|
Private Road
A private road is a road owned or controlled by a private person, persons or corporation rather than a road open to the public and owned by a government. Private roads can be on private land or can be constructed on government land for use by government agencies or by agreements for access to private facilities. Private roads are private property and are not usually open to the public. Unauthorized use of a private road may be trespassing. In some cases, the owner of a private road may permit the general public to use the road. Road regulations that apply to a public road may not apply to private roads. Common types of private roads include roads retained in subdivisions of land but not dedicated to the public, residential roads maintained by a homeowners association, Housing cooperative, housing co-operative or other group of homeowners and roads for access to industrial facilities such as forests, mines, power stations and telecommunications. By country There are also networks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan Industrial Road
The Sultan Industrial Road, also sometimes unofficially known as Ramsey Industrial Road, is a public–private forest access road in the Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. Originally built as a resource route for E. B. Eddy Company, E. B. Eddy's logging and lumber operations in the northwestern Sudbury District, Ontario, Sudbury District, the road is now owned and operated by Eacom Timber. It is under a public access agreement with the province, permitting its use for public travel since 1978. The Sultan Industrial Road is gravel-surfaced throughout its length. There are no services along the remote route. Route description The road, which has a gravel surface, begins at Ontario Highway 667, Highway 667 in the community of Sultan, Ontario, Sultan. It travels eastward through remote forests for approximately to the intersection of Ontario Highway 144, Highway 144 and Ontario Highway 560, Highway 560, north of Cartier, Ontario, Cartier and south of Gogama, Ont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road Transport
Road transport or road transportation is a type of transport using roads. Transport on roads can be roughly grouped into the transportation of goods and transportation of people. In many countries licensing requirements and safety regulations ensure a separation of the two industries. Movement along roads may be by Bicycle, bike, Car, automobile, bus, truck, or by Pack animal, animal such as horse or oxen. Standard networks of roads were adopted by Ancient Rome, Romans, Persians, Aztec, and other early empires, and may be regarded as a feature of empires. Cargo may be transported by Truck driver, trucking companies, while passengers may be transported via Public transport, mass transit. Commonly defined features of modern roads include defined lanes and Traffic sign, signage. Various classes of road exist, from two-lane local roads with at-grade Intersection (road), intersections to controlled-access highways with all cross traffic grade-separated. The nature of road transportat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirt Road
A dirt road or track is a type of unpaved road not paved with asphalt, concrete, brick, or stone; made from the native material of the land surface through which it passes, known to highway engineers as subgrade material. Terminology Similar terms Terms similar to dirt road are ''dry-weather road'', ''earth road'', or the "Class Four Highway" designation used in China. A ''track'', ''dirt track'', or ''earth track'' would normally be similar but less suitable for larger vehicles—the distinction is not well-defined. Laterite and murram roads, depending on material used, may be dirt roads or improved roads. Improved road Unpaved roads with a harder surface made by the addition of material such as gravel and aggregate (stones), might be referred to as dirt roads in common usage but are distinguished as improved roads by highway engineers. Improved unpaved roads include gravel roads and macadamized roads. Characteristics Compared to a gravel road, a dirt road is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Highways In The United States
There are relatively few private highways in the United States, compared to other parts of the world. The Philadelphia and Lancaster Turnpike, opened in 1795 between Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and Lancaster, Pennsylvania, was the first major American turnpike. According to Gerald Gunderson's ''Privatization and the 19th-Century Turnpike'', "In the first three decades of the 19th century, Americans built more than 10,000 miles 6,000 kmof turnpikes, in New England and the Middle Atlantic states. Relative to the economy at that time, this effort exceeded the post-World War II interstate highway system." Because electronics did not exist in that era, all tolls had to be collected by human cashiers at toll booths, creating high fixed costs that could only be covered by a large volume of traffic. As railroads and steamboats began to compete with the turnpikes, less profitable highways started to shut down or be turned over to governments. (See : Pre-freeway turnpikes in the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Highway
A private highway is a highway owned and operated for profit by private industry. Private highways are common in Asia and Europe; in addition, a few have been built in the United States on an experimental basis. Typically, private highways are built by companies that charge tolls for a period while the debt is retired, after which the highway is turned over to government control. This allows governments to fulfill immediate transportation needs despite their own budget constraints, while still retaining public ownership of the roads in the long term. An obstacle to private highways is that government regulation can stifle price flexibility and introduce negotiation and paperwork requirements that increase operational expenses, while having to compete against free public roads. In addition, private highways lack some advantages that governments have, such as sovereign immunity against liability for accidents, the use of eminent domain power to acquire private property for roads an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minarchism
A night-watchman state, also referred to as a minimal state or minarchy, whose proponents are known as minarchists, is a model of a state that is limited and minimal, whose functions depend on libertarian theory. Right-libertarians support it only as an enforcer of the non-aggression principle by providing citizens with the military, the police, and courts, thereby protecting them from aggression, theft, breach of contract, fraud, and enforcing property laws.Gregory, Anthony (May 10, 2004)"The Minarchist's Dilemma" ''Strike the Root: A Journal of Liberty''. . Retrieved February 1, 2020.Peikoff, Leonard (March 7, 2011)"What role should certain specific governments play in Objectivist government?". Peikoff.com. Retrieved January 2, 2020. In the United States, this form of government is mainly associated with libertarian and objectivist political philosophy. In other countries, minarchism is also advocated by some non-anarchist libertarian socialists and other left-libertarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
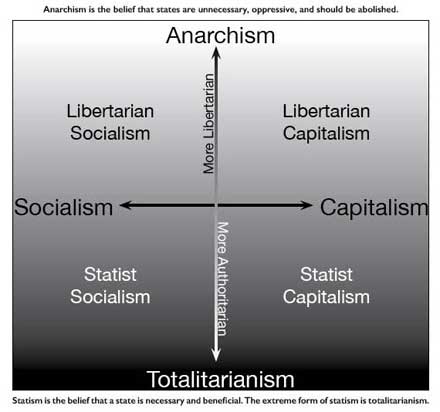
Anarcho-capitalism
Anarcho-capitalism (colloquially: ancap or an-cap) is a political philosophy and economic theory that advocates for the abolition of centralized states in favor of stateless societies, where systems of private property are enforced by private agencies. Anarcho-capitalists argue that society can self-regulate and civilize through the voluntary exchange of goods and services. This would ideally result in a voluntary society based on concepts such as the non-aggression principle, free markets and self-ownership. In the absence of statute, private defence agencies and/or insurance companies would operate competitively in a market and fulfill the roles of courts and the police, similar to a state apparatus. Some anarcho-capitalist philosophies understand control of private property as part of the self, and some permit voluntary slavery. The vast majority of anarcho‑capitalists deny this, and critics of capitalism argue that this minority opinion is not unique to anarcho- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-libertarian
Right-libertarianism,Rothbard, Murray (1 March 1971)"The Left and Right Within Libertarianism". ''WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action''. 7 (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.Goodway, David (2006). '' Anarchist Seeds Beneath the Snow: Left-Libertarian Thought and British Writers from William Morris to Colin Ward''. Liverpool: Liverpool University Pressp. 4. "The problem with the term 'libertarian' is that it is now also used by the Right. ..In its moderate form, right libertarianism embraces ''laissez-faire'' liberals like Robert Nozick who call for a minimal State, and in its extreme form, anarcho-capitalists like Murray Rothbard and David Friedman who entirely repudiate the role of the State and look to the market as a means of ensuring social order".Carlson, Jennifer D. (2012). "Libertarianism". In Miller, Wilburn R., ed. ''The Social History of Crime and Punishment in America''. London: Sage Publicationsp. 1006. . also known as libertarian capitalism, or righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-market Road
Free-market roads is the idea that it is possible and desirable for a society to have entirely private roads. Free-market roads and infrastructure are generally advocated by anarcho-capitalist works, including Murray Rothbard's ''For a New Liberty'', Morris and Linda Tannehill's '' The Market for Liberty'', David D. Friedman's '' The Machinery of Freedom'', and David T. Beito's '' The Voluntary City''. Arguments for free market roads "Private roads can have no free riders, reducing congestion" The free rider problem has been cited by proponents such as Murray Rothbard as a reason for privatizing roads: since traffic congestion is the result of excess demand for transportation infrastructure, it may be treated as any other economic shortage - in this case, a shortage of roads, lanes, exits, or other infrastructure. Seeing the pricing mechanism of a free market as a more efficient means of meeting demand than government planning (see Economic calculation problem), Peter Samuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , hosting a population exceeding 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of the present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. From the late 6th century, parts of modern Slovakia were incorporated into the Pannonian Avars, Avar Khaghanate. In the 7th century, the Slavs played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. When the Avar Khaghanate dissolved in the 9th century, the Slavs established the Principality of Nitra before it was annexed by the Great Moravia, Principality of Moravia, which later became Great Moravia. When Great Moravia fell in the 10th century, the territory was integrated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of with a mostly temperate Humid continental climate, continental and oceanic climate. The capital and largest city is Prague; other major cities and urban areas include Brno, Ostrava, Plzeň and Liberec. The Duchy of Bohemia was founded in the late 9th century under Great Moravia. It was formally recognized as an Imperial Estate of the Holy Roman Empire in 1002 and became Kingdom of Bohemia, a kingdom in 1198. Following the Battle of Mohács in 1526, all of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were gradually integrated into the Habsburg monarchy. Nearly a hundred years later, the Protestantism, Protestant Bohemian Revolt led to the Thirty Years' War. After the Battle of White ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |