synonymous from certain viewpoints, especially with regard to the molecular gene as contrasted with the Mendelian gene. The question of which scope of a subset of DNA (that is, how large a segment of DNA) constitutes a unit of selection is the question that governs whether cistrons are the same thing as genes. The word ''cistron'' is used to emphasize that molecular genes exhibit a specific behavior in a complementation test (cis-trans test); distinct positions (or loci) within a genome are cistronic. History The words ''cistron'' and ''gene'' were coined before the advancing state of biology made it clear to many people that the concepts they refer to, at least in some senses of the word ''gene'', are either equivalent or nearly so. The same historical naming practices are responsible for many of the synonyms in the life sciences. The term ''cistron'' was coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus (biology)
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |