|
Poxviruses
''Poxviridae'' is a family of double-stranded DNA viruses. Vertebrates and arthropods serve as natural hosts. The family contains 22 genera that are assigned to two subfamilies: ''Chordopoxvirinae'' and ''Entomopoxvirinae''. ''Entomopoxvirinae'' infect insects and ''Chordopoxvirinae'' infect vertebrates. Diseases associated with this family include smallpox. Four genera of poxviruses can infect humans: ''Orthopoxvirus'', ''Parapoxvirus'', ''Yatapoxvirus'', ''Molluscipoxvirus''. ''Orthopoxvirus'': smallpox virus (variola), vaccinia virus, cowpox virus, Mpox virus; ''Parapoxvirus'': Orf (disease), orf virus, pseudocowpox, bovine papular stomatitis virus; ''Yatapoxvirus'': tanapox virus, yaba monkey tumor virus; ''Molluscipoxvirus'': molluscum contagiosum, molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). The most common are vaccinia (seen on the Indian subcontinent) and molluscum contagiosum, but Mpox infections are rising (seen in west and central African rainforest countries). The similarly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making smallpox the only human disease to have been eradicated to date. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was transmitted from one person to another primarily through prolonged face-to-face contact with an infected person or rarely via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medications could poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapoxvirus
''Parapoxvirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae'', in the subfamily ''Chordopoxvirinae''. Like all members of the family Poxviridae, they are oval, relatively large, double-stranded DNA viruses. Parapoxviruses have a unique spiral coat that distinguishes them from other poxviruses. Parapoxviruses infect vertebrates, including a wide selection of mammals, and humans. Not all parapoxviruses are zoonotic. Notable zoonotic hosts of parapoxviruses include sheep, goats, and cow, cattle. The most recent species of parapoxviruses has been found in New Zealand Red Deer, red deer. There are also some tentative species in the genus, including Auzduk disease virus, Chamois contagious ecthyma virus, and sealpox virus. Structure Viruses in ''Parapoxvirus'' are enveloped, with ovoid geometries. These viruses are about 140–170 nm wide and 220–300 nm long, and have a regular surface structure; tubules with a diameter of 10–20 nm form a criss-cross patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscipoxvirus
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is a species of DNA poxvirus that causes the human skin infection molluscum contagiosum. Molluscum contagiosum affects about 200,000 people a year, about 1% of all diagnosed skin diseases. Diagnosis is based on the size and shape of the skin lesions and can be confirmed with a biopsy, as the virus cannot be routinely cultured. Molluscum contagiosum virus is the only species in the genus ''Molluscipoxvirus''. MCV is a member of the subfamily ''Chordopoxvirinae'' of family ''Poxviridae''. Other commonly known viruses that reside in the subfamily ''Chordopoxvirinae'' are Variola virus (the cause of smallpox) and Monkeypox virus. The poxvirus family uniquely contains both non-enveloped particles (mature virions), and enveloped particles (extracellular virions). The structure of the virions is consistent with that of others in the poxvirus family: they are composed of a nucleocapsid, core envelope, lateral body, and an extracellular envelope. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowpox
Cowpox is an infectious disease caused by Cowpox virus (CPXV). It presents with large blisters in the skin, a fever and swollen glands, historically typically following contact with an infected cow, though in the last several decades more often (though overall rarely) from infected cats. The hands and face are most frequently affected and the spots are generally very painful. The virus, part of the genus '' Orthopoxvirus'', is closely related to Vaccinia virus. The virus is zoonotic, meaning that it is transferable between species, such as from cat to human. The transferral of the disease was first observed in dairy workers who touched the udders of infected cows and consequently developed the signature pustules on their hands.Vanessa Ngan, "Viral and Skin Infections" 2009 Cowpox is more commonly foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopoxvirus
''Orthopoxvirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Poxviridae'' and subfamily ''Chordopoxvirinae''. Vertebrates, including mammals and humans, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include smallpox, cowpox, horsepox, camelpox, and mpox. The most widely known member of the genus is Variola virus, which causes smallpox. It was eradicated globally by 1977, through the use of Vaccinia virus as a vaccine. The most recently described species is the Borealpox virus, first isolated in 2015. Microbiology Structure Orthopoxviruses are enveloped with brick-shaped geometries and virion dimensions around 200 nm wide and 250 nm long. Genome Member viruses have linear double-stranded DNA genomes around 170–250 kb in length. Lifecycle Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral proteins to host glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), which mediate cellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Papular Stomatitis
Bovine papular stomatitis is a zoonotic farmyard pox caused by Bovine papular stomatitis virus (BPSV), which can spread from infected cattle to cause disease in milkers, farmers and veterinarians. Generally there are usually one or multiple skin lesions, typically on the hands or forearm. The disease is generally mild. BPSV is a member of the family ''Poxviridae'' and the genus ''Parapoxvirus''. Spread typically occurs by direct contact with the infected animal, but has been reported in people without direct contact. BPSV may appear similar to foot-and-mouth disease. It has been found to exhibit a size of around 320 nm by 190 nm, slightly larger than a typical parapoxvirus. BPSV exhibits an egg-like shape. It occurs worldwide in cattle. Most notably in conditions where cattle are in close contact with one another and in high-stress environments, such as fattening facilities. In other animals the lesions are reddish, raised, sometimes ulcerative lesions on the lips, muz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mpox
Mpox (, ; formerly known as monkeypox) is an infectious viral disease that can occur in humans and other animals. Symptoms include a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. The illness is usually mild, and most infected individuals recover within a few weeks without treatment. The time from exposure to the onset of symptoms ranges from three to seventeen days, and symptoms typically last from two to four weeks. However, cases may be severe, especially in children, pregnant women, or people with suppressed immune systems. The disease is caused by the monkeypox virus, a zoonotic virus in the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The variola virus, which causes smallpox, is also in this genus. Human-to-human transmission can occur through direct contact with infected skin or body fluids, including sexual contact. People remain infectious from the onset of symptoms until all the lesions have scabbed and healed. The virus may spread from infected a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long molecules of DNA or RNA that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccinia
The vaccinia virus (VACV or VV) is a large, complex, enveloped virus belonging to the poxvirus family. It has a linear, double-stranded DNA genome approximately 190 kbp in length, which encodes approximately 250 genes. The dimensions of the virion are roughly 360 × 270 × 250 nm, with a mass of approximately 5–10 fg. The vaccinia virus is the source of the modern smallpox vaccine, which the World Health Organization (WHO) used to eradicate smallpox in a global vaccination campaign in 1958–1977. Although ''smallpox'' no longer exists in the wild, ''vaccinia'' virus is still studied widely by scientists as a tool for gene therapy and genetic engineering. Smallpox had been an endemic human disease that had a 30% fatality rate. In 1796, the British doctor Edward Jenner proved that an infection with the relatively mild cowpox virus would also confer immunity to the deadly smallpox. Jenner referred to cowpox as ''variolae vaccinae'' (smallpox of the cow). However, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
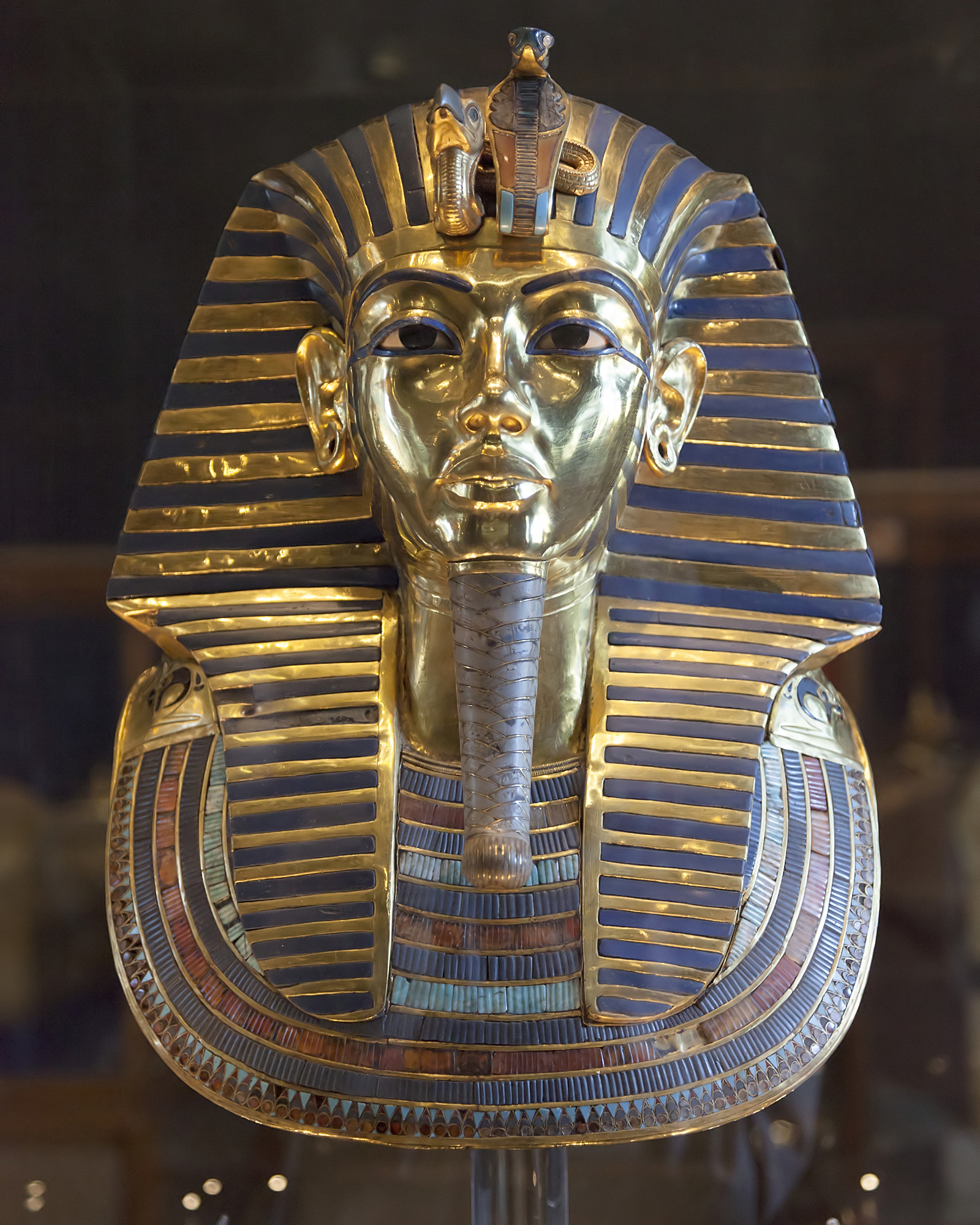
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty () until the Roman Egypt, annexation of Egypt by the Roman Republic in 30 BCE. However, the equivalent Egyptian language, Egyptian word for "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs, regardless of gender, through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The earliest confirmed instances of "pharaoh" used contemporaneously for a ruler were a letter to Akhenaten (reigned –1336 BCE) or an inscription possibly referring to Thutmose III (–1425 BCE). In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as ancient Egyptian royal titulary, three titles: the Horus name, Horus, the prenomen (Ancient Egypt), Sedge and Bee (wikt:nswt-bjtj, ''nswt-bjtj''), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
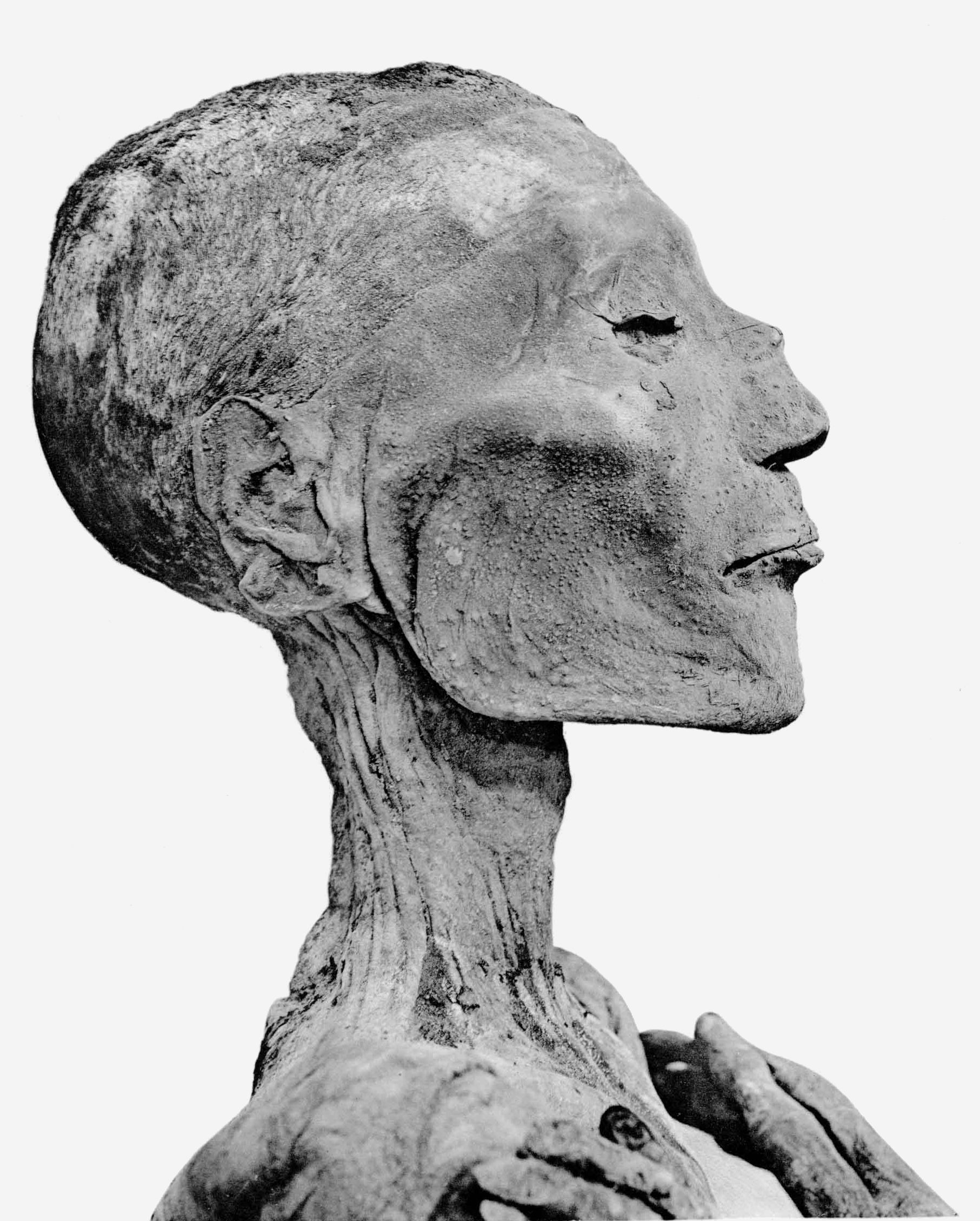
Ramses V
Usermaatre Sekheperenre Ramesses V (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the fourth pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt and was the son of Ramesses IV and Duatentopet. His mummy is now on display at the National Museum of Egyptian Civilization in Cairo. Reign Ramesses V's reign was characterized by the continued growth of the power of the priesthood of Amun, which controlled much of the temple land in the country and the state finances, at the expense of the ruling pharaohs. The Turin 1887 papyrus records a financial scandal during Ramesses' reign that involved the priests of Elephantine. Year 1 A period of domestic instability also afflicted his reign, as evidenced by the fact that, according to the Turin Papyrus Cat. 2044, the workmen of Deir el-Medina periodically stopped work on Ramesses V's KV9 tomb in this king's first regnal year, out of fear of "''the enemy''", presumably Libyan raiding parties, who had reached the town of Per-Nebyt and "''burnt its people''." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a single continent, the Americas or America is the 2nd largest continent by area after Asia, and is the 3rd largest continent by population. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. Along with their Lists of islands of the Americas, associated islands, the Americas cover 8% of Earth's total surface area and 28.4% of its land area. The topography is dominated by the American Cordillera, a long chain of mountains that runs the length of the west coast. The flatter eastern side of the Americas is dominated by large river basins, such as the Amazon basin, Amazon, St. Lawrence River–Great Lakes, Mississippi River System, Mississippi, and Río de la Plata Basin, La Plata basins. Since the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |