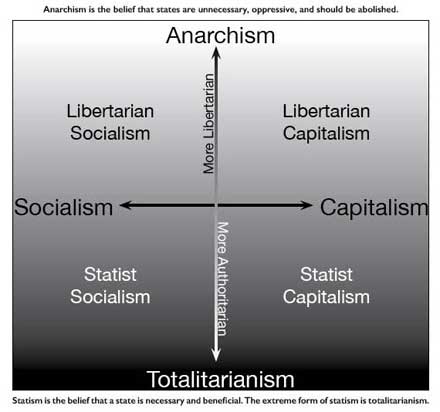
|
Propertarian
Propertarianism, or proprietarianism, is a political philosophy that reduces all questions of law to the right to own property. On property rights, it advocates private property on the basis of Lockean sticky property norms, where an owner keeps their property more or less until they consent to gift or sell it, rejecting the Lockean proviso. Propertarianism is often described by its advocates as either synonymous with capitalism or its logical conclusion. Closely related to and overlapping with right-libertarianism, it is also often accompanied with the idea that state monopoly law should be replaced by market-generated law centered on contractual relationships. Propertarian ideals are most commonly cited to advocate for an anarcho-capitalist or minarchist society, with governance systems either limited to enforcing contracts and private property or abolished through total privatization of its basic functions. History The term appears to have been coined by Edward Cain in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-libertarianism
Right-libertarianism,Rothbard, Murray (1 March 1971)"The Left and Right Within Libertarianism". ''WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action''. 7 (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.Goodway, David (2006). '' Anarchist Seeds Beneath the Snow: Left-Libertarian Thought and British Writers from William Morris to Colin Ward''. Liverpool: Liverpool University Pressp. 4. "The problem with the term 'libertarian' is that it is now also used by the Right. ..In its moderate form, right libertarianism embraces ''laissez-faire'' liberals like Robert Nozick who call for a minimal State, and in its extreme form, anarcho-capitalists like Murray Rothbard and David Friedman who entirely repudiate the role of the State and look to the market as a means of ensuring social order".Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: Sage Publicationsp. 1006. . also known as libertarian capitalism, or righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarcho-capitalism
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of centralized states in favor of stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by private agencies. Anarcho-capitalists argue that society can self-regulate and civilize through the voluntary exchange of goods and services. This would ideally result in a voluntary society based on concepts such as the non-aggression principle, free markets and self-ownership. In the absence of statute, private defence agencies and/or insurance companies would operate competitively in a market and fulfill the roles of courts and the police, similar to a state apparatus. Some anarcho-capitalist philosophies understand control of private property as part of the self, and some permit voluntary slavery. The vast majority of anarcho‑capitalists deny this, and critics of capitalism argue that this minority opinion is not unique to anarcho- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarcho-capitalist
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of Sovereign state, centralized states in favor of Stateless society, stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by private agencies. Anarcho-capitalists argue that society can self-regulate and civilize through the voluntary exchange of goods and services. This would ideally result in a voluntary society based on concepts such as the non-aggression principle, free markets and self-ownership. In the absence of statute, private defence agencies and/or insurance companies would operate competitively in a market and fulfill the roles of courts and the police, similar to a state apparatus. Some anarcho-capitalist philosophies understand control of private property as part of the self, and some permit voluntary slavery. The vast majority of anarcho‑capitalists deny this, and critics of capitalism argue that this minority opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Libertarian Studies
The Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, that is a center for Austrian economics, right-wing libertarian thought and the paleolibertarian and anarcho-capitalist movements in the United States. It is named after the economist Ludwig von Mises (1881–1973) and promotes the Misesian version of heterodox Austrian economics. The Mises Institute was founded in 1982 by Lew Rockwell, chief of staff to Texas Republican Congressman Ron Paul. Early supporters of the institute included economist F. A. Hayek, writer Henry Hazlitt, economist Murray Rothbard, Ron Paul, and libertarian coin dealer Burt Blumert. History The Mises Institute was founded in 1982 by Lew Rockwell, who was chief of staff to Texas Republican Congressman Ron Paul; previously Rockwell had been editor for the conservative Arlington House Publishers and had worked for the far-right John Birch Society and the tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray Bookchin
Murray Bookchin (; January 14, 1921 – July 30, 2006) was an American social theorist, author, orator, historian, and political philosopher. Influenced by G. W. F. Hegel, Karl Marx, and Peter Kropotkin, he was a pioneer in the environmental movement. Bookchin formulated and developed the theory of social ecology and urban planning within anarchist, libertarian socialist, and ecological thought. He was the author of two dozen books covering topics in politics, philosophy, history, urban affairs, and social ecology. Among the most important were ''Our Synthetic Environment'' (1962), '' Post-Scarcity Anarchism'' (1971), '' The Ecology of Freedom'' (1982), and ''Urbanization Without Cities'' (1987). In the late 1990s, he became disenchanted with what he saw as an increasingly apolitical " lifestylism" of the contemporary anarchist movement, stopped referring to himself as an anarchist, and founded his own libertarian socialist ideology called " communalism", which seeks to reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursula K
Ursula commonly refers to: * Ursula (name), feminine name (and a list of people and fictional characters with the name) * Ursula (''The Little Mermaid''), a fictional character who appears in ''The Little Mermaid'' (1989) * Saint Ursula, a legendary Christian saint Ursula may also refer to: * ''Ursula'' (album), an album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * Ursula (crater), a crater on Titania, a moon of Uranus *Ursula (detention center) Ursula is the colloquial name for the Central Processing Center, the largest U.S. Customs and Border Protection detention center for undocumented immigrants. The facility is a retrofitted warehouse that can hold more than 1,000 people. It was ope ..., processing facility for unaccompanied minors in McAllen, Texas * Ursula Channel, body of water in British Columbia, Canada * 375 Ursula, a large main-belt asteroid * HMS ''Ursula'', a destroyer and two submarines that served with the Royal Navy * Tropical Storm Ursula (other), a typhoon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Dispossessed
''The Dispossessed'' (subtitled ''An Ambiguous Utopia'') is a 1974 anarchist utopian science fiction novel by American writer Ursula K. Le Guin, one of her seven Hainish Cycle novels. It is one of a small number of books to win all three Hugo, Locus and Nebula Awards for Best Novel. It achieved a degree of literary recognition unusual for science fiction due to its exploration of themes such as anarchism and revolutionary societies, capitalism, utopia, individualism, and collectivism. It features the development of the mathematical theory underlying a fictional '' ansible'', a device capable of faster-than-light communication (it can send messages without delay, even between star systems) that plays a critical role in the Hainish Cycle. The invention of the ansible places the novel first in the internal chronology of the Hainish Cycle, although it was the fifth published. Background In her introduction to the Library of America reprint in 2017, Le Guin reflected on her past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space exploration, time travel, Parallel universes in fiction, parallel universes, and extraterrestrials in fiction, extraterrestrial life. The genre often explores human responses to the consequences of projected or imagined scientific advances. Science fiction is related to fantasy (together abbreviated wikt:SF&F, SF&F), Horror fiction, horror, and superhero fiction, and it contains many #Subgenres, subgenres. The genre's precise Definitions of science fiction, definition has long been disputed among authors, critics, scholars, and readers. Major subgenres include hard science fiction, ''hard'' science fiction, which emphasizes scientific accuracy, and soft science fiction, ''soft'' science fiction, which focuses on social sciences. Other no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Morgenthau
Hans Joachim Morgenthau (February 17, 1904 – July 19, 1980) was a German-American jurist and political scientist who was one of the major 20th-century figures in the study of international relations. Morgenthau's works belong to the tradition of realism in international relations theory; he is usually considered among the most influential realists of the post-World War II period. Morgenthau made landmark contributions to international relations theory and the study of international law. His '' Politics Among Nations'', first published in 1948, went through five editions during his lifetime and was widely adopted as a textbook in U.S. universities. While Morgenthau emphasized the centrality of power and "the national interest," the subtitle of ''Politics Among Nations''"the struggle for power and peace"indicates his concern not only with the struggle for power but also with the ways in which it is limited by ethical and legal norms. In addition to his books, Morgenthau wrote wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Probability Broach
''The Probability Broach'' is a 1979 science fiction novel by American writer L. Neil Smith. It is set in an alternate history, the so-called " Gallatin Universe", where a libertarian society has formed on the North American continent, styled the North American Confederacy (NAC). This history was created when the Declaration of Independence has the word ''unanimous'' added to the preamble, to read that governments "derive their just power from the ''unanimous'' consent of the governed". Plot summary Edward William "Win" Bear is an Ute Indian who works for the Denver Police Department in a version of the United States in an alternate history of 1987 that is controlled by an anti-capitalist, ecofascist government complete with a new police force created in 1984 called the Federal Security Police (FSP, or "SecPol" as it is more commonly known) reminiscent of the Gestapo. Henry M. Jackson is president, citizens' freedoms are very limited, and many laws and regulations have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternate History
Alternate history (also referred to as alternative history, allohistory, althist, or simply A.H.) is a subgenre of speculative fiction in which one or more historical events have occurred but are resolved differently than in actual history. As conjecture based upon historical fact, alternate history stories propose "what if?" scenarios about pivotal events in human history, and present outcomes very different from the historical record. Some alternate histories are considered a subgenre of science fiction, or historical fiction. Since the 1950s, as a subgenre of science fiction, some alternative history stories have featured the tropes of time travel between histories, the psychic awareness of the existence of an alternative universe by the inhabitants of a given universe, and time travel that divides history into various timestreams. Definition Often described as a subgenre of science fiction, alternative history is a genre of fiction wherein the author speculates upon how the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |