|
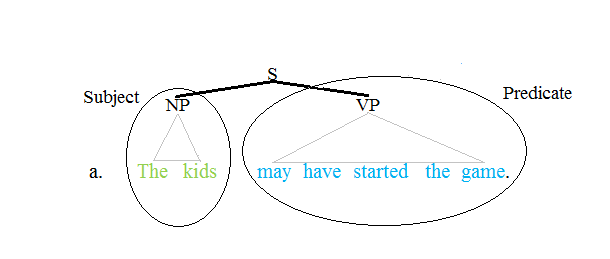
Predicand
In semantics, a predicand is an argument in an utterance, specifically that of which something is predicated. By extension, in syntax, it is the constituent in a clause typically functioning as the subject. Examples In the most typical cases, the predicand corresponds to the subject of a clause, and the predicate corresponds to a verb phrase (VP) that is the head of the clause. But there are also form-meaning mismatches, where the predicand is not a subject or where the predicate is not the head of the clause. Also, not every utterance has a predicand. When predicates correspond to the head of the clause The typical case involves a predicand corresponding to the subject and a predicate corresponding to a verb phrase that is the head of the clause. Subject predicands Predicands are usually expressed in the utterance, and they are typically the subject. In the English example (1), the predicand is the person being spoken to, which corresponds to the subject ''you.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject (grammar), subject, and the other defines it as only the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition, the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake'', while by the second definition, it is only the content verb ''likes'', and ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the argument (linguistics), arguments of this predicate. The conflict between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verbless Clause
Verbless clauses are comprised, semantically, of a predicand, expressed or not, and a verbless predicate. For example, the underlined string in 'With the children so sick,''''we've been at home a lot'' means the same thing as the clause ''the children are so sick''. It attributes the predicate "so sick" to the predicand "the children". In most contexts, *''the children so sick'' would be ungrammatical. History of the concept In the early days of generative grammar, new conceptions of the clause were emerging. Paul Postal and Noam Chomsky argued that every verb phrase had a subject, even if none was expressed, (though Joan Bresnan and Michael Brame disagreed). As a result, every VP was thought to head a clause. The idea of verbless clauses was perhaps introduced by James McCawley in the early 1980s with examples like the underlined part of ''with John in jail''... meaning "John is in jail". Examples English In Modern English, verbless clauses are common as the complemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raising (syntax)
In linguistics, raising constructions involve the syntactic movement, movement of an argument (linguistics), argument from an embedded or subordinate clause to a matrix or main clause. A raising predicate (grammar), predicate/verb appears with a syntactic argument that is not its semantic argument but rather the semantic argument of an embedded predicate. In other words, the sentence is expressing something about a phrase taken as a whole. For example, in ''they seem to be trying'', ''"to be trying"'' (the predicand of ''trying'') is the subject of ''seem''. English language, English has raising constructions, unlike some other languages. The term ''raising'' has its origins in the Transformational Grammar, transformational analysis of such constructions; the constituent (linguistics), constituent in question is seen as being "raised" from its initial deep structure position, as the subject of the embedded predicate, to its Deep structure and surface structure, surface structure p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predication (philosophy)
Predication in philosophy refers to an act of judgement where one term is subsumed under another. A comprehensive conceptualization describes it as the understanding of the relation expressed by a predicative structure primordially (i.e. both originally and primarily) through the opposition between particular and general or the one and the many. Predication is also associated or used interchangeably with the concept of ''attribution'' where both terms pertain to the way judgment and ideas acquire a new property in the second operation of the mind (or the mental operation of judging). Background Predication emerged when ancient philosophers began exploring reality and the two entities that divide it: properties and the things that bear them. These thinkers investigated what the division between thing and property amounted to. It was argued that the relationship resembled the logical analysis of a sentence wherein the division of Subject (grammar), subject and predicate arises sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clause
In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), subject and a syntactic Predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any object (grammar), objects and other Grammatical modifier, modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English grammar, English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated (dependent clause, ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject (grammar)
A subject is one of the two main parts of a Sentence (linguistics), sentence (the other being the Predicate (grammar), predicate, which modifies the subject). For the simple Sentence (linguistics), sentence ''John runs'', ''John'' is the subject, a person or thing about whom the statement is made. Traditionally the subject is the word or phrase which controls the verb in the clause, that is to say with which the verb Agreement (linguistics), agrees (''John is'' but ''John and Mary are''). If there is no verb, as in ''Nicola what an idiot!'', or if the verb has a different subject, as in ''John I can't stand him!'', then 'John' is not considered to be the grammatical subject, but can be described as the ''Topic and comment, topic'' of the sentence. While these definitions apply to simple English sentences, defining the subject is more difficult in more complex sentences and languages. For example, in the sentence ''It is difficult to learn French'', the subject seems to be the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dangling Modifier
A dangling modifier (also known as a dangling participle, illogical participle or hanging participle) is a type of ambiguous grammatical construct whereby a grammatical modifier could be misinterpreted as being associated with a word other than the one intended. A dangling modifier has no subject and is usually a participle. A writer may use a dangling modifier intending to modify a subject while word order may imply that the modifier describes an object, or vice versa. An example of a dangling modifier appears in the sentence "Turning the corner, a handsome school building appeared". The modifying clause ''Turning the corner'' describes the behavior of the narrator, but the narrator is only implicit in the sentence. The sentence could be misread, with the ''turning'' action attaching either to the ''handsome school building'' or to nothing at all. As another example, in the sentence "At the age of eight, my family finally bought a dog", the modifier ''At the age of eight'' is dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rules, a subject that includes phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, together with phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are, broadly speaking, two different ways to study grammar: traditional grammar and #Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency in a particular language variety involves a speaker internalizing these rules, many or most of which are language acquisition, acquired by observing other speakers, as opposed to intentional study or language teaching, instruction. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more direct instruction. The term ''grammar'' can also describe the linguistic behaviour of groups of speakers and writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent (grammar)
In linguistics, a grammatical agent is the thematic relation of the cause or initiator to an event. The agent is a semantic concept distinct from the subject of a sentence as well as from the topic. While the subject is determined syntactically, primarily through word order, the agent is determined through its relationship to the action expressed by the verb. For example, in the sentence "The little girl was bitten by the dog", ''girl'' is the subject, but ''dog'' is the agent. The word ''agent'' comes from the present participle , ('the one doing') of the Latin verb , to 'do' or 'make'. Theory Typically, the situation is denoted by a sentence, the action by a verb in the sentence, and the agent by a noun phrase. For example, in the sentence "Jack kicked the ball", ''Jack'' is the agent and ''the ball'' is the patient. In certain languages, the agent is declined or otherwise marked to indicate its grammatical role. Modern English does not mark the agentive grammatical role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thematic Relation
In certain theories of linguistics, thematic relations, also known as semantic roles or thematic roles, are the various roles that a noun phrase may play with respect to the action or state described by a governing verb, commonly the sentence's main verb. For example, in the sentence "Susan ate an apple", ''Susan'' is the doer of the eating, so she is an Agent (grammar), agent; ''an apple'' is the item that is eaten, so it is a Patient (grammar), patient. Since their introduction in the mid-1960s by Jeffrey Gruber and Charles J. Fillmore, Charles Fillmore, semantic roles have been a core linguistic concept and ground of debate between linguist approaches, because of their potential in explaining the relationship between syntax and semantics (also known as the syntax-semantics interface), that is how meaning affects the surface syntactic codification of language. The notion of semantic roles play a central role especially in functionalist linguistics, functionalist and language-com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impersonal Verb
In linguistics, an impersonal verb is one that has no determinate subject. For example, in the sentence "''It rains''", ''rain'' is an impersonal verb and the pronoun ''it'' corresponds to an exophoric referrent. In many languages the verb takes a third person singular inflection and often appears with an expletive subject. In the active voice, impersonal verbs can be used to express operation of nature, mental distress, and acts with no reference to the doer. Impersonal verbs are also called weather verbs because they frequently appear in the context of weather description. Also, indefinite pronouns may be called "impersonal", as they refer to an unknown person, like ''one'' or ''someone'', and there is overlap between the use of the two. Valency Impersonal verbs appear only in non-finite forms or with third-person inflection. In the third person, the subject is either implied or a dummy referring to people in general. The term "impersonal" simply means that the verb does no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |